| The capabilities described on this page are included in Appian's standard capability tier. Usage limits may apply. |
OverviewCopy link to clipboard
This page provides detailed design information about the integration object and its configuration options.
The information below applies most directly to HTTP, OpenAPI, and SQL integrations. If you are using a pre-built connected system, the fields you see may be different.
Note: External systems connected to Appian require Transport Layer Security (TLS) 1.2 or above. If you are trying to connect to an older system that only supports TLS 1.0 or 1.1, follow the steps in the Post-Install Configurations page.
- To learn how to use the integration designer to configure, test, and troubleshoot HTTP integrations, see Create an HTTP Integration.
- To learn how to create and use a SQL integration object, see Create a SQL Integration.
- To learn how to call an integration from other places in your application, see Call an Integration.
- To learn about connected systems, see Connected System Object.
- For a real-world example of how to build and use connected systems and integrations, see the Integration Tutorial.
PropertiesCopy link to clipboard
Each integration type has its own set of properties that can be configured.
HTTP integration propertiesCopy link to clipboard
Each HTTP integration has the following properties.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name that will be used when executing an integration. Follow the recommended naming standard when creating this name. |
| Description | Supplemental information about the integration that is displayed in the expression editor and in the objects grid of some Appian Designer views. |
| Save In | The rule folder that the integration is saved into. |
| Rule Inputs | Rule inputs are used to pass data into the integration.
|
| Integration Definition | The integration is defined using the configuration pane of the integration designer. |
SQL integration propertiesCopy link to clipboard
Each SQL integration has the following properties.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Connected System | This will be the custom JDBC connected system you created to go with this SQL integration. |
| Operation | The SQL integration type used for this integration. Value can be SQL Write Integration or SQL Query Integration. |
| Name | The name that will be used when executing the integration. Follow the recommended naming standard when creating this name. |
| Description | Supplemental information about the integration that is displayed in the expression editor and in the objects grid of some Appian Designer views. |
| Save In | The rule folder that the integration is saved into. |
Integration definitionCopy link to clipboard
Open the integration object to define the details of your integration.
HTTP integration definitionCopy link to clipboard
The configuration pane of the integration object allows you to define the HTTP request details for your integration.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Enter connection details below/ Use an existing connected system | Determines whether the integration will use a shared connection configuration from a connected system.
|
| URL | The HTTP URL that will be called. URL must begin with http:// or https://.Note: If you need to connect to this URL using a proxy server, that configuration can be enabled in the Admin Console. This field is not shown when using a connected system. |
| Base URL | The base URL from your connected system. This field is not shown when entering connection details directly. |
| Relative Path | Used to specify the endpoint for a given operation. Relative Path will be appended to Base URL to form the URL for your integration. This field is not shown when entering connection details directly. |
| URL Preview | The URL for your integration given the current rule inputs. The URL Preview is determined by evaluating the relative path expression and appending it to the end of the connected system’s base URL. |
| Connected System | The connected system being used. This connected system represents the external system or service, and contains the base URL and authentication details that the integration will use to connect to that service. This field is not shown when entering connection details directly. |
| Authentication |
Although basic authentication can be configured directly from an integration, connected systems are the best way to manage authentication. Using a connected system gives designers access to additional authentication options and allows them to manage authentication for several integrations in one place.
Note: This field is not shown when using a connected system. |
| Username | The username to use for the authentication. This value is encrypted and supports environment specific configuration. Note: This field is only shown when using basic authentication. |
| Password | The password to use for the authentication. This value is masked, encrypted, and supports environment specific configuration. Note: This field is only shown when using basic authentication. |
| Send credentials preemptively instead of waiting for a 401 authentication challenge | Determines whether or not authentication credentials are sent only after a 401 Not Authorized response or, when selected, before the system has challenged. Note: This field is only shown when using basic authentication. |
| Method | The HTTP method with which to call the URL. Available options are "GET", "POST", "PUT", "PATCH", "DELETE", "HEAD", "OPTIONS", and "TRACE". |
| Timeout (sec) | The time, in seconds, after which an integration should time out and throw an integration error if a response hasn't been returned. This time pertains to the entire integration runtime (prepare + execute + transform). If left blank, the integration will run indefinitely until a response is returned or a connection error terminates the call. |
| Usage | The type of interaction that the HTTP request has with data in the external system.
This field is automatically set to Modifies data and disabled when an integration response is configured to convert binary or base64 to Appian documents. |
| Parameters | The query parameters that will be appended to the URL using the format ?name1=value1&name2=value2.
|
| Ignore query parameters with empty values | Determines whether or not query parameters with null or empty values will be appended to the URL. When checked, developers can use a single integration object for an endpoint with optional query parameters. |
| Headers | The HTTP headers that will be added to the request.
|
| Ignore HTTP headers with empty values | Determines whether or not HTTP headers with null or empty values will be added to the request. When checked, developers can use a single integration object for an endpoint with optional HTTP headers. |
| Body | The body that will be sent with the HTTP request. This field can be used to send documents as either binary data or base64 data. The format of the body should match the defined content type. Size limitations
|
| Content Type | The content type of the body that will be sent with the HTTP request.
|
| Automatic Request Body Conversion | Checking this box causes the integration to automatically convert Appian values to the selected Content Type. If JSON is selected, you can pass either a dictionary or CDT as the request body. If XML is selected, you will need to use a CDT. This checkbox also enables you to send Appian documents to other systems as base64. When the dictionary or CDT contain documents, those documents will be converted to base64 and sent inline with the request body. Note: This field is only shown when the request body Content Type is set to JSON or XML. |
| Remove fields with null or empty values from generated JSON | Checking this box removes all fields with values that are null, empty strings, or empty arrays from the generated JSON request body. This behavior matches the removeNullOrEmptyFields parameter of the a!toJson function. This is important for certain web services, such as those that follow the OData protocol. Some web services treat fields with null values differently from fields that aren't included in the request body at all. Omitting a field may mean "don't modify the field," while sending a null value for that field would mean "write a null value to the field." Note: This field is only shown when the request body Content Type is set to JSON. |
| Response Body Parsing | If the service returns a binary or JSON response body, the response body can be converted to an Appian value. The following options are available:
Selecting the binary option enables the integration to stream and download a binary file from the response body to create an Appian document. These documents can be as large as 250 MB. It also sets the Usage field to Modifies data. If you see Convert JSON to Appian Value (prior version) for the Response Body Parsing, it means your integration was migrated from an earlier version of Appian that converts the JSON using a!fromJson_19r2(). You could choose to convert it to Convert JSON to Appian Value, but that may cause issues with parts of your application that rely on the integration. Because of this, for existing integrations we recommend continuing to use Convert JSON to Appian Value (prior version). |
| Document Name and Extension | When an integration is configured to convert a binary response body to an Appian document, this field specifies the document name and/or extension. It is recommended to provide an extension at design time in order to ensure its accuracy. If this field contains period(s), the document extension will be set to everything after the last period and the document name will be set to everything before the last period. So profilePicture.jpg would set the document name to profilePicture and the extension to jpg. If this field doesn’t contain a period, the document name will be set to the entire field value and Appian will try to infer an extension from the response using the Content-Disposition and Content-Type HTTP headers. So profilePicture would set the document name to profilePicture and the extension would be inferred. Note: This field is only shown when Response Body Parsing is set to Convert binary to Appian document. |
| Convert base64 values to Appian documents | When Response Body Parsing is set to Convert JSON to Appian value, checking this box enables the integration to convert base64 values in a JSON response body to Appian documents. Once checked, further configuration will be required. Checking this box enables the integration to stream up to 75MB of files as base64 in a single response body (one 75MB file, three 25MB files, etc), with the limitation that base64 strings longer than 4,000 characters are truncated. It also sets the Usage field to Modifies data and exposes a table, allowing you to specify the Response Body Location of each file in the JSON response body and (optionally) provide a Name for that document. The Response Body Location dropdown contains the structure of the most recently received response body. At runtime, selected locations that are found in the response body will be converted to Appian documents. Locations that aren’t found in the response body will be ignored. This allows the grid to support optional document fields. The Name field specifies the name and/or extension for each document. It is recommended to provide an extension for each document at design time in order to ensure their accuracy. If this field contains period(s), the document extension will be set to everything after the last period and the document name will be set to everything before the last period. So profilePicture.jpg would set the document name to profilePicture and the extension to jpg. If no extension is specified, Appian will try to infer an extension by using the Apache Tika library to analyze the bytes. Note: This field is only shown when Response Body Parsing is set to Convert JSON to Appian value. |
| Save Document(s) In | When an integration is configured to receive documents in the response, this field determines the document folder in which to save those documents. This can be configured using an expression, allowing the designer to set document security per integration call. Each user who will call an integration must have at least Editor permission to the selected folder. Note: This field is only shown when an integration is configured to pull back documents in the response as binary or base64 values in a JSON response body. |
| Error Handling | Override error handling to customize error messages or update the criteria for success to check for error messages in the body. The following options are available:
|
| Success Criteria | Return false when this integration should return an error. Use fv!success, fv!error, and fv!result to reference the default integration outputs.
|
| Error Message | Return an error message when this integration success criteria returns false. Use fv!success, fv!error, and fv!result to reference the default integration outputs. Use a!integrationError() to create the custom error message.
|
| Enable HTTP request/response logging for this integration object | This field enables HTTP request/response logging for this integration. Integration calls will only ever be logged to integration_req_resp_activity.log if it is enabled in both the integration object and the Admin Console.The HTTP request/response logs may contain sensitive data or credentials. Before enabling HTTP request/response logs, it's important to understand the integration logging guidelines below. |
SQL integration definitionCopy link to clipboard
The configuration pane of the integration allows you to define the SQL statements you will use in your integration.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Connected System | The custom JDBC connected system you are using for the integration. |
| Operation | The SQL integration type used for this integration. Value can be SQL Write Integration or SQL Query Integration. |
| SQL Statements | The SQL statement or statements to be executed. Multiple statements can be executed in a single integration to allow for batch statement execution against the same external data source. Statements will be executed in the order they appear. |
| Parameters | Placeholders for specific values that can be passed into your SQL statements during execution on the database server. A single parameter can be shared across multiple SQL statements but the parameter value will remain consistent. You can also define all values with a single expression. A parameter value can use an expression or reference a rule input. |
| Timeout | The amount of time each statement can run. The default is 30 seconds but the value is configurable. For example, if you have 5 statements and the value is set to 60 seconds, then each statement can run for up to 60 seconds for a total value of 5 minutes for the entire integration. |
| Auto-commit | The auto-commit mode for your SQL statements. This mode determines whether the database will automatically issue a "COMMIT" operation after every SQL statement. Enable this feature if your database requires it for the JDBC Connected System. However, it is important to note that when auto-commit is enabled, it may consume significant processing time and resources. |
Encrypted valuesCopy link to clipboard
Certain integration fields contain sensitive values like passwords. These values are managed differently depending on whether they are defined directly or are defined using expressions:
- Values entered directly are encrypted and will not be included in the package when the integration object is exported. Use an import customization file to set environment-specific values when importing into other Appian environments.
- Expressions should be used only when you cannot enter values directly. Appian does not manage encryption or environment-specific import for values populated by expressions and
a!scsField()is not supported (instead, use a connected system to share credentials across multiple integrations).
HTTP request/response logging guidelinesCopy link to clipboard
Integrations that enable HTTP request/response logging are much easier to troubleshoot when integrations fail. However, it's important to understand the safeguards we have in place before deciding whether a specific integration should be logged.
HTTP request/response logging safeguardsCopy link to clipboard
There are a number of safeguards in place to ensure that HTTP request/response logging doesn't store sensitive data when used correctly:
- Administrator-only access: The
APPIAN_HOME/logs/perflogs/http-requests-and-responses/subdirectory and theintegration_req_resp_activity.loglog are only accessible by system administrators. This prevents any privilege escalations for designers who shouldn't be able to see certain integrations. - Credentials: Credentials sent in the HTTP request will be masked. This includes all connected system credentials marked as sensitive, as well as anything sent in HTTP headers with the key
Authorization,X-Amz-Security-Token, orCredential. - HTTP request body: Appian will only log the first 100,000 characters of the HTTP request body. Anything beyond that will be truncated. Additionally, any binary files sent in the request body will be replaced with the string
"<binary>". - Log rollover policy: The log files roll over based on time and size. No HTTP request/response log will ever last more than 7 days. The cumulative size of all rollver over HTTP request/response logs will never exceed 100 MB. To learn more about the log rollover policy, see the Logging page.
When not to log HTTP request/responses for an integrationCopy link to clipboard
There are three cases under which you should not enable HTTP request/response logging for an integration:
- Unsupported authentication method: Do not enable logging if you are using an unsupported authentication method. Doing so will result in the credentials being logged in plain text. Logging should only be enabled if one of the following is true:
- The integration uses connected system authentication.
- The integration uses Basic Authentication (for integrations that don't use a connected system).
- The endpoint is unauthenticated.
- Sensitive data in HTTP request: Do not enable logging if the integration sends sensitive data, such as a credit card number, in the request body, HTTP headers, or query parameters. Doing so will result in the sensitive data being logged in plain text.
- Sensitive data in HTTP response: Do not enable logging if the integration returns sensitive data, such as a social security number, in the response body or HTTP headers. Doing so will result in the sensitive data being logged in plain text.
OutputsCopy link to clipboard
Integrations return a result, an error, and a connected system as their output. To learn how to use these outputs, see Call an Integration.
HTTP resultCopy link to clipboard
The result output contains the HTTP response details.
| Field | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| headers | Any Type | The list of HTTP response headers. |
| statusLine | Text | The HTTP response status line, containing the HTTP protocol version and response status code. |
| body | Any Type | The body of the HTTP response. If the HTTP response returns a JSON body, Appian can convert this to an Appian value by enabling automatic parsing. This allows Designers to use dot notation or indexing without the need to create a wrapper rule or expression first. Response bodies over 5 MB cannot be processed and will cause the integration to return an error. |
| contentType | Text | The content type of the HTTP response body, as specified in the Content-Type response header. |
| statusCode | Number (Integer) | The HTTP status code that was returned. For example, 200 for a successful request. |
SQL resultCopy link to clipboard
SQL statements return as a List of Map type:
- When you use a SQL Write integration template, the update count for each separate statement returns as an integer with a Map type.
- When you use a SQL Query integration template, the result set for each separate statement will return as a List of Map with each returned row representing a single Map.
ErrorCopy link to clipboard
The error output contains the information about an unsuccessful request. An Integration error will output the following fields:
| Field | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| title | Text | The general error summary. |
| message | Text | The specific error message. |
| detail | Text | The details about the error. |
Designers can use fv!success, fv!error, and fv!result to create custom error messages using a!integrationError(). Otherwise, a default error message is used after an unsuccessful request.
Note: In general, if an error is returned for a SQL statement in a SQL integration, the transaction will not be committed and any changes will be canceled. If there are multiple statements and at least one statement executes and one does not, then neither transaction will be committed and all changes will be canceled. However, certain database commands are automatically committed and therefore cannot be rolled-back. See your database's specific documentation for more details on what type of statements are set for autocommit.
OAuth connected systemCopy link to clipboard
When an OAuth connected system is used, its value will be stored as part of the integration output. This value is used to generate an authorization link when a user needs to obtain a new access token.
When an OAuth connected system is not used for an integration, the value is null.
VersionsCopy link to clipboard
Each time you modify and save an integration, a new version is created. All objects that use the integration will use the latest version. All versions are accessible to designers who can view the integration, and an integration can be reverted back to a previous version at any time.
For information on how to manage object versions, see Managing Object Versions.
SecurityCopy link to clipboard
The security role map of an integration controls which developers can see or modify it and its properties. By default, integrations inherit the security of the folder that they are saved in. However, after creating the integration, you can disable that inheritance and modify the integration's security. See Editing Object Security to modify an integration's security.
The following table outlines the actions that can be completed for each permission level in an integration's security role map:
| Actions | Administrator | Editor | Viewer | Deny |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Execute the integration | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| View the integration definition | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Duplicate the integration | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Test request | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Update the integration definition | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| View the security | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Rename the integration | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Update the security | Yes | No | No | No |
| Delete the integration | Yes | No | No | No |
DuplicateCopy link to clipboard
Developers with Viewer permissions to this object can duplicate it. There are two ways to duplicate an object:
- From any view in an application, you can select the object you wish to duplicate and use the toolbar option to launch the duplication dialog. The duplicated object will be added to the application you're working in. This capability is only available for single object selections from the grid.
- If you are in an interface, expression rule, integration or decision object, you can select Duplicate from the object's settings menu . From there, you can specify the target application for the new object.
Once you select the Duplicate option, you will see the following dialog:
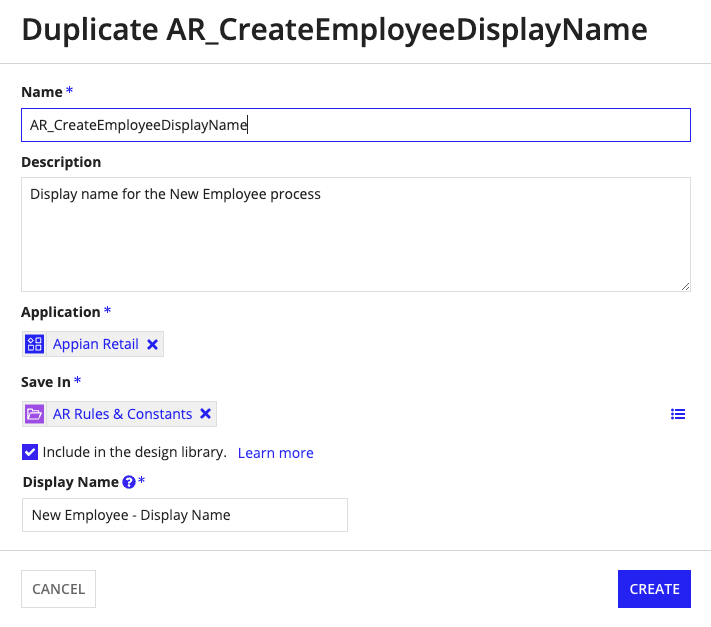
You can only duplicate the most recent version of an object. If you have unsaved changes and attempt to duplicate the object from within the designer, the most recent saved version of the object will be duplicated without the unsaved changes. A banner appears when there are unsaved changes to remind you before duplicating.
LimitsCopy link to clipboard
The HTTP and OpenAPI integrations have limits on both the request body and the response body to ensure proper use.
Binary and base64 encoded documents have higher limits than plain text because they are streamed, and so they stay out of memory. See the request body limits and response body limits for more information on limits related to HTTP and OpenAPI integrations.
Note: The 75 MB base64 limits apply to the combined total of all documents in a single request/response. This means you can send one 75 MB file, or three 25 MB files, but you cannot exceed 75 MB across all the files that are sent. These documents do not count towards the 5 MB body limit.
For SQL integrations, note that the maximum number of rows per result set returned is 1,000. Result sets that exceed the default limit are truncated and a warning will appear.
To change the default value, modify conf.sqlIntegration.limits.maxRowsPerResultSet=.
Note: If you are an Appian Cloud customer, open a support case to change the default value.
Request body limitsCopy link to clipboard
Request body limits are determined by the Content Type value in the Request Body section.
| Request Body Content Type | Request Body Limit |
|---|---|
| JSON (application/json) | 5 MB + 75 MB of base64 |
| XML (application/xml) | 5 MB + 75 MB of base64 |
| Document (auto-detect) | No limit. Best practice is to limit your binary request body to 250 MB. |
| Multipart Form Data (multipart/form-data) | 5 MB, no limit on documents. Best practice is to limit total size of documents for a single multipart request to 250 MB. |
| Text (text/plain) | 5 MB |
| Custom | 5 MB |
Response body limitsCopy link to clipboard
Response body limits are determined by the Response Body Parsing value in the Response section.
| Response Body Parsing | Response Body Limit |
|---|---|
| Return raw response body | 5 MB |
| Convert JSON to Appian value | 5 MB + 75 MB of base64. Note: base64 strings longer than 4,000 characters are truncated. |
| Convert binary to Appian document | 250 MB |
ExamplesCopy link to clipboard
HTTP integration examplesCopy link to clipboard
Using Relative PathCopy link to clipboard
When using a connected system with a base URL attached, designers should construct the URL for an integration using the Relative Path field.
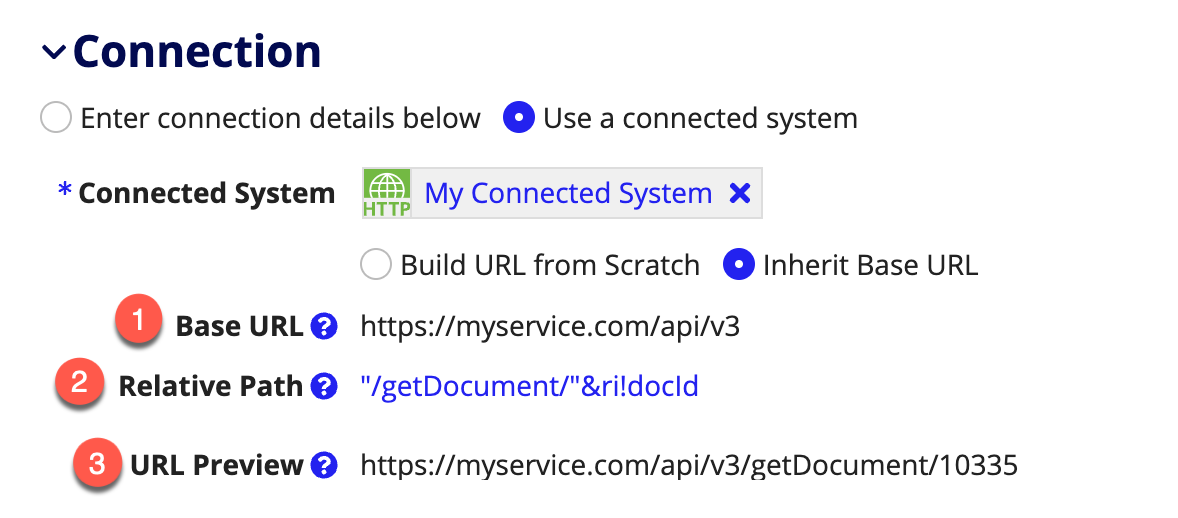
- Base URL should be used to store a consistent prefix for the URLs of all an integrations for that connected system. Base URL is set on the connected system.
- Relative Path specifies the endpoint for a given operation. It is fully expressible, allowing for a dynamic URL based on rule inputs.
- URL Preview is determined by evaluating the relative path and appending it to the connected system’s base URL. This field shows you how Relative Path and Base URL will be combined at runtime to build the integration's URL.
These fields are only displayed when Inherit Base URL is selected. If you would prefer not to leverage the base URL for an integration, you can select Build Base URL from Scratch.
Sending a binary documentCopy link to clipboard
Designers can send documents in the request body as binary. To do so, they must first set the content type to Document (auto-detect) and enter a document in the request body.
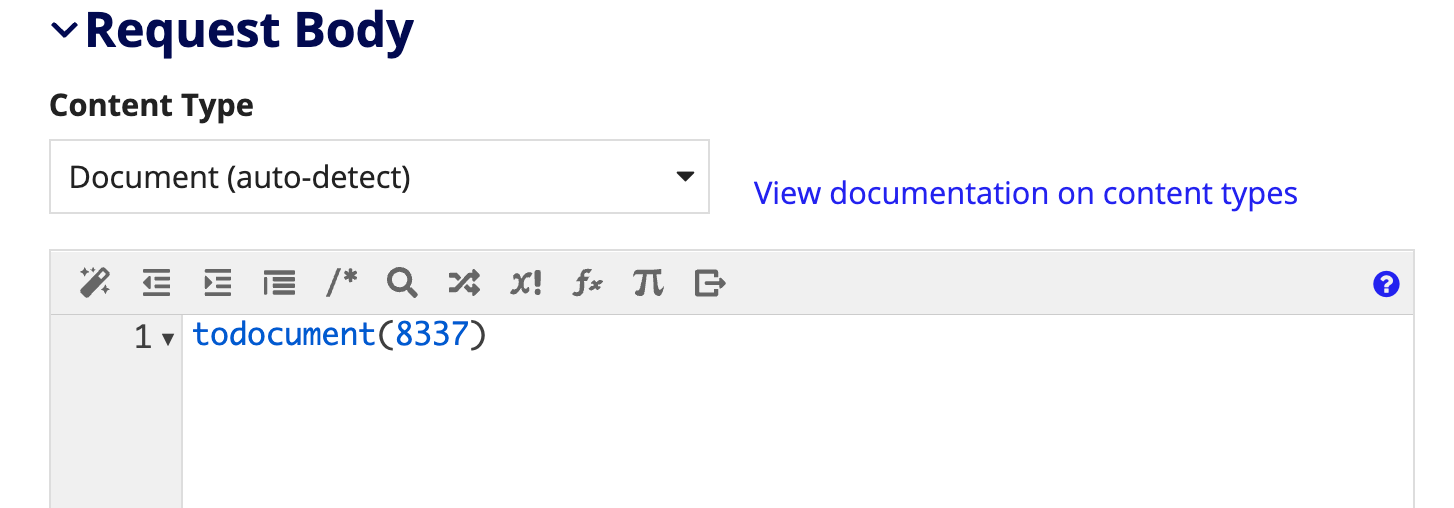
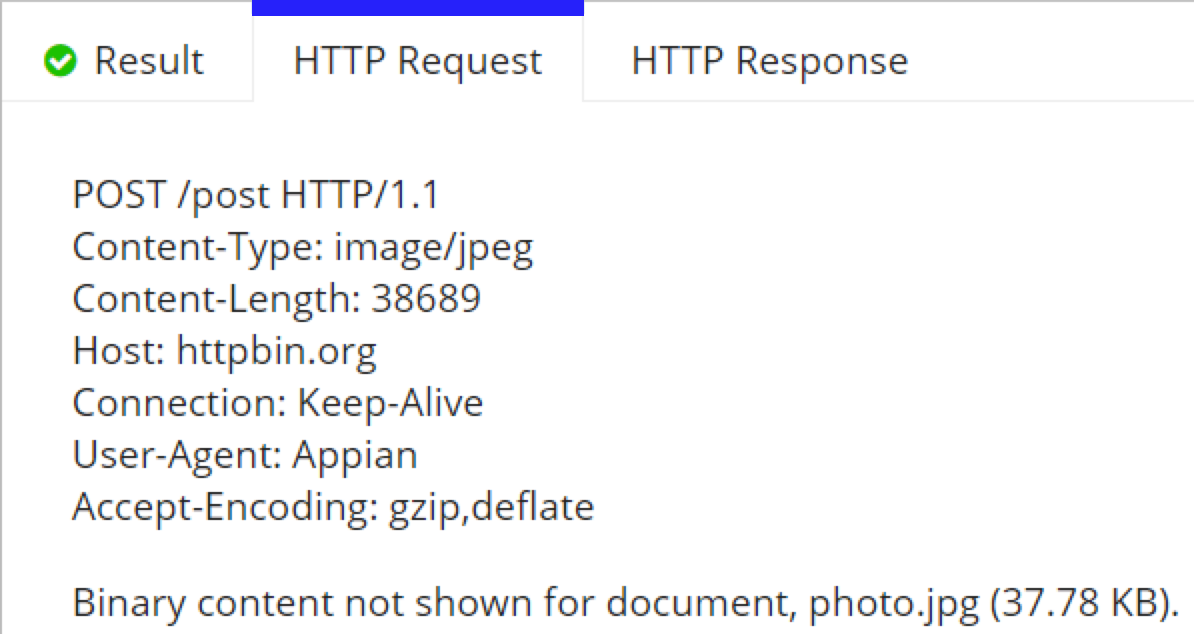
In this example, we cast an integer to type document, but this can also be a constant pointing to a document or a rule input of type document.
When the integration is executed, the content type is automatically detected and the document is streamed as binary data.
Sending base64 inline with JSONCopy link to clipboard
Designers can send base64 documents inline with JSON using a dictionary, a CDT, or a list of either. For this example, we will use a dictionary.
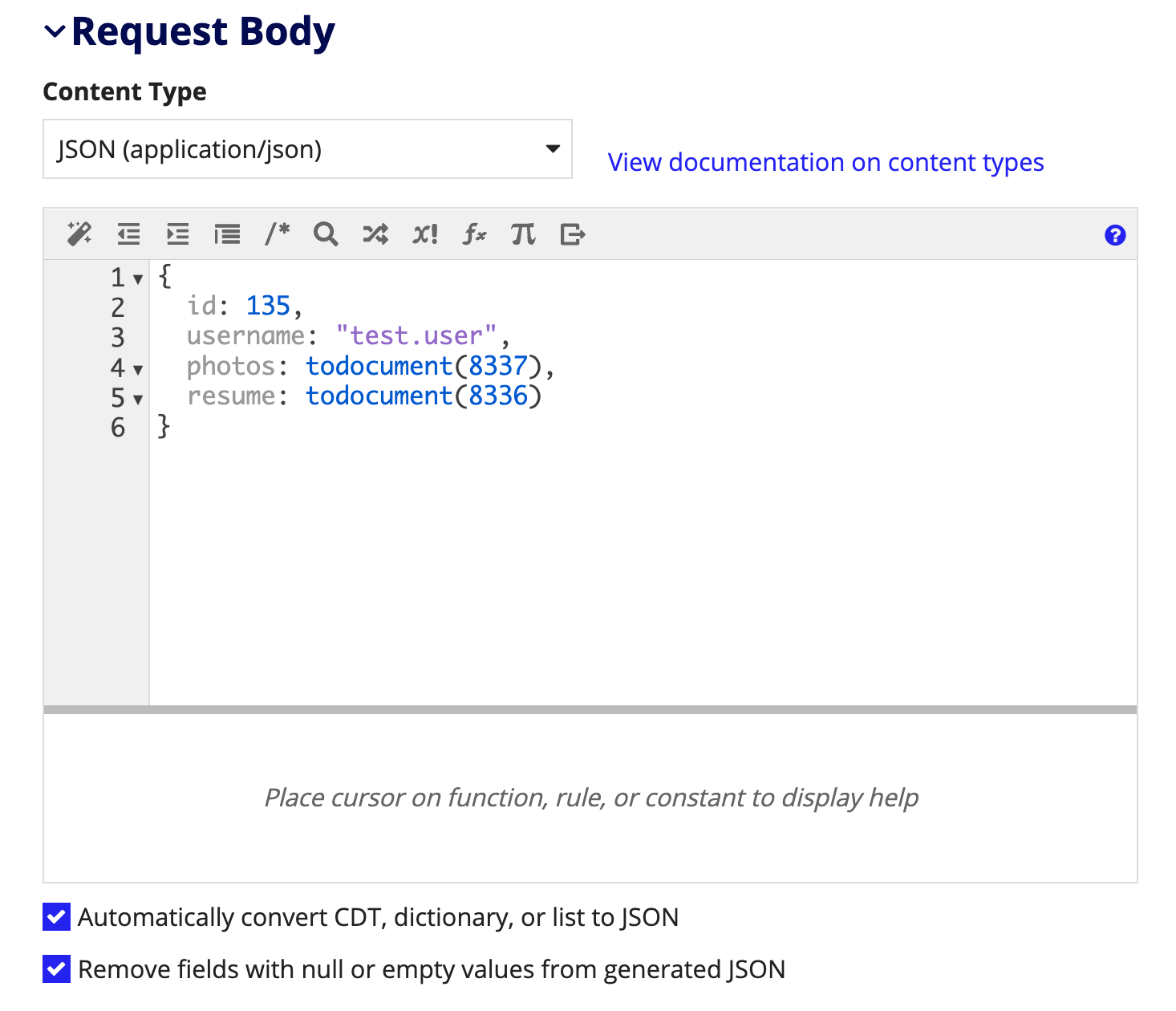
- Set the content type of your request body to JSON (application/json).
- Enter a dictionary containing one or more documents.
- In this example, we cast integers to documents, but these can also be constants pointing to documents or rule inputs of type document. In fact, if you can pass in the whole dictionary as a rule input if you want to.
- Make sure that Automatically convert CDT, dictionary, or list to JSON is selected.
Note: Base64 can only be sent when an Appian value is entered and automatically converted to JSON or use the . If you use a!toJson() to construct the JSON string, documents will not be converted to base64 or streamed.
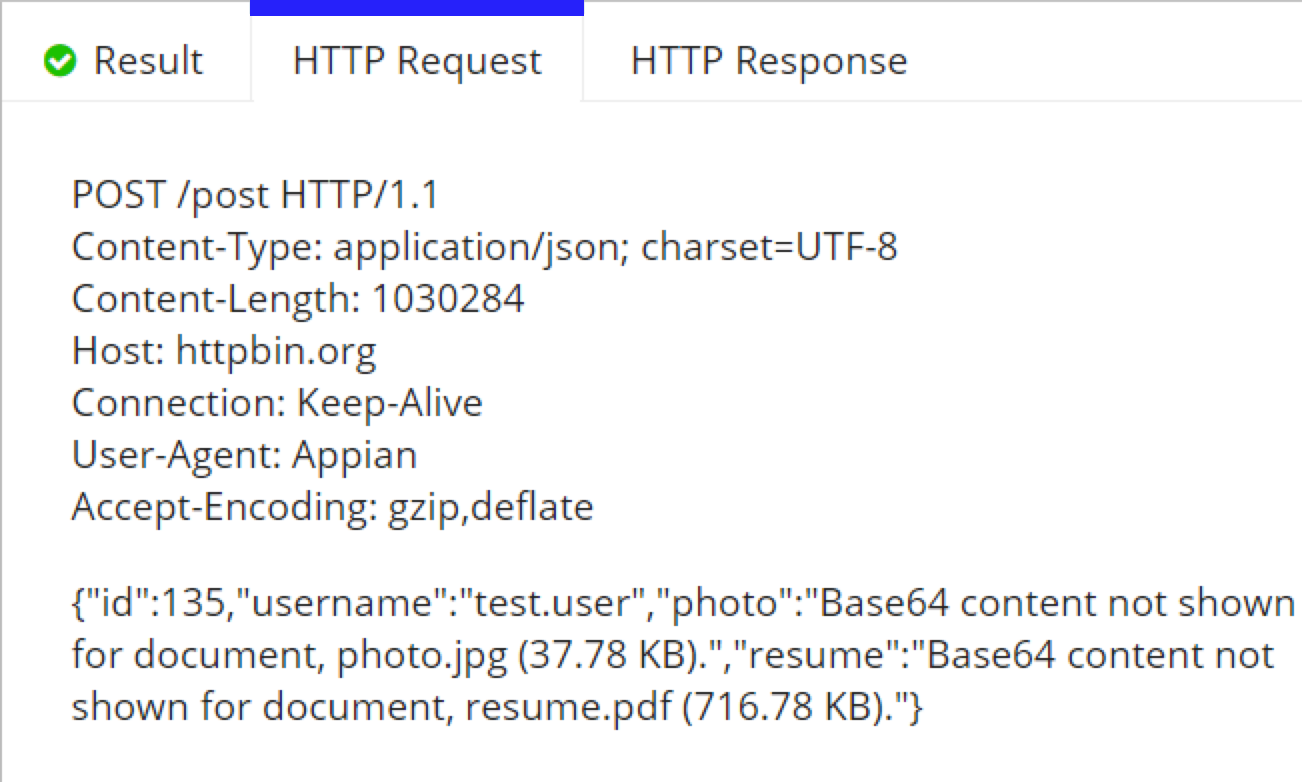
When the integration is executed, the dictionary is automatically converted to JSON and the documents are streamed as base64 data.
Sending base64 inline with XMLCopy link to clipboard
Designers can send base64 documents inline with XML using a CDT. First, they must create the CDT, structured like the XML they want to send and containing one or more fields of type document.
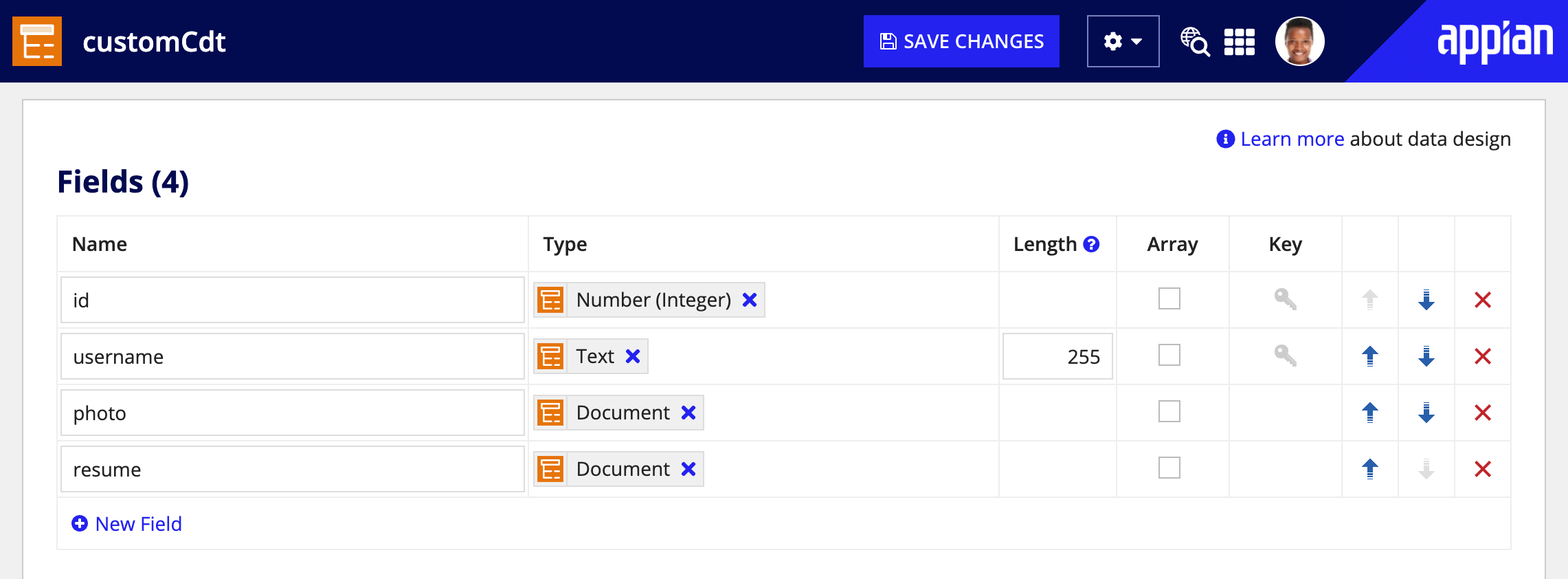
Once the CDT is created, you can configure the integration request body.
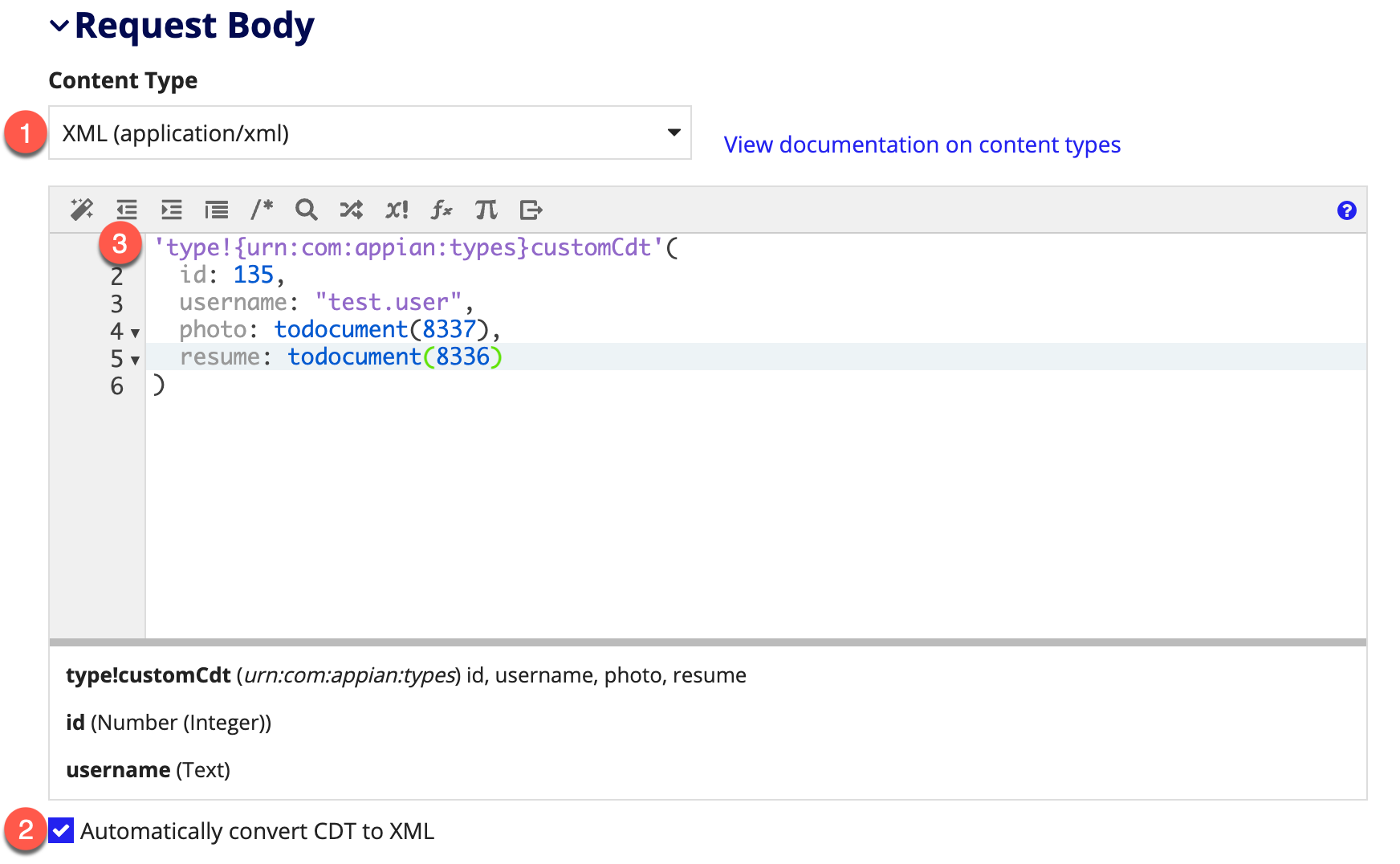
- Set the content type of your request body to XML (application/xml).
- Ensure that the checkbox for automatic request body conversion is enabled.
- Enter the CDT you created. In this example, we cast integers to documents, but these can also be constants pointing to documents or rule inputs of type document. In fact, you can pass in the whole CDT as a rule input.
Note: Base64 can only be sent when a CDT is entered and automatically converted to XML. If you use toxml() to construct the XML string, documents will not be converted to base64 or streamed.
When the integration is executed, the CDT is automatically converted to XML and the documents are streamed as Base64 data.
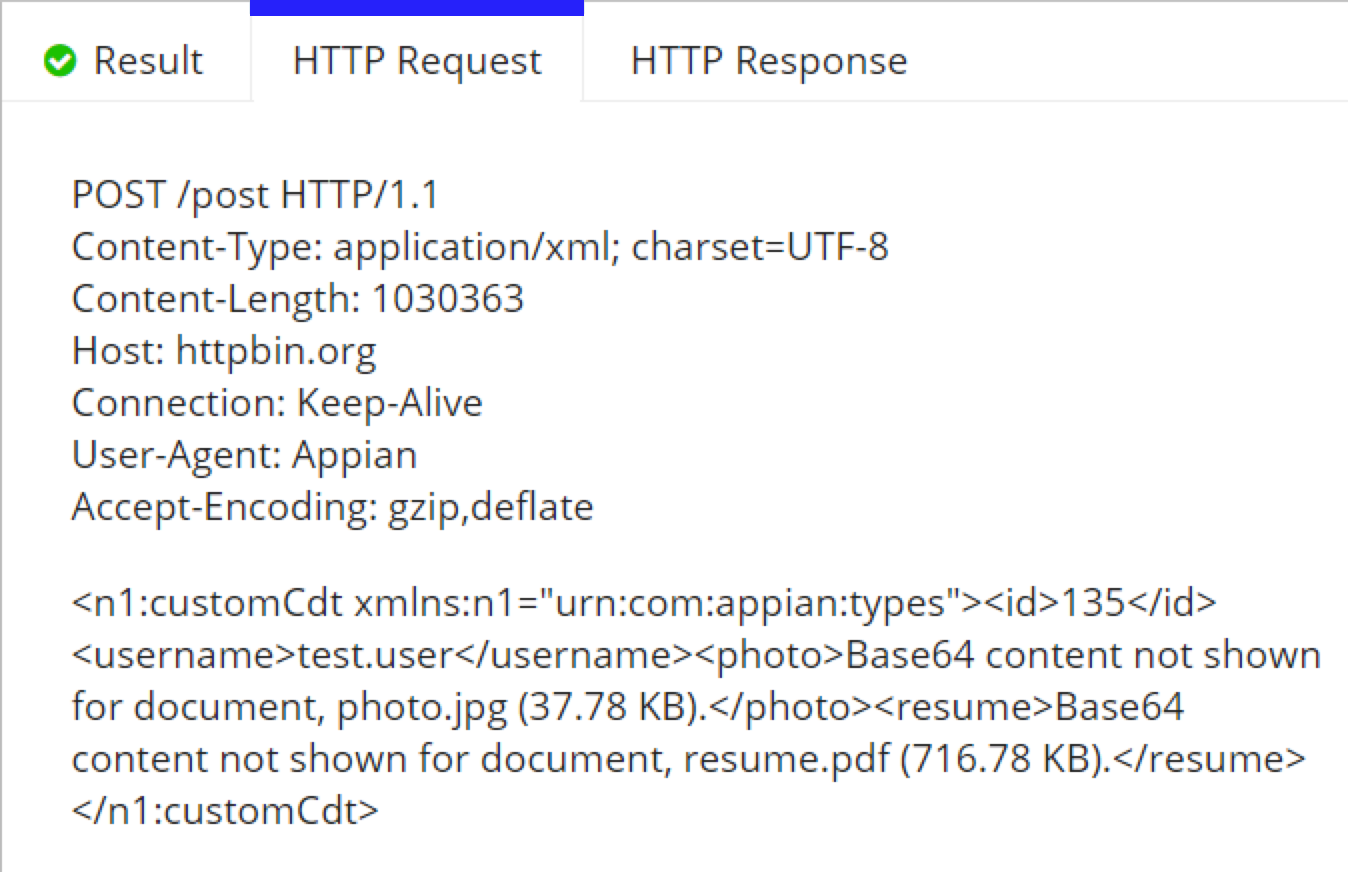
Receiving a binary documentCopy link to clipboard
Designers can configure an integration to pull a binary document from external systems. To do so, you will need to configure the integration response.
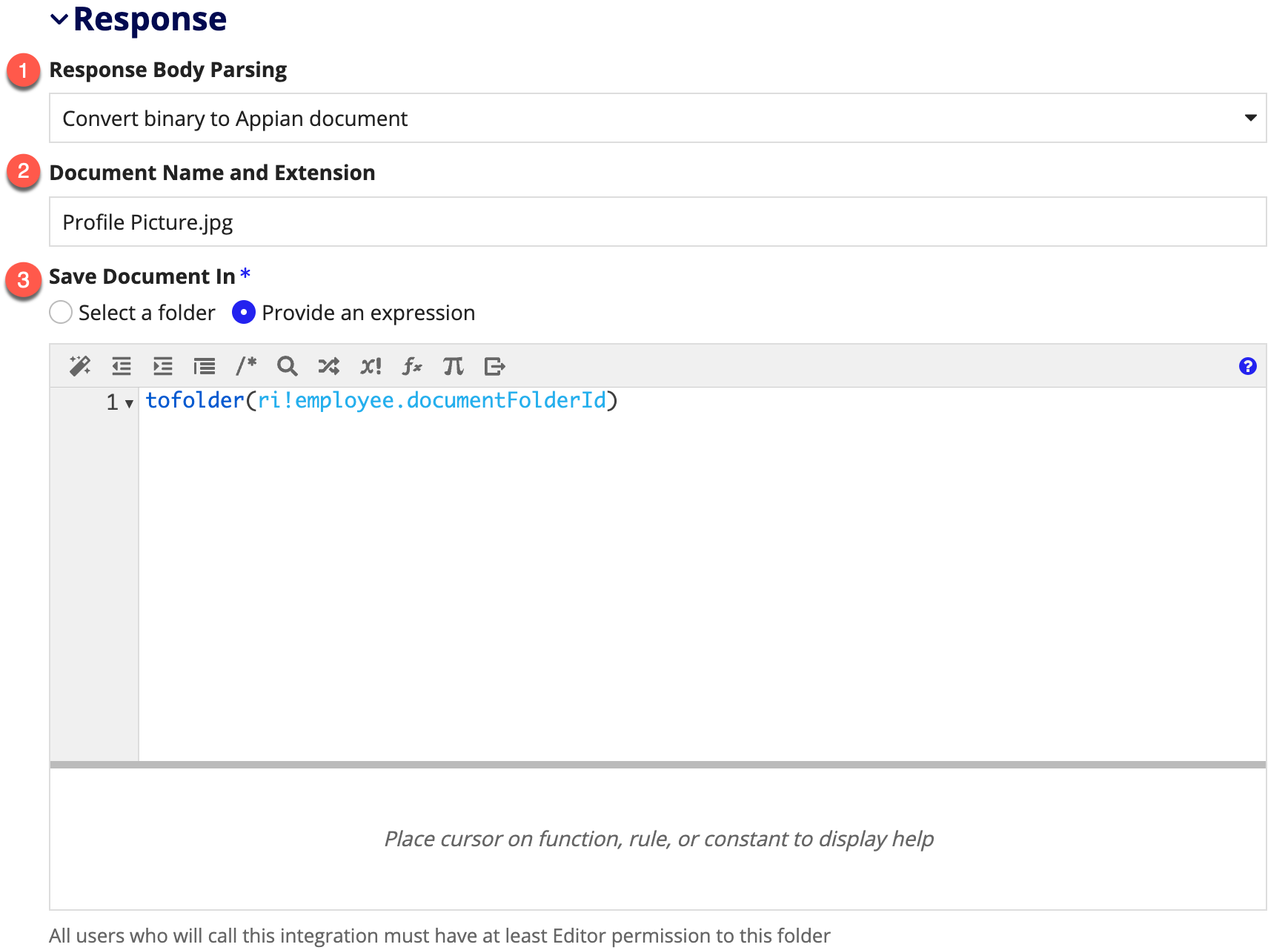
- Set Response Body Parsing to Convert binary to Appian document. This will cause two new fields to appear and also set Usage to Modifies Data.
- Document Name and Extension should be provided to give the document a human-readable name and ensure that it's created with the correct extension. If this field is left blank, Appian will try to infer a name and extension from the response headers.
- Save Document In determines which folder the returned document should be saved in. This can be configured using an expression, allowing the designer to set document security per integration call. Each user who will call an integration must have at least Editor permission to the selected folder.
When the integration is successfully executed, a document will be created with the given name and extension and saved to the selected folder. Integrations can stream a binary file as large as 250 MB from the response body. Because integrations that pull documents are automatically set to modify data, they must be called as a smart service. This means they can only be called in a saveInto parameter, web API, or process model.
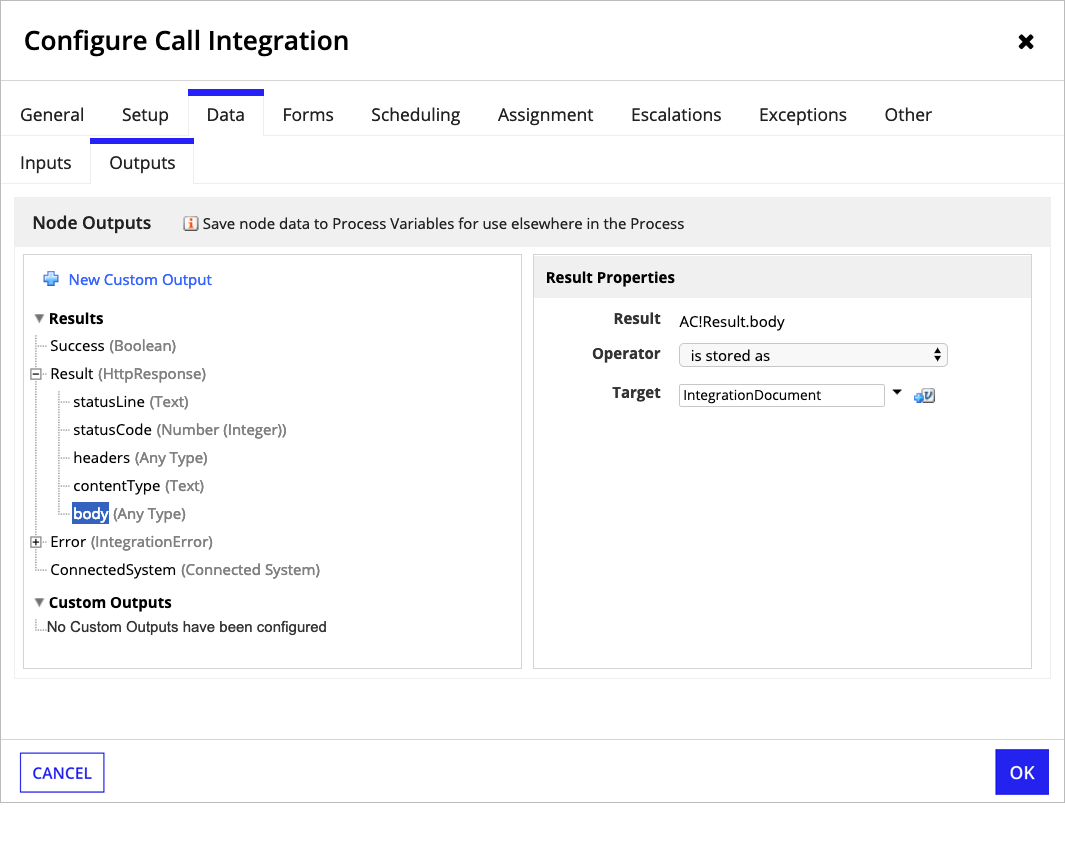
When calling the integration from a process model, map a process variable of type Document to the output AC!Result.body:
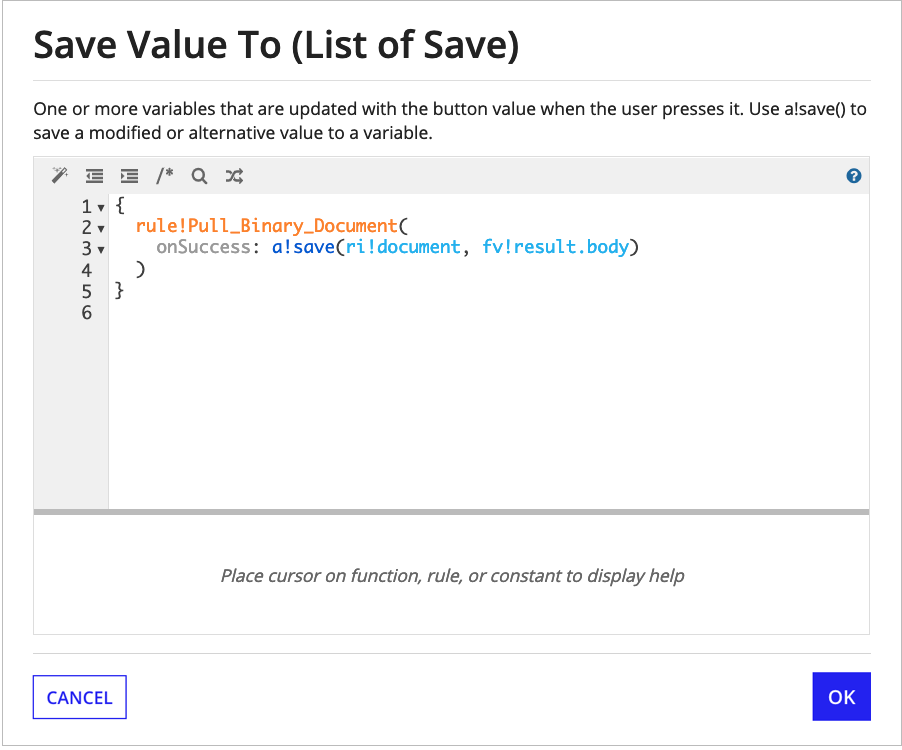
When calling the integration from a web API or a saveInto on an interface, use the onSuccess parameter to save the document in fv!result.body to a variable:
Receiving base64 inline with JSONCopy link to clipboard
Designers can configure an integration to convert base64 values in a JSON response body to Appian documents. To do so, you will need to configure the integration response.
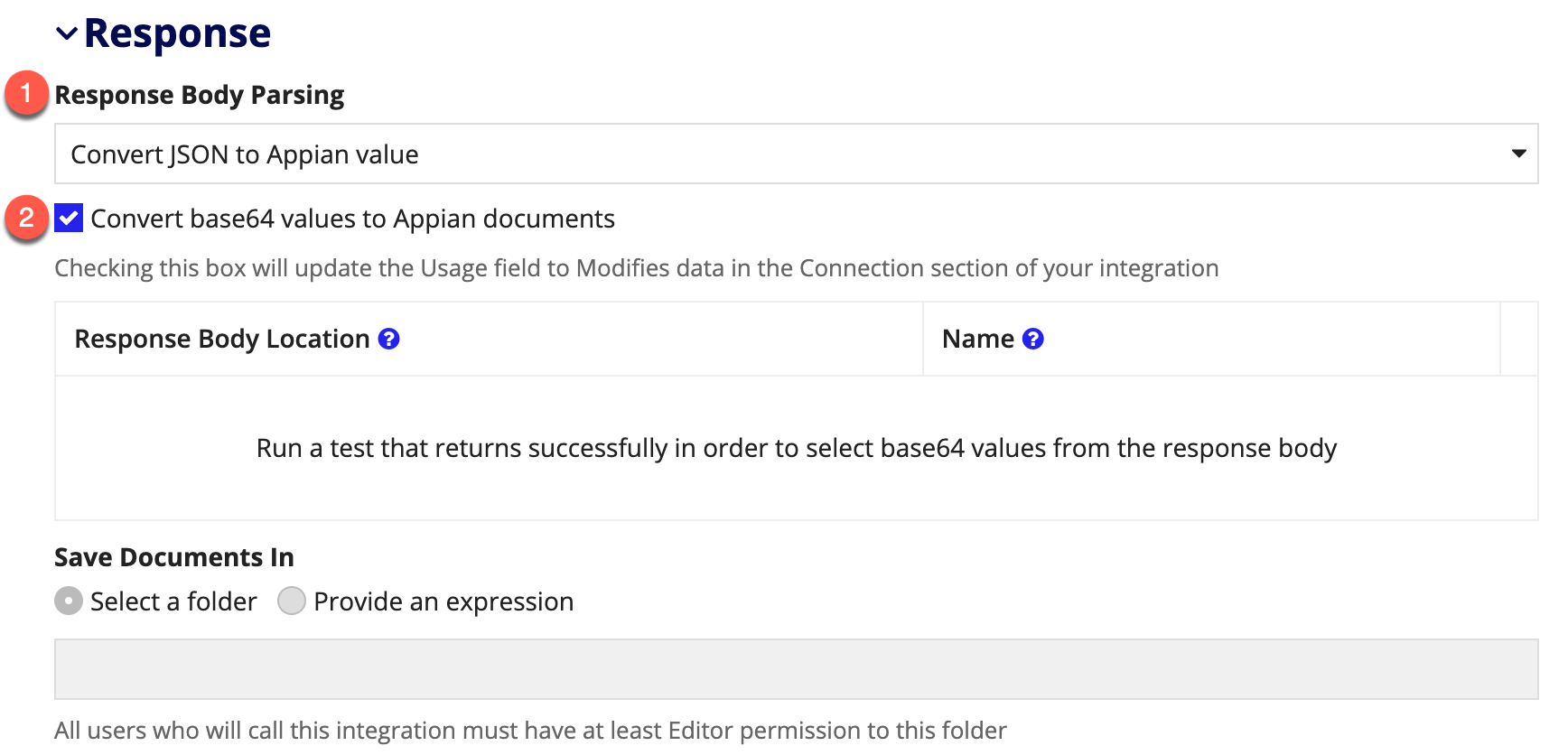
- First, set Response Body Parsing to Convert JSON to Appian value. This will cause a checkbox to appear.
-
Next, select the checkbox. In addition to disabling Usage and setting it to Modifies data, this will expose an empty grid and a disabled folder picker. As the instructional text states, you will need to run a test that returns successfully to proceed with configuration. At that point, the grid and picker will become enabled.
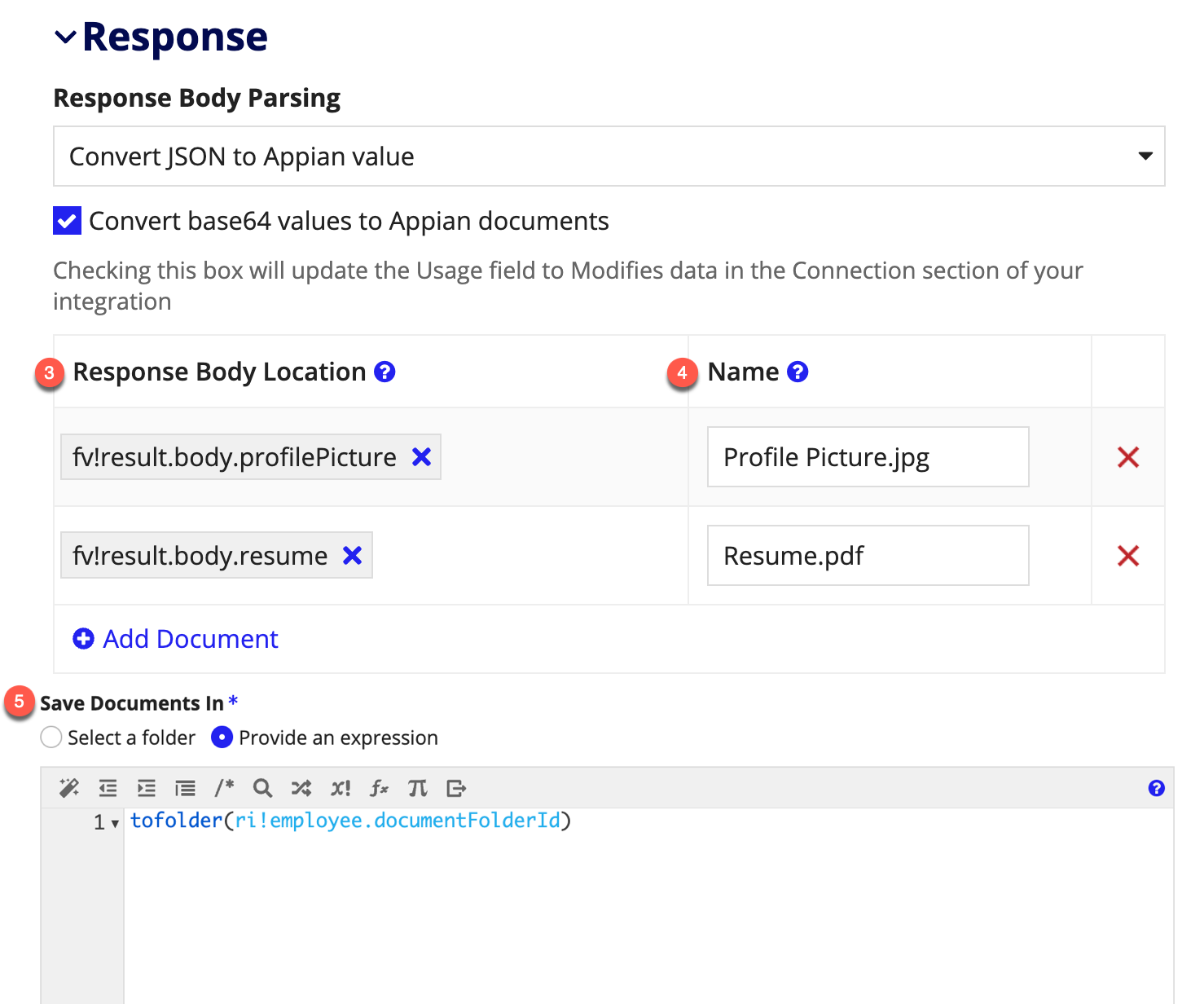
- Select the locations of the base64 strings in the response body from which you want to create documents.
- A name with an extension should be provided to give the document a human-readable name and ensure that it’s created with the correct extension. If this field is left blank, Appian will try to infer a name and extension from the response.
- Save Documents In determines which folder the returned documents should be saved in. This can be configured using an expression, allowing the designer to set document security per integration call. Each user who will call the integration must have at least Editor permission to the selected document folder.
At runtime, configured locations that are found in the response body will be converted to Appian documents. Configured locations that aren’t found in the response will be ignored. This allows the grid to support optional document fields.
When the integration is successfully executed, each document will be created with the given name and extension and saved to the selected folder. Integrations can stream up to 75MB of files as base64 in a single response body (one 75MB file, three 25MB files, etc). Integrations that pull documents are automatically set to modify data, they must be called as a smart service. This means they can only be called in a saveInto parameter, web API, or process model.
When calling the integration from a process model, you can create a CDT for the response and map it to AC!Result.body. Alternately, you can map a process variable of type Document to a custom output for each document location:
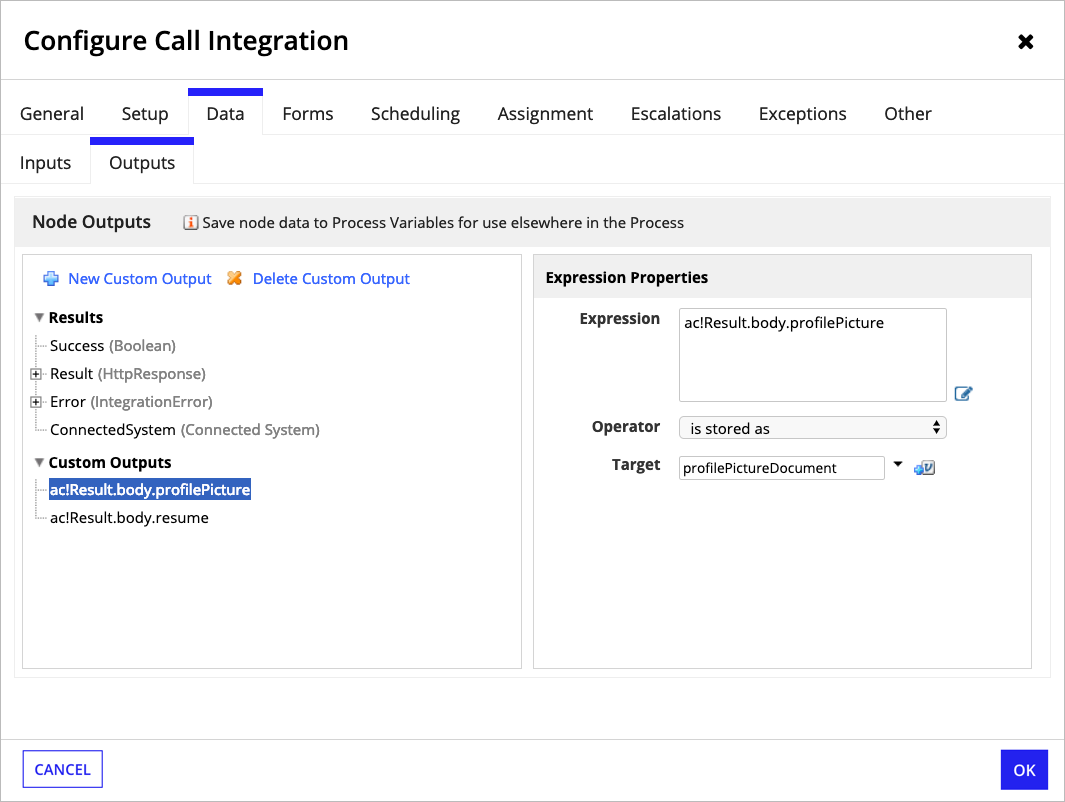
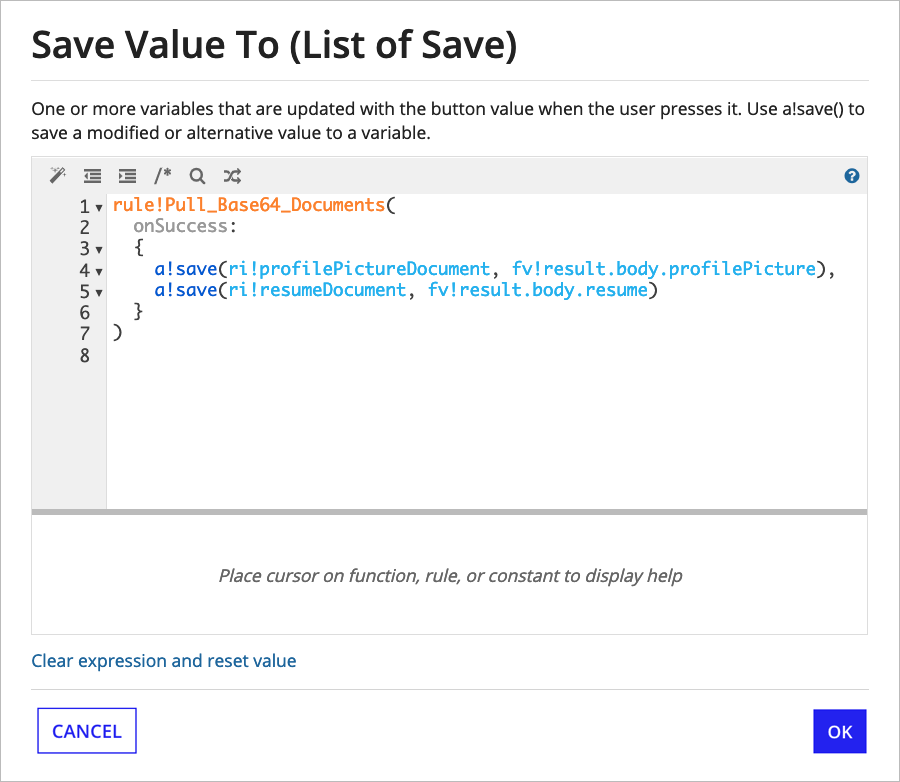
When calling the integration from a web API or a saveInto on an interface, use the onSuccess parameter to save documents to variables:
SQL integration examplesCopy link to clipboard
Building SQL statements to query with static valuesCopy link to clipboard
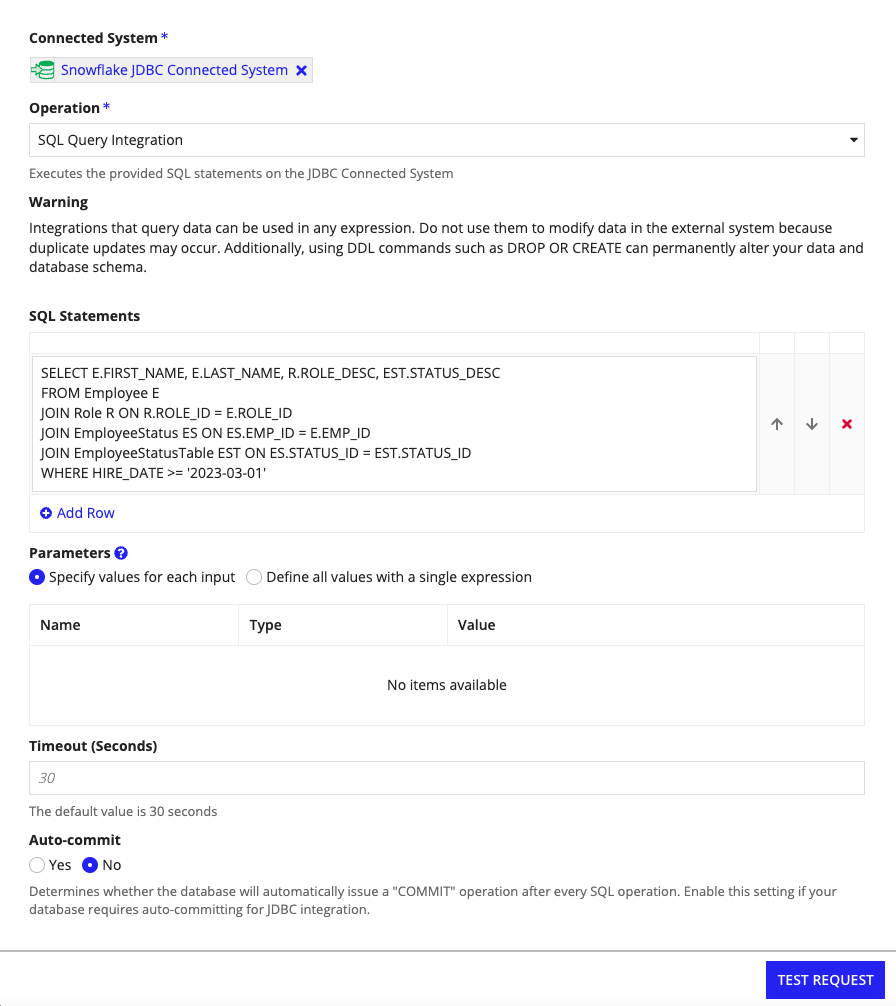
You can query your database with static values, such as HIRE_DATE >= '2023-03-01' used in the following example, by using syntax specific to the database you're querying for the custom JDBC connected system.
Building SQL statements to query with parameterized valuesCopy link to clipboard
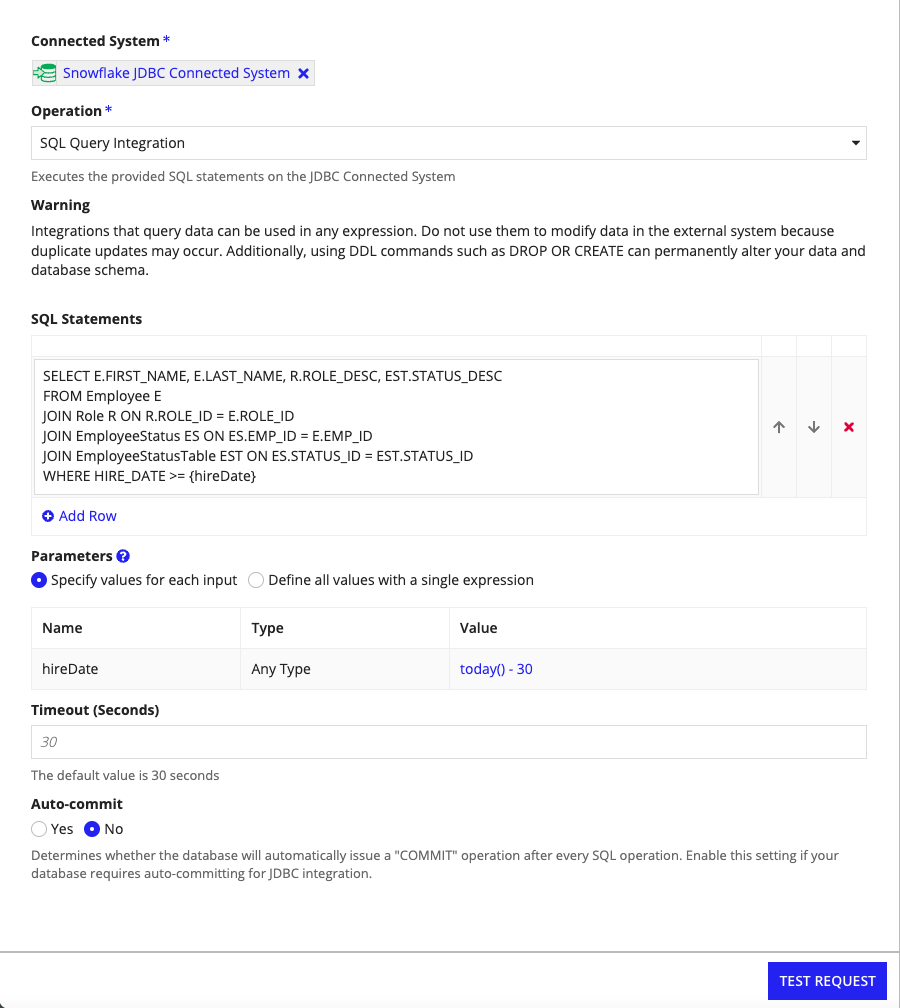
You can parameterize your query directly in the SQL statement. Use curly brackets to define a parameter placeholder, such as {hireDate} in the following example. The parameter value can then be defined using an expression, such as the today() function used in the following example.
Note: Parameter names can only contain alphanumeric characters, dashes, and underscores and must begin with an alphabetic character.
Each parameter in the SQL query can accept a single or a list of input values separated by commas, such as the {"HOUSEHOLD","BUILDING"} used in the following example.

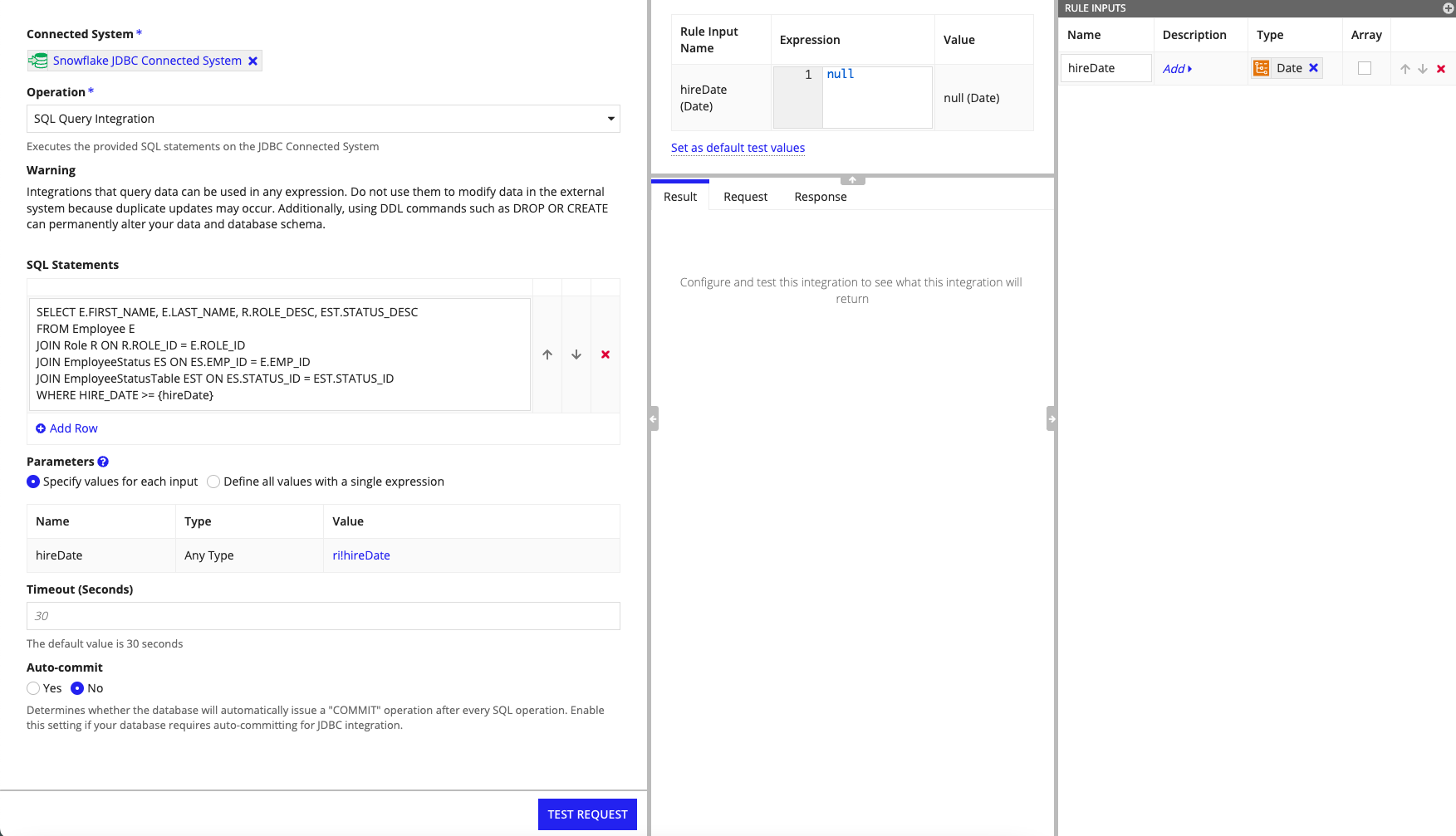
Building SQL statements to query with parameterized values using a rule inputCopy link to clipboard
If you use an expression to define a SQL statement parameter, you can reference a rule input, such as ri!hireDate in the following example.