| The capabilities described on this page are included in Appian's standard capability tier. Usage limits may apply. |
OverviewCopy link to clipboard
This page describes the recommended minimum configurations for running Appian RPA, as well as other considerations to make sure your environment is well-suited to successfully execute robotic tasks.
Version compatibilityCopy link to clipboard
Appian RPA is a capability of the Appian platform, but Appian RPA releases are independent from the rest of the platform. This release process allows for more rapid development so you get access to new features, bug fixes, and improvements faster. Some of these updates may rely on feature availability in the Appian platform. Therefore, if you're using an older version of the Appian platform, Appian RPA may not be able to take advantage of all the latest capabilities.
Appian RPA is backwards compatible with the Appian platform. In other words, each new Appian RPA release works for previous versions of Appian that are still supported.
Host machine requirementsCopy link to clipboard
A host machine is the physical or virtual machine where a robotic task executes. These requirements are our minimum recommendation to ensure the host machine can adequately handle the robotic task execution and interaction with programs and applications on the host machine. The agent, which connects the host machine to the RPA console, doesn't require significant memory in order to operate.
At a minimum, host machines must have the following configuration:
- RAM: 4GB
- Operating system: 64-bit OS (x64-based)
- Processor: Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2686 v4 @ 2.30GHz
- Display environment: A web browser with a graphical interface (GUI) is required for all browser actions. Headless browsers aren't supported.
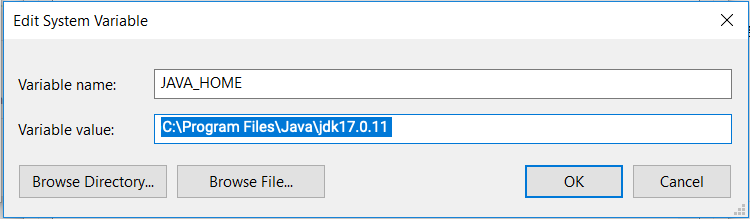
Java 17 must be installed on the host machine to launch the agent and run robotic tasks. Ensure your environment and host machines have Java 17. To ensure compatibility, choose the 32-bit or 64-bit Java version that matches your operating system.
Note: After installing Java, you must set the JAVA_HOME environment variable to point to the Java installation directory.
The following image is an example for Windows:
Communication and port usageCopy link to clipboard
Appian RPA secures its communication pathways and operates its components with precision using an approach that facilitates encrypted data transfers and streamlined internal processes.
FirewallsCopy link to clipboard
Appian RPA uses encrypted data transfers for communication between the Operations Console and robots. Robots do not act as servers, meaning they don't require open ports. Since robots don't act as servers, ensure your corporate firewalls permit outgoing HTTPS traffic over port 443 from host machines and incoming HTTPS traffic on port 443 to the Appian Cloud site. This configuration is necessary for robots to execute robotic tasks.
In addition to the port 443 requirement, for the automatic sign-in process to operate correctly, make sure the Windows firewall on the virtual machine (VM) allows Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) traffic from localhost to localhost - meaning the VM itself - on port 3389. This setting ensures the automatic sign-in process works within the VM without being blocked.
Secure communications via port 443Copy link to clipboard
The Operations Console primarily uses HTTPS on port 443 for all its communications, ensuring that all data transferred between the agent and the Operations Console is encrypted and secure. By leveraging this standard internet security protocol, Appian RPA provides a robust layer of protection, maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of your data.
RDP usage for automatic sign inCopy link to clipboard
The agent interacts with Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) solely for the purpose of session creation on the same host machine where it resides. This functionality does not extend to traditional remote desktop capabilities. Therefore, the agent does not serve as a remote desktop server, nor does it keep open ports for RDP connections, ensuring a secure and controlled operational environment.
Viewing live robotsCopy link to clipboard
A common assumption is that robots within Appian RPA might act as servers with open ports, and that the option to view a live robot utilizes the RDP protocol for its operations, but this is not the case. Appian RPA robots are designed to perform tasks without serving as open port servers, enhancing the system's security. Furthermore, no firewall configuration is necessary for operation. Similarly, the option to view a live robot operates via the Operation Console's port 443, and does not utilize RDP protocol. These design choices further solidify Appian RPA's commitment to security and operational efficiency.
Browser requirementsCopy link to clipboard
See System Requirements for the Appian platform.
The host machine requires a web browser with a graphical interface (GUI) for any browser actions. Headless browsers aren't supported.
Database supportCopy link to clipboard
If you are a self-managed customer using RPA on Appian Kubernetes, you may only use Maria DB.
Visit System Requirements to learn more about which databases are supported for your version of Appian.
Development environment requirementsCopy link to clipboard
Appian recommends the following development environment for extending robotic tasks via workflow libraries or custom code:
- Java 17. Learn how to set up JDK using Configurator.
- Maven 3.0.0 or higher. Learn how to setup Maven for Appian RPA.
- An IDE such as IntelliJ or Eclipse Luna or higher. Learn how to import the project to your IDE.
CertificatesCopy link to clipboard
If you customize your Appian Cloud site domain, you must provide signed certificates issued by a Certificate Authority (CA) to ensure Appian RPA functions correctly. Both Appian Cloud and Appian RPA accept certificates from public or private CAs.
Learn how to configure a custom domain for your Appian Cloud site.
