OverviewCopy link to clipboard
This page provides guidance on how to use automated testing for expression rules. Learn how you can use automated testing to test your rules more quickly and efficiently.
Appian provides a way to perform batch testing of test cases from outside of the expression rule. You can easily access batch execution from the Settings menu in the Appian Designer. The Manage Test Cases dialog allows you to run the test cases for any number of expression rules in an application.
There are additional batch testing tools available for integration with already existing pipelines, which allow for batch testing at the system or application level and can be started from process models, SAIL interfaces, or web APIs. See Common Uses for additional details.
Test smart servicesCopy link to clipboard
There are two smart services which can be used to run batch tests:
These smart services support the execution of test cases at the application(s) and system levels. After starting a test run, the execution time is dependent on the total number and complexity of the test cases. You can check on the status of the test run with the a!testRunStatusForId() function. Once the test run is complete, you can retrieve the results with the a!testRunResultForId() function. Check out Parsing Batch Test Results for Expression Rules.
Usage ScenariosCopy link to clipboard
Expression rules are one of the smallest parts of an Appian application and thus they provide you with a way to perform unit testing for much of the logic in your applications.
We recommend that all expression rules that are important or reused across your applications have test cases to provide confidence that changes to application logic do not unexpectedly break important functionality.
Depending on your needs, you can start these tests based on an event, such as the end of a sprint, before and / or after a major deployment to your test environment.
Application testing at the end of a sprintCopy link to clipboard
During development, a team of developers work on adding new functionality to one or more applications. Because changes to an expression rule may have implications in other parts of the application, it is recommended to run a test on all applications that had changes at the end of the sprint. Doing this ensures the test is executed more quickly than when executing a system test in an otherwise cluttered environment. The Start Rule Tests (Applications) - Smart Service allows you to start a test run for all expression rules in an application.
Regression testing before a major deploymentCopy link to clipboard
Since many of your expression rules may be shared across applications, before releasing a new version of your application, you want to make sure that changes to your rules don't break functionality across applications.
It is recommended that you perform regression testing on all expression rules in the system after you deploy all of your changes to your test environment. This will ensure a stable upgrade because you will find out whether there are any dependent expression rules which are impacted by changes to the application you are about to release. The Start Rule Tests (All) - Smart Service allows you to start a test run for all expression rules on the system.
During the direct deployment of an individual application or patch, you will be prompted to run the test cases and add test coverage for rules prior to promoting your changes. See Inspect the Package for more information on reviewing test coverage during direct deployments.
Common UsesCopy link to clipboard
There are different ways in which you can initiate automated testing for expression rules. Within Appian, you can use an interface embedded in a report; or a process model, which is exposed to users as an action.
Additionally, you can integrate with external systems by creating web APIs to wrap around the testing smart services and functions, and invoke them from outside of Appian.
Testing in AppianCopy link to clipboard
InterfaceCopy link to clipboard
If you want to provide your developers with the ability to run tests for expression rules for an application or system, you can build an interface using the Start Rule Tests smart services. There is an existing solution on the App Market that already allows you to do so. See the Automated Rule Testing application.
Using a link or button, you can use the Start Rule Tests (All) smart service to run all tests for expression rules on the system. You will also want to use a refresh button or link that checks the status of the current run and updates your data. In the example below, the Rerun Tests button uses the Start Rule Tests (All) smart service to run all test cases on the system.
From the results of the test execution you can generate statistics such as the time spent executing the test cases, who executed the test, and how many test cases failed or completed successfully.
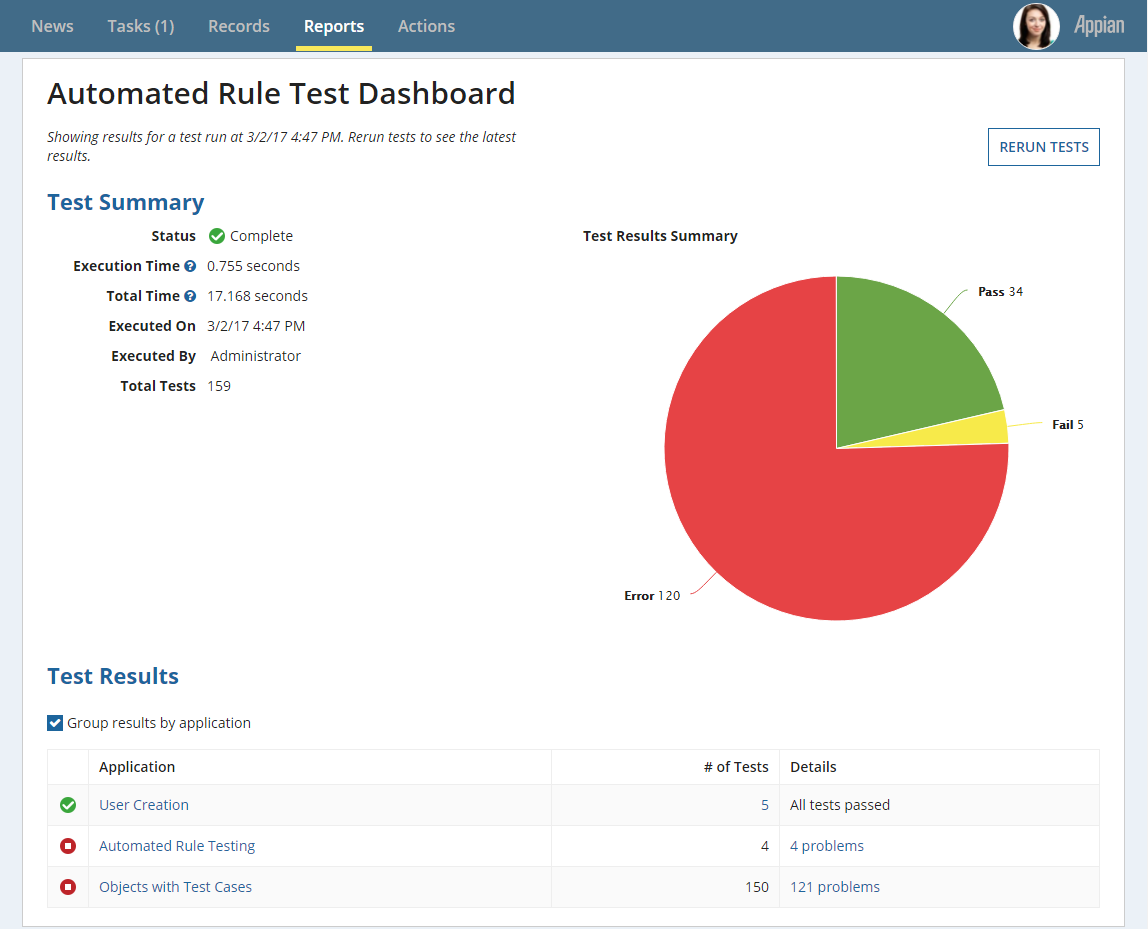
Using the data from the test run results, you can breakdown results by application and drill into applications to view and address any failures by clicking the links in the Details column.
For additional details on the data types used to store test results, see Parsing Batch Test Results for Expression Rules for additional details.
Note: This approach works if you are running a test for a few applications. However, if you have thousands of expression rules, you may want to create an action instead so you don't have to wait a long time before the test finishes executing.
Process modelCopy link to clipboard
You can perform automated testing on expression rules using an action. This approach is recommended if you have thousands of expression rules to test, either in a few applications or across the entire system. By using an action, you don't have to wait until the test is finished and instead, configure the action to send an email upon completion of the test; and include a grid summary of the expression rules that contain failed test cases, including:
- The expression rule name
- The username that last modified the rule
- A link to the expression rule, which will open the rule in a browser so you can immediately address the root cause of the failure
Integrating with external systemsCopy link to clipboard
You can perform automated testing on expression rules from external systems. For example, you can create a Jenkins project that can run a test of all expression rules in a system, or one or more applications.
This integration is possible by creating web APIs to wrap around the testing smart services and functions. These web APIs can then be invoked from a project in Jenkins, using a gradle task to start a test run, check the status of the test run until the test is complete, and then retrieve the results of the test in an xml file representation of the TestRunResult data type.
This XML can then be transformed to the Junit format so it can be interpreted as a test result by Jenkins and displayed in a report similar to the one shown below.
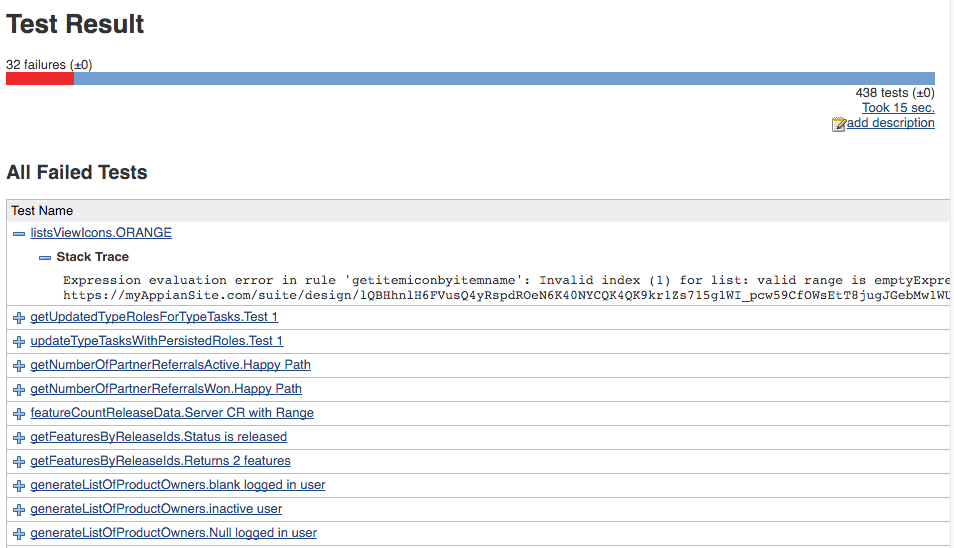
See Running Automated Tests on Expression Rules from Jenkins for a recipe on how to accomplish the above.
See alsoCopy link to clipboard
- Start Rule Tests (All)
- Start Rule Tests (Applications)
- Expression Rule Testing Functions
- Parsing Batch Test Results for Expression Rules
- Smart Services Library
