OverviewCopy link to clipboard
Appian Records give you the power to access all of your enterprise data in a single location, regardless of where your data lives.
With a single point of data management, you can easily build interfaces, reports, and other interactive elements that put important business data at your users' fingertips. But how do you know which data you need to build a useful app that will speed up business processes?
By collecting information from stakeholders to build a data model, you'll gain a deeper understanding of the way the application will be used and the problems it will solve. We recommend investing time in comprehensive data design before you start building other aspects of your application (such as the interfaces users will interact with).
This page explains how to model data using the latest Appian Records features, some of which require that you enable data sync on your record types. To see the biggest benefits of working with your data in Appian, it is recommended that you enable data sync for your new record types to accelerate your application design. Your application can use any combination of record types regardless of whether they have data sync enabled.
Benefits of data modelingCopy link to clipboard
There are several advantages to data modeling that will make your eventual development process simpler. Here are a few reasons why building a data model is a recommended way to start the app-building process.
Enable work with stakeholdersCopy link to clipboard
First, the model should be used as a collaborative communication tool with business stakeholders to confirm your understanding of the application’s data requirements. A complete model shows how the application collects and relates data from a number of sources, so stakeholders can confirm that important business processes are being modeled effectively in Appian. They can also provide input into the interfaces and other end-user-facing elements required to make the application useful.
Plan your applicationCopy link to clipboard
A well-defined, stakeholder-approved model can then act as a map for the rest of the application. Whether you're building as a solo developer or as part of a team, understanding the data model's representation of the way information is stored and flows through different parts of the application is a critical aspect of app development.
On development teams, the model provides a central and accessible view of the most important part of an application: your business data. When all developers are able to make design decisions based on a shared understanding of the data, development will take less time and be more responsive to changing requirements.
Verify your data needsCopy link to clipboard
Finally, your model helps ensure that you can answer important business questions using queries against your data and then quickly build reports using the answers. Appian has many features that make queries easy to build and update, and those features work best with a foundation of data that is crafted to show relationships in previously siloed information.
What is a data model?Copy link to clipboard
A data model is a representation of all of the information available for your application. The model includes:
- The sources of your data, such as databases or web services.
- The record types you want to create using those sources.
- The relationships between your data. This is how you will connect currently siloed data to expand your users' ability to understand and work with that data.
- The fields available in the record type that will be used in queries throughout the application. These can be source fields or custom record fields.
A data model should be examined from two perspectives: a conceptual angle and a logical angle. Each provides a different level of detail important to the design and helps you confirm that your plan allows data to move seamlessly through different parts of the application.
Conceptual data modelCopy link to clipboard
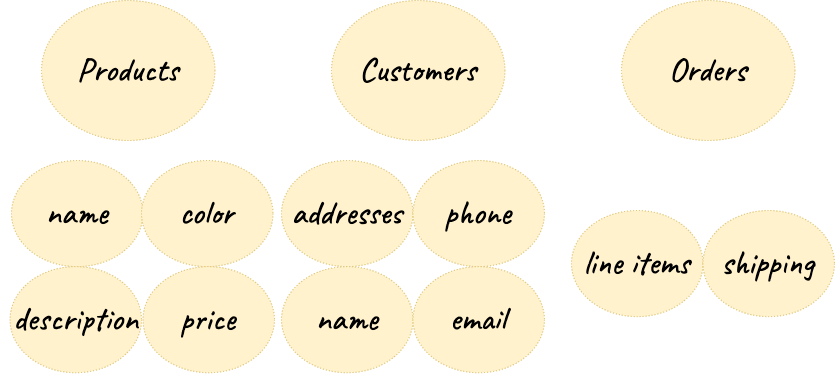
The conceptual angle is a high-level view of your data model. In it, you draw the basic connections between the data available in your app. Using a tool of your choice, you can quickly assemble a sketch of your data model. For example, a retail application might have a conceptual model like this:
The sketch highlights the main data categories for the app, Orders and Customers, and shows some of the supporting data that provides more detail for each. Customers have names and addresses, as well as contact info like phone numbers and email addresses. Noting these attributes early on helps you take a deeper look at the data needed for the app.
The concept can serve as reference for business stakeholders. It will allow them to confirm two things in particular:
- The model is organizing and connecting data correctly.
- Core business data, like Customers and Orders, is centered in the model to accurately capture its importance for one or more business processes.
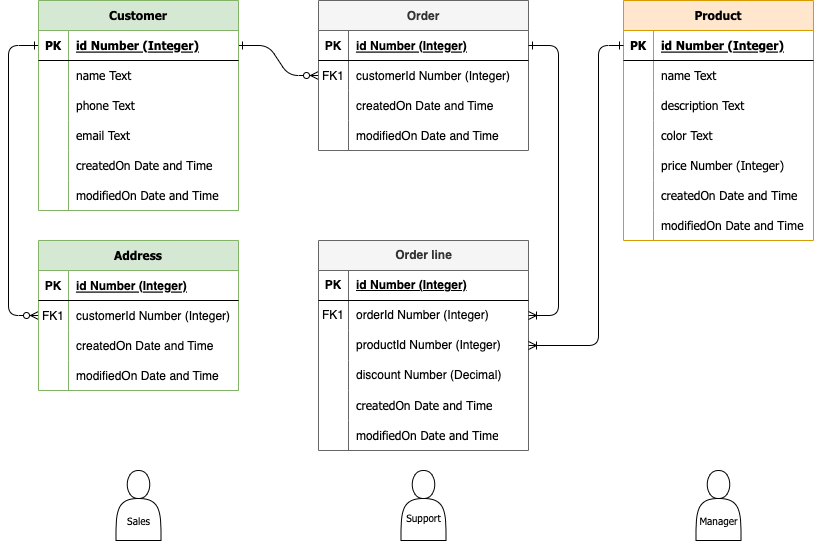
Logical data modelCopy link to clipboard
Once you have constructed a concept, you can enhance the level of detail with a logical angle of the data model. This more comprehensive explanation shows the specific fields that will be available on each record type and the common fields for establishing relationships between them. It can also note any filtering or security that needs to be applied to keep the data secure.
The structure of the model is an important factor in the design. In the conceptual phase, we noted that customers have addresses. While you could store address data with basic details like their phone number, your customers may want to have orders shipped to their home or office, or they may want to send a gift directly to another person. You can build in this flexibility by separating the address data from the customer and creating a relationship between them (one customer has one or more addresses).
Each core data category plays a major role in the application, and they can impact what interfaces you build and how you give users the ability to work with the data through the data lifecycle—creating, viewing, updating, and deleting data as required for their role. You may want to create a few different sections of the logical model, each centered on a different type of core data, to see the data from the perspective of different users.
For example, Customers may be the most important data for a salesperson, but a support rep will be more concerned with the Orders placed by those customers. You can add the data types for each field, including the common fields relating Customers to their Orders and Addresses.
You can also indicate the user personas that should be able to access Customer data in the application (in this case, salespeople, customer service reps, and warehouse managers).
Record type data modelCopy link to clipboard
Once you've built your logical model, create your record types based on your data model. This lets you realize both the conceptual and logical levels and then enhance it with other sync-enabled features.
If you need to build your data sources from scratch, Appian will guide you in creating the fields and relationships for each record type.
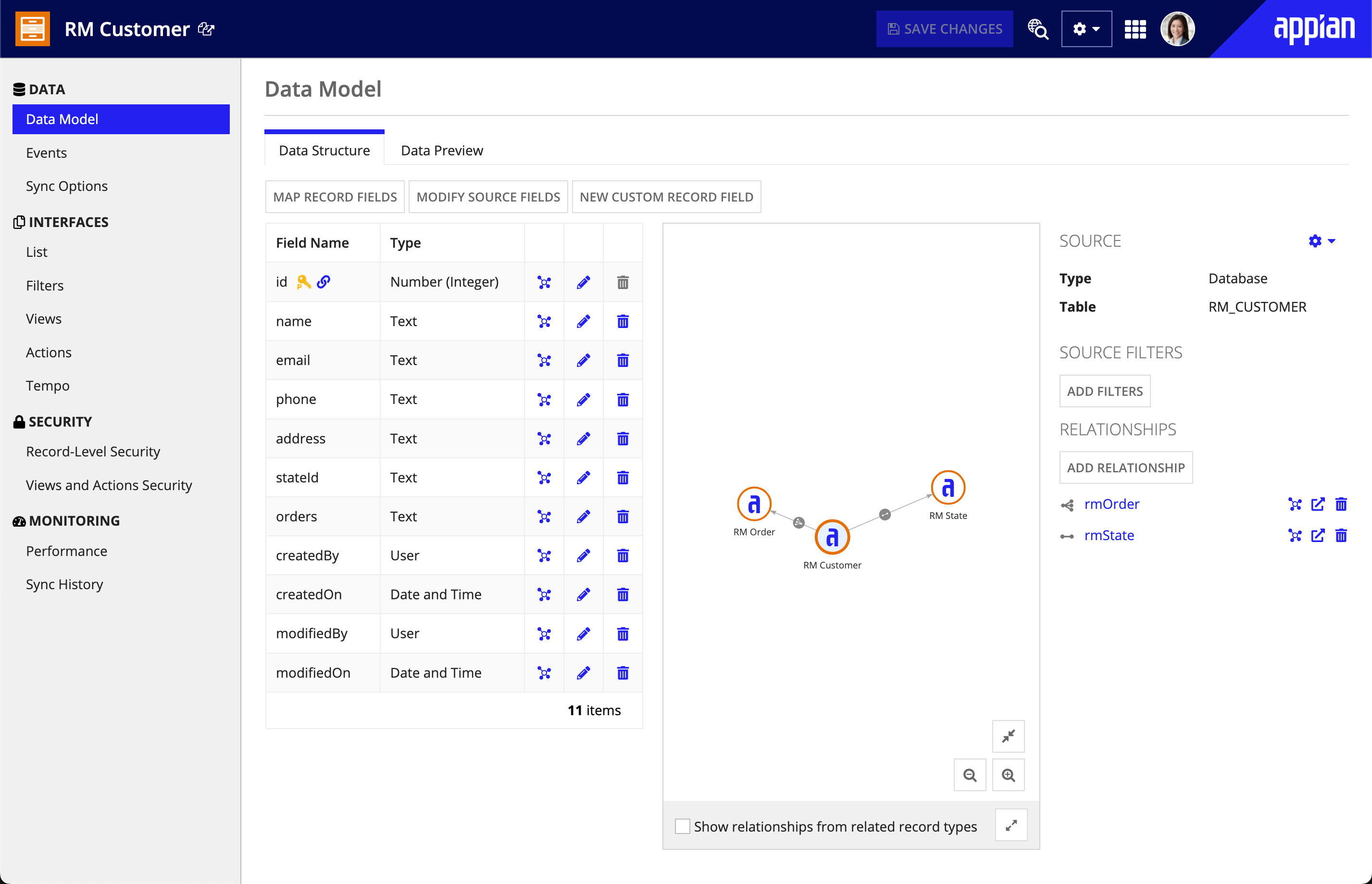
On the Data Model page of the record type, you can see and interact with the model.
The relationship diagram shows all of the logical connections you've established between record types, and the suggested relationships can help you find even more ways to intelligently link your data. The Data Structure table gives logical details, including the data types of each field and the common fields used to relate your data.
Data modeling best practicesCopy link to clipboard
As you start to build your data model in Appian, consider the following best practices.
Design for extensibility and expansion of your modelCopy link to clipboard
Record types function in two basic ways in your application to meet two overarching goals:
- Move business data through the application in such a way that you and other developers can understand and use to build useful features.
- Maintain separate data separately. Data should be scoped so you can create, change, and delete record data without needing to duplicate those changes in related record types.
The first goal is met when a record type is a representation of a core business concept. These concepts are often tasks or actions central to the day-to-day workings of the business and modeled as an Appian process. In a retail application, a core concept like order management would require an Order record type to power a process that creates, updates, or deletes orders.
Similarly, as you examine your source data, you'll probably notice where relatively stable data may be shared between two or more record types. When this is apparent, consider using a separate record type to store this data. For example, if you have Customer and Warehouse record types, basic location data like state or province, postal code, and country can be stored in a separate record type called Location since it's unlikely to change.
Finding a clean boundary between concepts is not always possible, but you can design more flexible record types by leaning on the relationships you built in the initial model. For example, an Order might be composed of information like the date and total cost, as well as any number of Order Line Items describing the product and quantity being purchased. By maintaining the line item data separately, it can be updated independently of the overall Order, and you can add events to track the status of each item as the order is compiled.
In a database, this separate record type would be called a lookup table. Storing your lookup data in a record type has many benefits, like:
- You don't need to repeatedly store actual location data for each Customer or Warehouse, but you can refer to it if needed for an interface or report.
- Maintenance is easier because there is a single place to update data that rarely changes.
- When you add a new record type that needs location information, you can quickly add a record type relationship and continue building new features. This shared data can be used to build a report that lets users explore customer and warehouse data in each region.
Use data syncCopy link to clipboard
Record types with data sync enabled are the best way to work with your data in Appian. You can seamlessly connect to your database tables and work with the data in the ways you need to. With automatic performance tuning and powerful sync-enabled features that allow you to relate, transform, and secure your data, you can build your applications faster.
You may choose not to enable data sync due to data sovereignty restrictions, including privacy concerns for health, financial, or other protected data. Record types without data sync enabled can still take advantage of Appian's flexible platform to bring together data in powerful applications regardless of where that data lives.
Work with large datasetsCopy link to clipboard
You can use any database, Salesforce, or web service as the source of your record type. When you enable data sync on a record type, you can sync up to 4,000,000 rows of data per record type. While this is a significant amount of data, very large datasets may require you to adapt your data model to work within Appian's current constraints.
To ensure you have flexible access to the data needed for your application, consider using source filters to divide up large datasets into multiple record types, each with a specific purpose.
For example, let's say your data source is a database table with seven million rows of client appointment data. You could create multiple record types from this source, some with data sync enabled and some without, to use different aspects of the data:
- Record types by appointment status:
- Use the status of the appointment to filter the data into Pending/Active Appointments and All Appointments. The Pending/Active Appointments should have data sync enabled because your users will need to see new and recent records and updates to those records to complete their tasks.
- An All Appointments record type could be configured without data sync enabled to give users on-demand access to the archive of appointments. This record type would not be used for more complex interfaces requiring relationships.
- Record types by time period:
- Use the date of the appointment to filter this year's data into one record type with data sync enabled.
- Create additional record types for previous years. Since this data is unlikely to change, those record types could be configured without data sync enabled.
- Record types by location:
- Use the address of the appointment to filter the data into HQ Appointments and Appointments for other corporate locations (such as NYC Appointments and London Appointments).
- Create a Virtual Appointments record type for those without an address.
Creating multiple record types from the same data increases the complexity of your model; this may result in a higher maintenance burden over the life of the application. The flexibility of record types lets you decide what combination of data will work best for your application so you can meet the needs of your stakeholders.
Track record eventsCopy link to clipboard
Record events allow you to track what happens in your applications, with minimal configuration on your part. Once you start tracking record events, you can display your event data as an activity log to business users or use that data to drive process improvements for your organization.
We recommend configuring record events on the record types that relate your major business processes. For example, in an Retail Orders application, you should configure record events on the Order record type to track events related to creating and managing orders.
Review the guidelines before configuring record events.
Protect sensitive data with record-level securityCopy link to clipboard
Enterprise data often includes information that must be protected for business, privacy, or regulatory reasons. For example, you may want to restrict customer information to the salesperson working with a client, or you may need to allow only managers and executives to view company financial data.
As you construct your data model, identify the information that requires protection and the users or groups that are allowed to access it. When you build the record type that includes sensitive data, you can then configure security controls to ensure protected record data can only be viewed by certain users or groups.
To learn more about the security features available for record types with data sync enabled, see Record-Level Security.
Data model development checklistCopy link to clipboard
To help you follow Appian's recommended process for designing your data model, use the following checklist to ensure you've met the baseline requirements.
- Stakeholder needs have been researched, understood, and reflected in the model's design.
- Each business concept has its own record type.
- Record events are configured on each record type that represents a major business concept.
- Data sync is enabled whenever possible; data sync is required to use record type relationships, custom record fields, record-level security, and other powerful features.
- For datasets with more than 4 million entries, multiple record types are created with different source filters.
- Lookup data is split into its own record type and uses record type relationships to connect to other record types that represent larger business concepts.
- Custom record fields are defined to easily reuse calculations.
- All username or group fields are converted to an Appian data type (User or Group).
- Data security requirements are implemented using record-level security.
Sample data modelCopy link to clipboard
Now that you've reviewed the best practices and recommendations, let's look at a sample data model that leverages a large dataset, multiple record types, and numerous sync-enabled features.
We've been tasked with combining information from multiple sources to construct a retail store management app. This app will be used by employees in a few different roles (sales, customer service, and managers), and each role has its own functional and reporting requirements for the app. Let's examine these roles and look at what the data model needs to include for each.
The sales team needs to track each sale made by individual team members (represented as Employees). They also want to see which products are most popular and who the most active customers are in a given time period. A salesperson needs the following information:
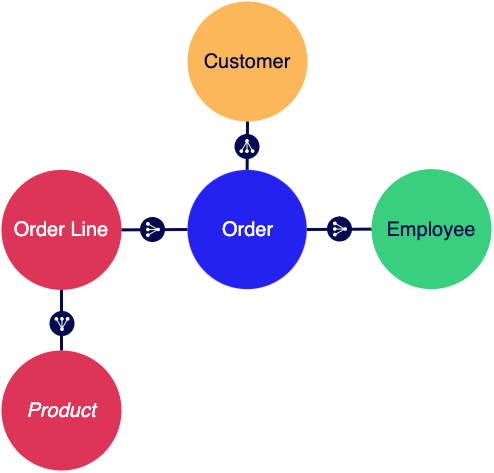
The customer service team must track each support request through their established workflow and they want to discover what products are returned or exchanged and at what rate. The data needs of a user in this role are similar to the sales role, but instead of employee data, they need to access the support cases for orders.
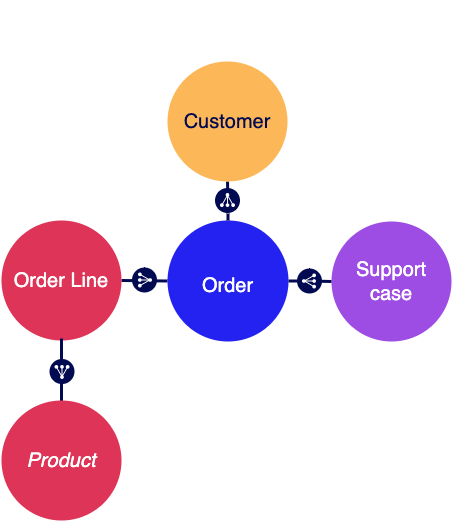
The store's management team wants to know which salesperson has the most sales in a given time period and how many requests each customer service representative resolves each week. The management team is not responsible for product inventory or customer relationships, so their data needs are simpler than the other roles.
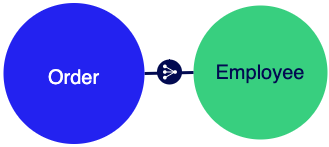
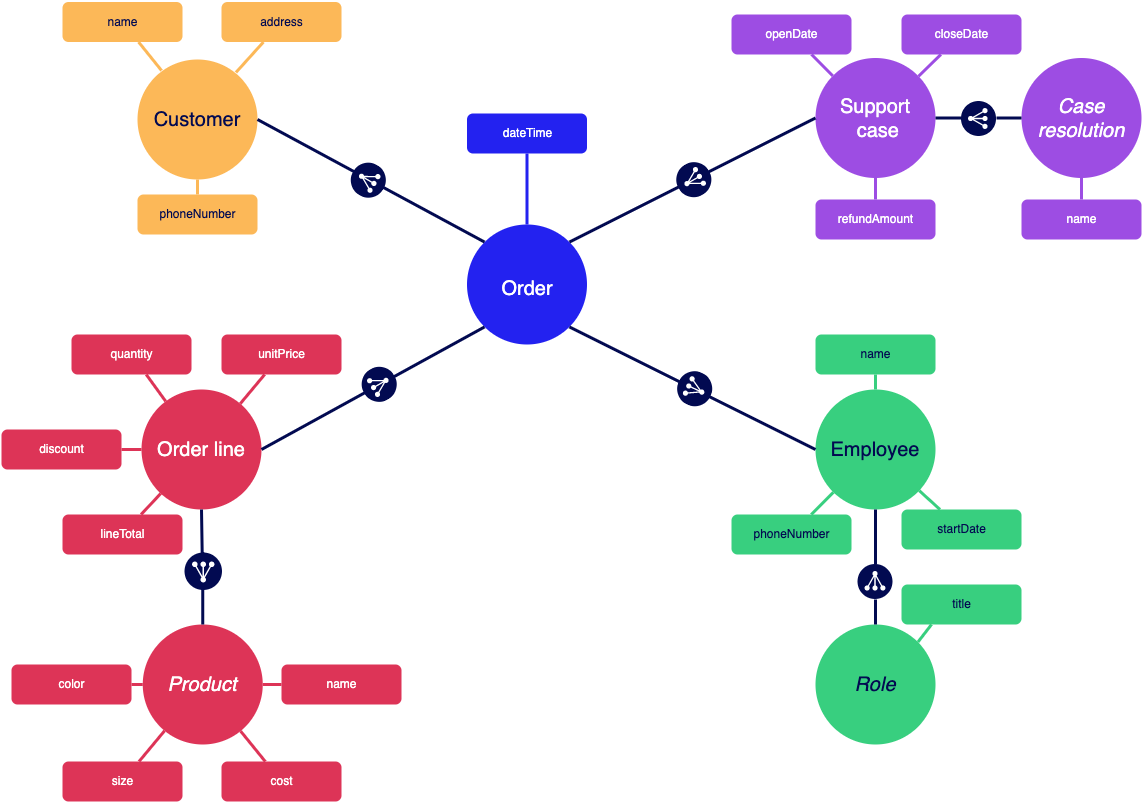
To cover the major business concepts, the retail application could be built using five record types with data sync enabled. This allows us to create relationships between our record types so we can quickly build interfaces and reports for each persona.
- Customer record type: Contains customer details like name, address, and phone number.
- Support Case record type: Contains case details like when the case was opened and closed and how it was resolved.
- Order Line record type: Contains product quantity, unit price, discounts, and the total for the line. This acts as the join table to connect the Order and Product and establish a many-to-many relationship.
- Employee record type: Contains employee details like name, tenure, and role. Depending on their role, an employee could have related data for orders or customer support requests.
- Order record type: Contains references to a Customer, an Employee, and one or more Products, plus information like the order date and time.
Some data is also stored in separate reference record types. This allows data like the list of employee roles or support case resolutions to change as needed.
- Role record type: Contains the names of the roles an employee can fill (like
salespersonandsupport agent). - Case Resolution type: Contains the types of case resolutions (such as
refundedandexchanged). - Product record type: Contains product name, cost, and attributes like size and color.
How to get started in AppianCopy link to clipboard
To begin implementing your own data model, start by creating a record type. Once you create the design object, learn how to configure the new record type by:
- Choosing the source of your record type
- Enabling data sync
- Filtering your source data
- Adding relationships
- Creating custom record fields
For a guided experience creating and configuring a record type, see the Appian Database-Backed Record Type Tutorial.