OverviewCopy link to clipboard
Data source connected systems contain authentication and connection information for data sources, allowing you to connect supported databases to Appian.
This page provides details about data source connected systems. For information that pertains to all connected systems, see Connected System Object.
Supported data sourcesCopy link to clipboard
When you create a connected system, you can choose any Appian-supported database to connect to. The following data sources are available when creating a connected system:
- DB2 Data Source
- MariaDB Data Source
- MySQL Data Source
- Oracle Data Source
- PostgreSQL Data Source
- SQL Server Data Source
- Aurora MySQL Data Source
- Aurora PostgreSQL Data Source
Choosing how to connect to data sourcesCopy link to clipboard
You can also connect to data sources in the Admin Console. Most of the time, you will want to use a connected system. However, there are certain cases where you will need to use the Admin Console.
Benefits of using a data source connected systemCopy link to clipboard
We highly recommend using data source connected systems to take advantage of the following benefits:
- Control access to your data source details using role map security.
- Deploy authentication information for data sources across environments.
- Rename data sources without having to manually update all of the objects that refer to the data source.
- Specify the maximum number of active connections that can be allowed to the database from the data source.
For plug-ins that connect to data sources, use the a!getDataSourceForPlugin functionCopy link to clipboard
If you are using a plug-in that needs to connect to a data source, you can reference that data source by using the a!getDataSourceForPlugin() function.
Migrating data sources from the Admin ConsoleCopy link to clipboard
If you decide to migrate your data sources from the Admin Console to a connected system, keep in mind that you will have to update any objects that refer to the data source.
These objects include:
- Data store objects.
- Record type objects.
- Query database smart service nodes in process model objects.
Additionally, if you are using the data source for the default Quick Apps data source in the Admin Console, you will have to update that data source in the Admin Console.
Enabling one-way SSL/TLS connectionsCopy link to clipboard
You can use Secure Socket Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) in Appian to encrypt a connection to a supported database. SSL/TLS connections provide an additional layer of security by encrypting data transferred between Appian and your database instance or cluster.
In one-way SSL, only Appian validates the server certificate to ensure that it receives data from the intended database server.
Note: The way you enable SSL/TLS connections to a database varies depending on the database. Refer to your database vendor’s documentation for configuration details.
You cannot enable one-way SSL/TLS connections to DB2 database using a self-signed or private certificate authority (CA) signed certificate.
To enable one-way SSL/TLS connections to an Appian-supported database:
- Enable SSL/TLS on your database server.
- Ensure that a valid SSL certificate has been uploaded to the Trusted Server Certificates in the Admin Console, especially if you are using a self-signed or private certificate authority (CA) signed SSL certificate on your database server.
- Add SSL connection properties to your database connection URL. Below is an example connection URL for each supported RDBMS:
- MariaDB
jdbc:mariadb://yourserver.example.com:3306/your_db_name?useOldAliasMetadataBehavior=true&useSSL=true&sslMode=VERIFY_IDENTITY - MySQL
jdbc:mysql://yourserver.example.com:3306/your_db_name?useOldAliasMetadataBehavior=true&useSSL=true&sslMode=VERIFY_IDENTITY - Oracle
jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcps)(HOST=yourserver.example.com)(PORT=2484))(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=YOUR_DB_NAME))) - SQL Server
jdbc:sqlserver://yourserver.example.com:1433;databaseName=your_db_name;encrypt=true;sslProtocol=TLS;trustServerCertificate=false - PostgreSQL
jdbc:postgresql://yourserver.example.com:5432/your_db_name?escapeSyntaxCallMode=callIfNoReturn&ssl=true&sslmode=verify-full
- MariaDB
Using schemas to control access to data in the Appian Cloud databaseCopy link to clipboard
If you are using the Appian Cloud database, members of the Database Administrators group can create new schemas in the database which generates credentials. You can use these credentials to create MariaDB data source connected systems to connect to the newly created schemas. You can then give certain developers access to certain schemas.
For example, you may want to restrict access to human resources data to developers who are specifically working on human resources applications. Furthermore, you may want to give developers access to this data in development environments, but restrict access in testing and production environments.
To learn more about creating schemas in the Appian Cloud database to control access to data, see Appian Cloud Database Administration.
Deploying data source connected systemsCopy link to clipboard
Keep the following caveats in mind when deploying data source connected systems between environments.
Before deploying, create any additional Appian Cloud database schemas in the target environmentCopy link to clipboard
If you are using additional schemas in the Appian Cloud database to control access to data, manually create the schema in the target environment before deploying the data source connected system.
Deploy database scripts separately from their data source connected systemCopy link to clipboard
If your application includes a data source connected system, the data source connected system object must exist in the target environment before you can run database scripts against it. Furthermore, when a data source connected system object is a part of a direct deployment, you cannot run database scripts for that data source in the same deployment.
As a result, there are additional considerations for direct deployments if you're creating or updating a data source connected system object and deploying database scripts at the same time.
For these specific deployments, perform the following two-part process:
- Deploy a package that contains the connected system object, but does not include database scripts for the data source being deployed.
- After the first package successfully deploys, deploy a package that includes the database scripts and any relevant design objects, but leaves out the connected system object.
Don't update multiple schemas in one SQL scriptCopy link to clipboard
If you are using additional schemas in the Appian Cloud database to control access to data, each schema has a different database user. This database user doesn't have access to other schemas in the environment, but it does have access to the default "Appian" schema.
Compare and deploy uses the database user for the Data Source that is selected. Therefore, if you are using compare and deploy to run SQL scripts, make sure you don't try to update any additional schemas.
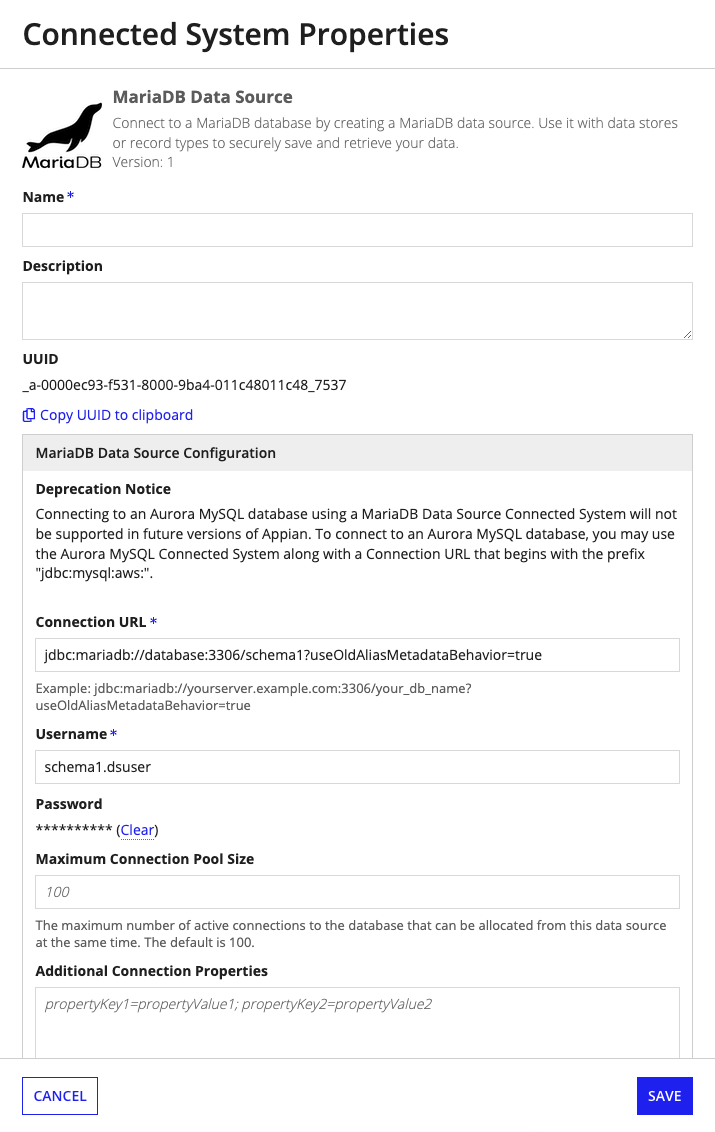
PropertiesCopy link to clipboard
Data source connected systems have the following properties:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the data source that will appear in the Appian design objects, such as data store objects. |
| Description | Supplemental information about the connected system. |
| Connection URL* | The URL for the data source. Should include: the hostname, port, and database name of the data source. However, the exact syntax will vary by database type. If you do not know the URL for the data source, consult your database administrator. Refer to Configuring Relational Databases for special considerations when configuring databases for use with Appian. |
| Username* | The username for connecting to the data source. |
| Password* | The password for connecting to the data source. The password will be stored in an encrypted format. |
| Maximum Connection Pool Size* | The maximum number of active connections to the database that can be allocated from this data source at the same time. The default is 100. Since there is a limited number of connections that applications can make to the database, this field prevents one connected system from hogging the entire connection pool. You can raise or lower this number to control the number of connection pools for a data source. For example, if you have a data source for an application with low usage, you can lower this number to further limit the number of connection pools for the application. This would prevent the application from taking up too many resources. |
| Additional Connection Properties | A list of properties that are passed to a JDBC driver to create database connections. These properties can be driver-dependent and should be separated by semicolons. |
*This value is included in import customization files so that you can specify a different value for each environment.
Automating property updatesCopy link to clipboard
This object's properties can also be updated programmatically using the Update Connected System endpoint. This lets you change passwords, API keys, and other values without needing to sign in to Appian.
The following properties can be included in the JSON request body of the PATCH /connected-system/<UUID> call.
connectionUrlusernamepasswordmaxConnections
