Note: Customers who wish to use Google services in Appian will need to bring their own Google Cloud credentials to do so.
OverviewCopy link to clipboard
This page provides detailed information about how Appian can connect to the Google Cloud APIs that leverage Google Service Account authentication. Designers can configure these integrations using an HTTP and OpenAPI connected systems.
Google Service Account authentication refers to Google's implementation of the OAuth 2.0 JWT Bearer grant type.
Google Cloud configurationCopy link to clipboard
A service account is a special kind of Google account that represents a non-human user. Appian can use these service accounts to call Google APIs so that end users don't need to be directly involved.
There are several steps that must take place in order to generate the service account key
Creating and managing Google service accountsCopy link to clipboard
To use Google Service Account authentication, you will need a service account in Google.
To learn about creating and managing service accounts, see the Google IAM documentation on creating and managing service accounts.
Granting roles to service accountsCopy link to clipboard
In order to be authorized to access data in a specific Google API, your service account must have the proper roles.
To learn about granting roles to service accounts, see the Google IAM documentation on granting roles to service accounts.
Generating a service account keyCopy link to clipboard
To use Google Service Account authentication, you will need a service account key for your service account. This file should be download in JSON format.
To learn about creating and managing service account keys, see the Google IAM documentation on creating and managing service account keys.
Performing G Suite domain-wide delegation of authority (Optional)Copy link to clipboard
In some cases, you may want to take advantage of domain-wide delegation of authority. Google allows G Suite administrators to configure domain-wide delegation in order to grant Google Service Accounts permission to impersonate specific G Suite users. This can be used with a number of G Suite services such as Google Groups (the Admin SDK Directory API), Google Calendar, and Gmail.
To learn more about configuring domain-wide delegation of authority for an API, you should view the documentation for that service.
Note: Different services have slightly different documentation to explain domain-wide delegation of authority. For example, there are different pages for the Admin SDK Directory API, the Google Calendar API, the Google Drive API, and the Gmail API.
Appian configurationCopy link to clipboard
Once you have configured your service account in Google and exported your service account key, you are ready to set up your connected system.
Using your service account keyCopy link to clipboard
When creating a connected system with Google Service Account authentication, Appian allows designers to upload a service account key JSON file rather than manually filling out each field.
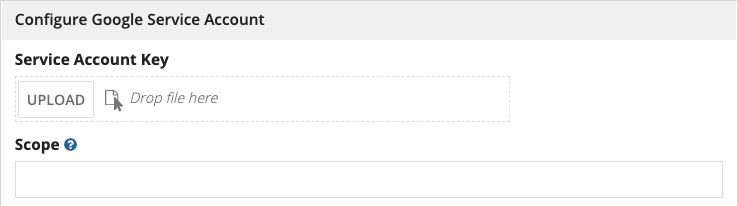
This will populate the Project ID, Client ID, and Client Email fields.
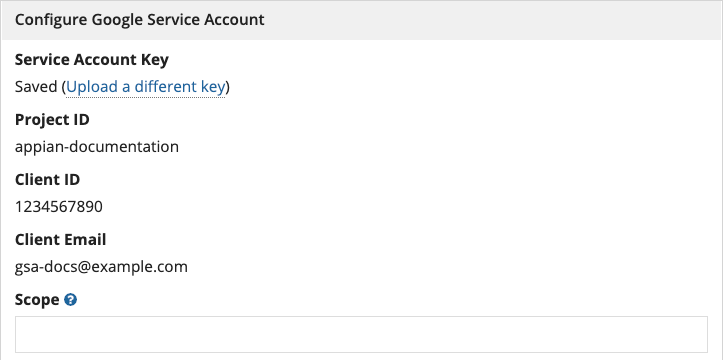
Note: These field values will need to be manually specified using an import customization file when deploying to higher environments.
Setting the scopeCopy link to clipboard
In order to successfully call an API, you will also need to set the required scopes for your connected system. Several scopes can be entered and separated by spaces. If left empty, the default scope is https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-platform.
To find the required scopes for an API, you should view the documentation for that service. For example, when using Google Calendar refer to the documentation on authorizing requests to the Google Calendar API and the documentation for each API endpoint. In this case, to call the Calendars: update endpoint you will need to request a scope of https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.
Impersonating a G Suite domain user (optional)Copy link to clipboard
If you have configured domain-wide delegation, Appian supports the ability for your service account to impersonate a G Suite domain user. To do so, simply check Impersonate G Suite domain user on the connected system and provide the email address of the G Suite domain user to impersonate. All integrations leveraging your connected system will be executed as this user in accordance with the permissions they have been granted to your G Suite domain.
Parameters set in the connected systemCopy link to clipboard
The following properties are available for configuration when Google Service Account is selected as the authentication type:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Service Account Key* | Optional. A JSON file containing service account information. This file is obtained from the Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Console. |
| Project ID* | Required/Read-Only. The Project ID for the service account key. |
| Client ID* | Required/Read-Only/Sensitive. The Client ID for the service account key. |
| Client Email* | Required/Read-Only. The Client Email for the service account key. |
| Private Key ID* | Required/Sensitive. The Private Key ID for the service account key. |
| Private Key* | Required/Sensitive. The Private Key for the service account key. The Private Key starts with/includes the string -----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----\n and ends with/includes the string \n-----END PRIVATE KEY-----\n |
| Scope | Optional. The permissions that will be requested from the protected resource. If left empty, the default scope is https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-platform. |
| Impersonate G Suite domain user | Optional. Checking this allows integrations to impersonate a specific G Suite domain user. Requires a service account with domain-wide delegation of authority. |
| G Suite Domain User Email* | Required (Conditionally). When using domain-wide delegation, this is the email for the G Suite Domain User that should be impersonated. This field is only exposed if Impersonate G Suite domain user is selected. Included in import customization files so that you can specify a different value for each environment. |
* This value is included in an import customization file so that you can specify a different value for each environment. Sensitive values will not be exported in the import customization file and must be added manually. Required fields must have a value upon import or else import will fail. For more information on import/export behavior, see the Connected Systems Object page.
