OverviewCopy link to clipboard
The custom JDBC connected system allows you to connect to unsupported databases that support the JDBC protocol. Providing an alternative to using HTTP integrations or third-party plug-ins, this connection uses a SQL integration object to exchange data with your business data source through SQL statements.
Note: Any database that is not in this list is considered an unsupported database.
This page provides details about custom JDBC connected system properties. For information that pertains to all connected systems, see Connected System Object.
To use the custom JDBC connected system, you will need to do the following:
Deploy a driverCopy link to clipboard
The process for deploying a driver differs based on your Appian installation.
If you are an Appian Cloud customerCopy link to clipboard
Open an Appian Support case to request the deployment of your driver. You will need to attach the .jar file for the desired JDBC driver and a database logo image file to the support case. Supported image file types include .svg, .png, .jpg, and .jpeg.
If you are a self-managed customerCopy link to clipboard
To deploy the desired driver to your site, run the creation script found in <APPIAN_HOME>/_admin/_scripts/tools/jdbc/create-jdbc-driver-plugin.sh. You will need to input the following information to run the script:
- File path to the
.jarfile. - Driver class name (
-driverClass). - Plug-in name (
-name). - Plug-in key (
-key).- The key is case-sensitive and unique within a site. It is used to determine whether to create a new custom JDBC connected system template or update an existing one.
- The key will be displayed in the name, description, and configuration properties of the custom JDBC connected system template.
- Plug-in version (
-version).- We recommend that you use the same plug-in version as the driver
.jarfile version.
- We recommend that you use the same plug-in version as the driver
- File path to the logo image file (
-logo)..svg,.png,.jpg, and.jpegare supported image file types.
Create a custom JDBC connected systemCopy link to clipboard
After deploying a driver to your site, you will see a new connected system template created in the Create Connected System picklist window.
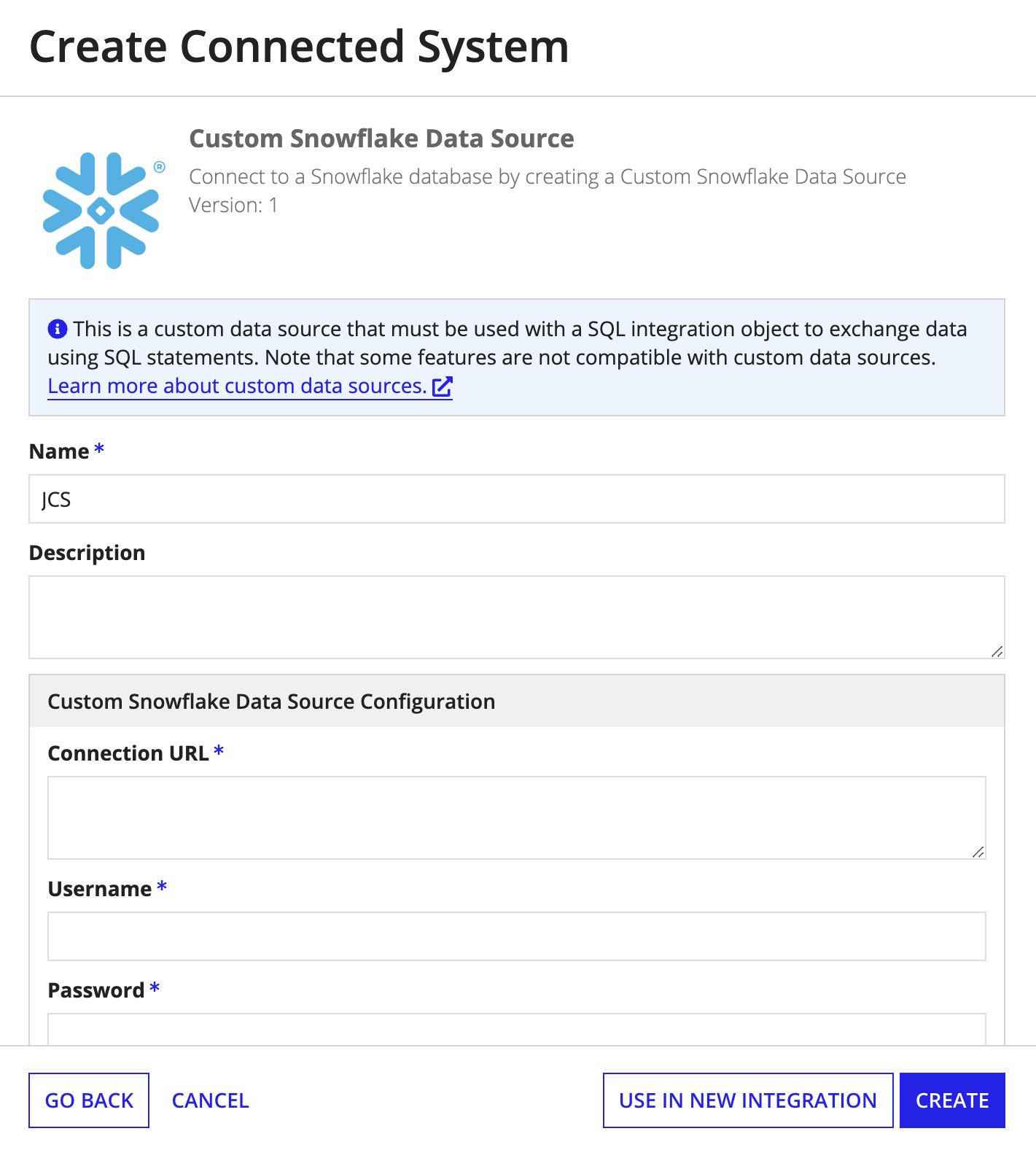
For example, if you deployed Snowflake driver, you would see a new Custom Snowflake Data Source when you go to create a new connected system.

PropertiesCopy link to clipboard
To create a custom JDBC connected system using the newly generated template, configure the following properties.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the connected system. Use a name that will uniquely identify this connection to the external database. |
| Description | Supplemental information about the connected system that is displayed in the objects grid of some Designer views and when selecting the system in an integration object. |
| Connection URL | The URL for the data source. Should include: the hostname, port, and database name of the data source. The exact syntax will vary by database type, but the connection URL should always be prefixed by jdbc. |
| Username | The username for connecting to the database. |
| Password | The password for connecting to the database. |
| Maximum Connection Pool Size | The maximum number of active connections to the database that can be allocated from this data source at the same time. The default is 20. Since there is a limited number of connections that applications can make to the database, this field prevents one connected system from using the entire connection pool. You can raise or lower this number to control the number of connection pools for a data source. For example, if you have a data source for an application with low usage, you can lower this number to further limit the number of connection pools for the application. This would prevent the application from taking up too many resources. |
| Transaction Isolation Level | The degree of isolation or concurrency control applied to transactions in a database system. This determines how transactions interact with each other and how they access and modify data concurrently. There are four transaction isolation levels available in the JDBC API. It's important to note that not all database vendors support all four levels.
|
Automating property updatesCopy link to clipboard
This object's properties can also be updated programmatically using the Update Connected System endpoint. This lets you change passwords, API keys, and other values without needing to sign in to Appian.
The following properties can be included in the JSON request body of the PATCH /connected-system/<UUID> call.
connectionUrlusernamepasswordmaxConnectionstransactionIsolationLevelKey
Next stepsCopy link to clipboard
After you have deployed a driver and set up your connected system, you will need to create a SQL integration object.
