| The capabilities described on this page are included in Appian's standard capability tier. Usage limits may apply. |
IntroductionCopy link to clipboard
In this page you will learn how to create and configure a SQL integration object for use with a custom JDBC connected system. The custom JDBC connected system combined with the SQL integration object allows you to connect your Appian application to an unsupported database that supports the JDBC protocol to exchange data using SQL statements.
Note: Any database that is not in this list is considered an unsupported database.
Before you begin, ensure that you have:
Create the SQL integration objectCopy link to clipboard
After you have deployed a database driver and created the custom JDBC connected system, you can then create your SQL integration object.
To create a SQL integration object in Appian:
- Open the destination application for the new integration.
- In the Build view, click New > Integration.
- Select Use a connected system.
- Select your custom JDBC connected system from the Connected System field.
-
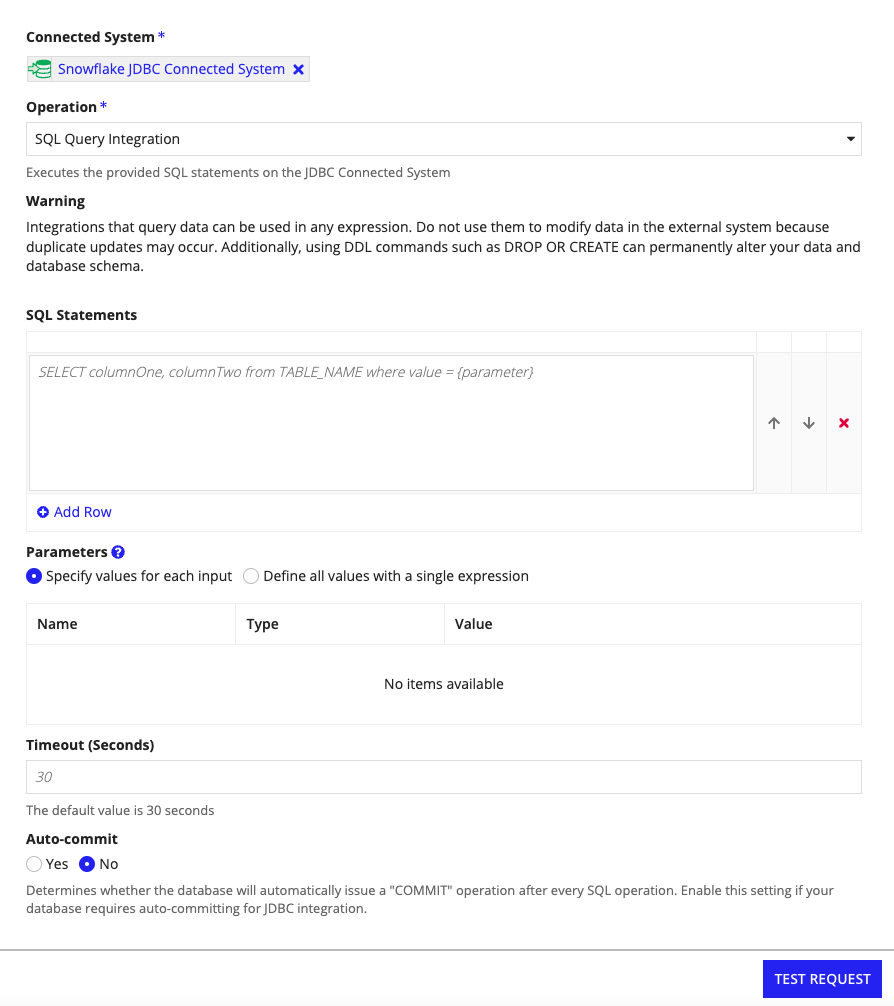
Select a SQL integration type from the Operation dropdown list.
Caution: Integrations that query data can be used in any expression. Do not use them to modify data in the external system because duplicate updates may occur. Additionally, using DDL commands such as
DROPorCREATEcan permanently alter your data and database schema. -
Configure the following properties.
Property Description Name Enter a name that follows the recommended naming standard. Description (Optional) Enter a brief description of the integration. Save In Browse to and select an existing folder to store the integration object, or click Create New Rule Folder to create and select a new folder for the object. - Click Create. Appian displays the new integration for designing.
Design the SQL integrationCopy link to clipboard
After you have created a SQL integration object with a custom JDBC connected system, you can design the SQL statements you will call in your integrations. To see what you can do with your newly designed integration, see Call an Integration.
In the integration object, enter the SQL statements you want to use. The SQL statement must meet the following requirements:
- All SQL queries must be predefined with specific field names, table names, and where-clause operators and conditions. Dynamic SQL query generation at runtime using expression rules is not allowed.
- Each parameter in the SQL query must take a single input value. If you provide a list of values separated by a delimiter, it will be treated as a single string parameter rather than multiple individual values.
For specific examples, see the following:
- Queries with a static value.
- Queries with parameterized values.
- Queries with parameterized values referencing a rule input value.
