OverviewCopy link to clipboard
This page provides guidance on how to use the Execute Stored Procedure smart service in your process model.
Stored procedures are a set of SQL statements that you can save in your database and use to query or modify data over and over again. The Execute Stored Procedure smart service lets you execute a stored procedure that is defined on any of the Appian supported relational databases that you have connected to.
To execute a stored procedure you need to provide:
- A data source connected system constant. Or for Admin console data sources, the name of the data source.
- The name of the stored procedure.
- Inputs to the stored procedure which correspond to the IN and INOUT parameters.
More information about the parameters can be found in the configuration options and database specific behaviors sections.
After a stored procedure is successfully executed, a map containing a list of result sets and a list of parameters corresponding to the OUT and INOUT values of the stored procedure is returned.
Permissions neededCopy link to clipboard
If using a data source connected system, the user executing this activity must have Viewer permissions to the selected data source connected system in order to execute stored procedures.
PropertiesCopy link to clipboard
-
Category: Data Services
-
Icon:
-
Assignment Options - Unattended
Configuration optionsCopy link to clipboard
This section contains tab configuration details specific to this smart service. For more information about common configurations see the Process Node Properties page.
Data tabCopy link to clipboard
Node inputsCopy link to clipboard
| Name | Data Type | Description | Required | Multiple |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Source | Any Type | The data source that contains the stored procedure. The value depends on how your data source is connected. For data source connected systems, enter the connected system constant. For data sources connected in the Admin Console, enter the name of the data source or a Text constant that stores the name. | Yes | No |
| Procedure Name | Text | Name of the stored procedure. Case sensitivity requirements are specific to each type of database. For Oracle and Db2 databases, enter the name in uppercase. For PostgreSQL databases, enter the name in lowercase. | Yes | No |
| Pause Node On Error | Boolean | If set to true, pauses the node if the stored procedure execution fails. Default: true. | Yes | No |
| Run Validation | Boolean | If set to true, runs validations on the stored procedure before execution. See the running without validations section below before setting to false. | Yes | No |
| Timeout | Number | The amount of time (in seconds) until the stored procedure execution is cancelled. Default: 30 seconds. | No | No |
| Auto-commit | Boolean | Determines whether the database will automatically issue a COMMIT operation after every SQL operation. Default: False. |
No | No |
Note: If you do not see the Auto-commit input in your Execute Stored Procedure node, drag-and-drop a new node into your process model to use the latest version of the node.
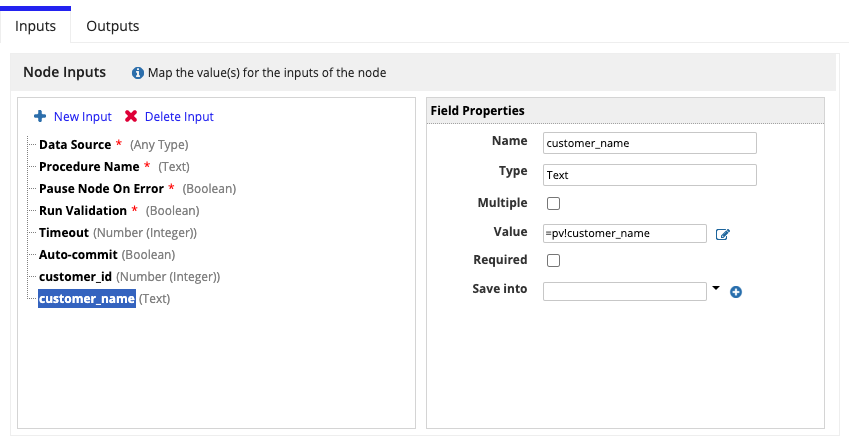
In addition to the parameters above, inputs with names corresponding to the IN and INOUT parameters of the stored procedure must be created manually. A custom input parameter must be provided for every IN and INOUT parameter in order to pass validations. IN and INOUT parameters can be configured to pass values into the stored procedure by setting the Value field. Remember, the name of each custom input must match the name of a corresponding stored procedure parameter.
Example of passing custom stored procedure inputsCopy link to clipboard
Given a stored procedure with the following IN and INOUT parameters:
- IN parameter: customer_name
- INOUT parameter: customer_id
You can pass customer_name and customer_id into the stored procedure from a process variable by configuring a custom input as you see in the image below.
Note that the output for the INOUT parameter customer_id will be available in an activity class parameter in the outputs tab.
Running without validationsCopy link to clipboard
It is strongly recommended to run validations when executing stored procedures unless severe performance degradations are observed as a result.
If you choose not to run validations, the following rules will apply:
- You must add an input for each IN, INOUT, and OUT parameter to the stored procedure in the same order that they are listed in the stored procedure’s signature. If OUT parameters are not added as inputs, they will not be available in the
ac!parametersactivity class parameter. - For most databases, stored procedures must not contain parameters with data types outside of Integer, Double, Date, Time, Timestamp, Varchar, and Boolean. In addition, the type of each input must correspond to the SQL data type of the stored procedure parameter, as reflected in the table below.
| Appian Data Type | Inferred SQL Data Type |
|---|---|
| Number (Integer) | Integer |
| Number (Decimal) | Double |
| Date | Date |
| Time | Time |
| Timestamp | Timestamp |
| Text | Varchar |
| Boolean | Boolean |
Depending on the type of database you are using, exceptions to the data type mappings above may apply. See database specific behaviors for more details.
Node outputsCopy link to clipboard
| Name | System Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Error Occured | Boolean | Whether the stored procedure has returned an error. |
| Error Message | Text | The error message if an error occurred. |
| Result Sets | List of Map | Result sets returned by the stored procedure. |
| Parameters | Map | OUT and INOUT parameters returned by the stored procedure. |
In addition to the outputs above, custom outputs with names corresponding to the OUT, INOUT, and resultSets parameters of the stored procedures can be configured in the outputs tab.
Parameters can be accessed using the ac!parameters activity class parameter. Similarly, result sets can be accessed using the ac!resultSets activity class parameter. By parsing these outputs in a custom output expression, you can save individual stored procedure parameters and result sets into process variables.
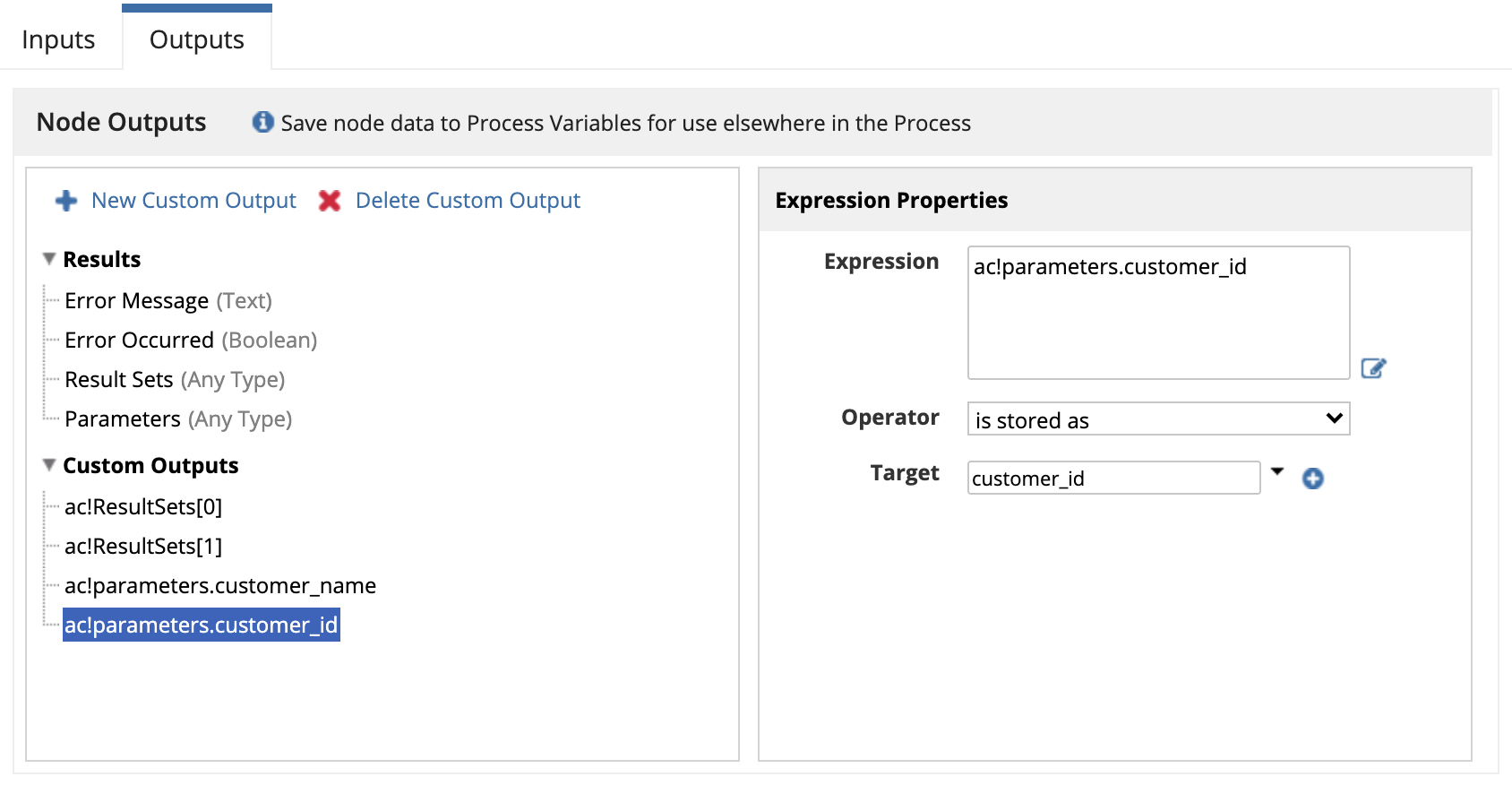
Example of saving custom stored procedure outputsCopy link to clipboard
Given a stored procedure that returns two result sets and the following OUT parameters:
- OUT parameter: customer_name
- OUT parameter: customer_id
You can save each result set and each OUT or INOUT parameter in its own process variable by using custom outputs with the following configurations.
ac!parameters.customer_nameis stored aspv!customer_nameac!parameters.customer_idis stored aspv!customer_idac!resultSets[0]is stored aspv!first_resultac!resultSets[1]is stored aspv!second_result
In the image below, you can see how these configurations can be applied in the outputs tab of the smart service node.
Usage considerationsCopy link to clipboard
LimitationsCopy link to clipboard
Keep in mind the following default values and limitations when executing stored procedures:
| Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
| Max timeout | The default maximum value for timeout for a stored procedure is 600 seconds. There is a built-in 60 minute timeout imposed on some Smart Service nodes. As a result, this can effectively limit the actual timeout period to 3600 (seconds). This limit is only imposed on the Smart Service, so the Execute Stored Procedure functions will still run with respect to the maxTimout value configured in custom.properties. Contact Appian Support if you have a procedure that runs longer than 60 minutes and you are encountering timeout issues when calling stored procedures from the Smart Service. |
| Max rows per result set | The default maximum value for number of rows per result set is 1000. Result sets that exceed this threshold will be truncated. |
| Max total rows | For stored procedures with multiple result sets, the default maximum value for the collective number of rows is 10,000. Once the collective maximum is reached, all subsequent rows and result sets will be absent from the output. |
These properties can also be configured to increase or decrease the default maximum value:
-
For Appian Cloud customers, you can update these values by opening a support case.
-
For self-managed installations, you can update these values by modifying the following properties in
custom.properties:conf.executeStoredProcedure.limits.maxTimeout= conf.executeStoredProcedure.limits.maxRowsPerResultSet= conf.executeStoredProcedure.limits.maxTotalRows=
For example:
conf.executeStoredProcedure.limits.maxTimeout=500
The configured value is
500seconds. With this setting, the value provided for the timeout parameter cannot exceed 500 seconds.
Note: The default maximum values represent the recommended settings even though there are no upper bounds limiting custom configurations. Be aware that configuring these guardrails to a value that is significantly greater than the default maximum value may increase your risk of encountering a system error or crash. While unlikely with most configurations, you should still plan to review and test any custom settings accordingly.
Data sync behavior for record typesCopy link to clipboard
If you use this smart service to add, update, or delete data in a database table, and that table is the source of a record type with data sync enabled, those changes will not be automatically synced in Appian.
To sync changes made by this smart service, use the Sync Records smart service. Any data changed by this smart service will also be synced during the next scheduled sync or if you trigger a manual sync.
To automatically sync changes made to a database table, consider using the following smart services instead:
Database specific behaviorsCopy link to clipboard
Stored procedures can be executed on any Appian supported relational databases. Below, we have listed some database specific behaviors that impact how you execute stored procedures from Appian.
OracleCopy link to clipboard
- Capitalize all letters in the stored procedure name and input parameters.
- For a stored procedure that is defined within a package in an Oracle database, enter the procedure name as PACKAGE_NAME.STORED_PROCEDURE_NAME
- Access the stored procedure query results in the
parameterskey using the name that corresponds to the cursor parameter, instead of inresults.
DB2Copy link to clipboard
- Capitalize all letters in the stored procedure name and input parameters.
- Access the stored procedure query results in the
parameterskey using the name that corresponds to the cursor parameter, instead of inresults.
PostgreSQLCopy link to clipboard
- The stored procedure name and input parameters are case sensitive.
- Add the
escapeSyntaxCallMode=callIfNoReturnorescapeSyntaxCallMode=callparameter to the connectionURL of the data source. - Access the stored procedure query results in the
parameterskey using the name that corresponds to the cursor parameter, instead of inresults. - When executing stored procedures from a process model node with validations disabled, parameters of type Number (Integer) in Appian will be passed to the stored procedure as type BIGINT.
a!executeStoredProcedureOnSave()Copy link to clipboard
The Execute Stored Procedure smart service is available as an expression function that can be executed inside a saveInto on a component or as part of a Web API.
For information on how to execute a read-only stored procedure from anywhere in Appian, see the a!executeStoredProcedureForQuery() function. Unlike the smart service function, a!executeStoredProcedureForQuery() is not restricted to being called inside a saveInto. However, the a!executeStoredProcedureForQuery() function should not be used to execute stored procedures that modify data.
SyntaxCopy link to clipboard
a!executeStoredProcedureOnSave( dataSource, procedureName, inputs, timeout, autoCommit, onSuccess, onError )
ParametersCopy link to clipboard
| Keyword | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Any Type |
The data source that contains the stored procedure. The value depends on how your data source is connected. For data source connected systems, enter the connected system constant. For data sources connected in the Admin Console, enter the name of the data source or a Text constant that stores the name. |
|
|
Text |
Name of the stored procedure. Case sensitivity requirements are specific to each type of database. For Oracle and Db2 databases, enter the name in uppercase. For PostgreSQL databases, enter the name in lowercase. |
|
|
List of Map |
A list of names and values of the IN and INOUT parameters to the stored procedure created using |
|
|
Integer |
The amount of time (in seconds) until the stored procedure execution is cancelled. Default: 30 seconds. |
|
|
Boolean |
Determines whether the database will automatically issue a |
|
|
Any Type |
A list of saves or an HTTP response to execute after the function executes successfully. Created with |
|
|
Any Type |
A list of saves or an HTTP response to execute when the smart service does not execute successfully. Created with |
ExampleCopy link to clipboard
For the example below, we define a stored procedure that writes to a database and show how it can be executed using the a!executeStoredProcedureOnSave() function.
Stored procedure details:
- Stored procedure name:
add_or_update_customer_and_case - INOUT parameters: customer_id, case_id
- IN parameters: name, status, description
- MariaDB stored procedure definition:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
DELIMITER // CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE add_or_update_customer_and_case( INOUT customer_id INT, IN name VARCHAR(255), INOUT case_id INT, IN status VARCHAR(255), IN description VARCHAR(255) ) BEGIN IF(customer_id IS NULL) THEN INSERT INTO customers(name, email, phone_number) VALUES (name, null, null); END IF; IF(case_id IS NULL) THEN INSERT INTO cases(status, description) VALUES (status, description); ELSE UPDATE cases SET status = status, description = description WHERE case_id = case_id; END IF; END // DELIMITER ;
Copy
To call the stored procedure that we've defined, we can use the code below inside a saveInto.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
a!executeStoredProcedureOnSave(
dataSource: cons!MARIADB_POINTER,
procedureName: "add_or_update_customer_and_case",
inputs: {
a!storedProcedureInput(name: "customer_id", value: local!customerId),
a!storedProcedureInput(name: "name", value: local!name),
a!storedProcedureInput(name: "case_id", value: local!caseId),
a!storedProcedureInput(name: "status", value: local!status),
a!storedProcedureInput(name: "description", value: local!description),
},
onSuccess: {
a!save(local!customerId, fv!parameters.customer_id),
a!save(local!caseId, fv!parameters.case_id),
},
onError: {
a!save{local!errorMessage, fv!errorMessage}
}
)
Copy
After the stored procedure is successfully executed, you can see that the INOUT parameters customer_id and case_id will be loaded into local variables from the fv!parameters function variable. Note that for this stored procedure there are no queries, so the fv!resultSets function variable will contain an empty list.
In the event that an error occurs, local!errorMessage will be populated with the error message from the function variable fv!errorMessage.
Feature compatibilityCopy link to clipboard
The table below lists this smart service function's compatibility with various features in Appian.
| Feature | Compatibility | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Portals | Partially compatible | Can be used with Appian Portals if it is connected using an integration and web API. |
| Offline Mobile | Incompatible | |
| Sync-Time Custom Record Fields | Incompatible | |
| Real-Time Custom Record Fields | Incompatible | Custom record fields that evaluate in real time must be configured using one or more Custom Field functions. |
| Process Reports | Incompatible | Cannot be used to configure a process report. |
| Process Events | Incompatible | Cannot be used to configure a process event node, such as a start event or timer event. |
| Process Autoscaling | Compatible |