|
This page applies to Appian Cloud only. It may not reflect the differences with Appian Government Cloud. |
OverviewCopy link to clipboard
For customers who require that their Appian Cloud environments are accessed over a private connection, such as VPN tunnel or AWS PrivateLink, and through the public Internet at the same time, Appian Cloud offers the ability to configure a dual access configuration. This page outlines the steps required to set up an Appian Cloud environment with this configuration.
Appian Cloud also offers the ability to configure inbound web access only over an IPsec VPN tunnel or PrivateLink connection. For more details, see Configuring Inbound Access over VPN or Access an Appian Cloud Environment Using AWS PrivateLink.
Note: Appian Cloud environments running in a high availability configuration will require additional configuration. If you set up static VPN tunnels, you need to set up the necessary network configuration on your infrastructure to forward web requests to a healthy web server. Web servers are accessible on the Appian Network interface IP addresses configured when setting up your VPN tunnel.
Step 1: Set up a private connectionCopy link to clipboard
Required role: Network Administrator or Authorized support contact
Configure one of the following:
- VPN tunnel(s) from your corporate network to your Appian Cloud environment. See Appian Cloud VPN Integration for instructions.
- AWS PrivateLink Connection from your corporate network to your Appian Cloud environment. See Configuring Inbound Access over AWS PrivateLink for instructions.
Step 2: Set up name resolutionCopy link to clipboard
Required role: DNS/Server administrator
Update your DNS infrastructure to resolve the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of your Appian Cloud environment to one of two values based on the source of the DNS query:
- For DNS queries originating over the public Internet:
- For sites using Appian owned domains such as appiancloud.com or appiancloud.us, no changes are required. Appian provisions the required publicly resolvable DNS records automatically.
- For sites using custom domains, you should configure a DNS Canonical Name (CNAME) record pointing to the Appian Cloud public infrastructure DNS name that Appian Support provided you with during custom domain setup.
- For DNS queries originating from within your corporate network, you should configure a DNS Address (A) record in your internal DNS infrastructure pointing to your inbound private connection's IP address.
- For PrivateLink connections, this will be the private IP address associated with the interface VPC endpoint. See Configuring Inbound Access over AWS PrivateLink for more details.
- For VPN connections, this will be the assigned private IP address of the VPN tunnel.
Step 3: Create a support caseCopy link to clipboard
Required role: Authorized support contact
Schedule a maintenance window for the environment by opening a new Support Case with Appian Support.
During the maintenance window, Appian Support will enable the environment to receive inbound HTTPS traffic over the public Internet and your private connection. Once the maintenance window has completed, the environment will be accessible through both methods.
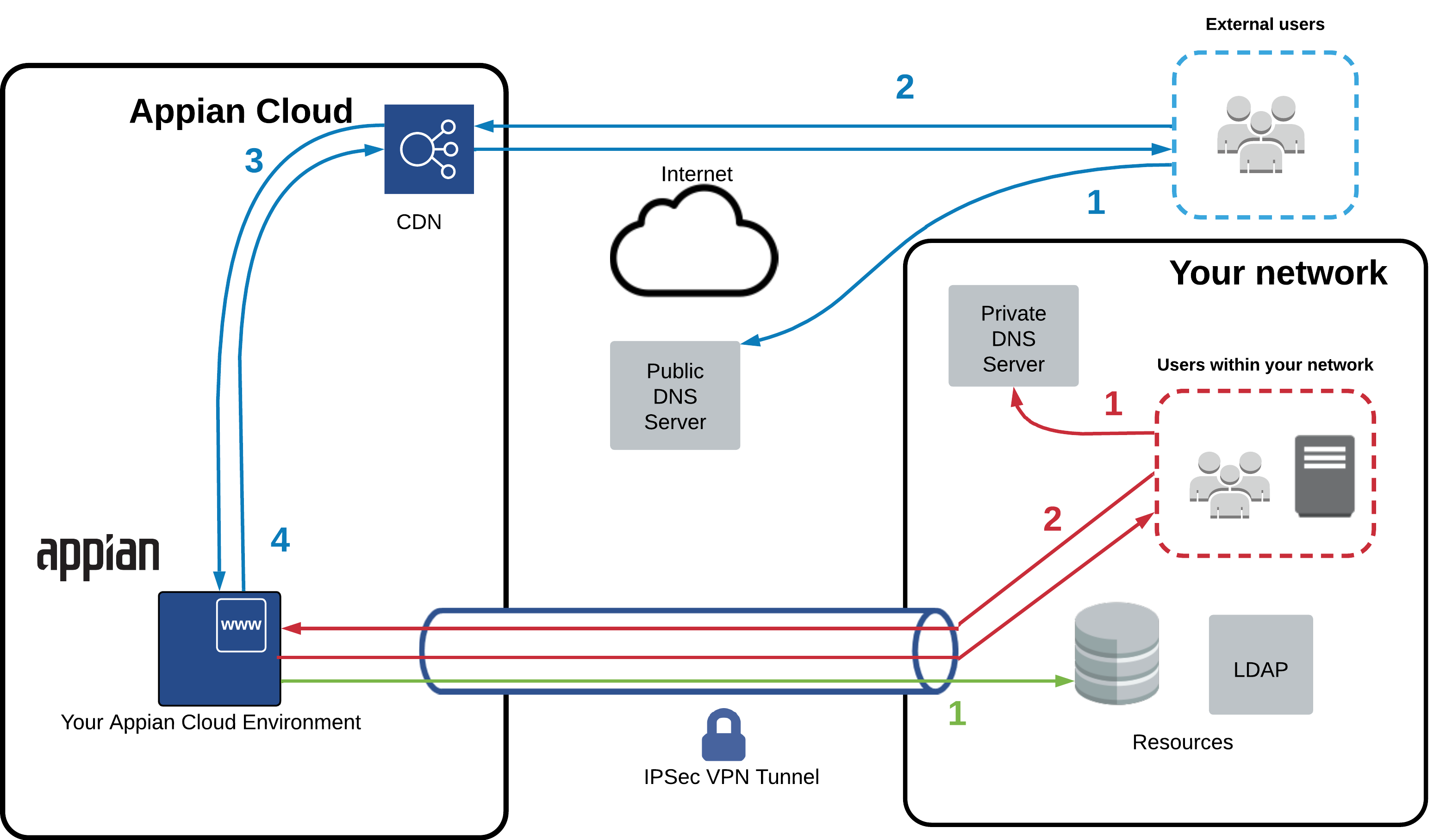
Example traffic flow for inbound web traffic over public Internet and VPNCopy link to clipboard
The diagram below illustrates a sample traffic flow when end users and systems access an Appian Cloud environment over the public Internet and the VPN tunnel at the same time. This diagram assumes a publicly resolvable DNS record has been configured by Appian or the customer such that traffic originating from the public Internet resolves to Appian Cloud's public infrastructure. It also assumes a private DNS record has been configured in the customer's DNS infrastructure such that traffic originating from the customer network will resolve to the private connection's IP address. End users will access the environment using its FQDN.
| Traffic Type | Site Domain Type | Flow Description |
|---|---|---|
| Inbound traffic over the public Internet (blue arrows) | Appian Owned |
|
| Inbound traffic over the public Internet (blue arrows) | Custom |
|
| Inbound traffic over private connections (red arrows) | Appian Owned and Custom |
|
| Outbound traffic (green steps) | Appian Owned and Custom |
|