| The capabilities described on this page are included in Appian's standard capability tier. Usage limits may apply. |
OverviewCopy link to clipboard
For your portal users to complete their workflows and tasks with ease, they'll likely need to enter or view data within your portal. Writing and querying data in a portal allows you and your users to easily get and share information.
For example, users may need to view data, like:
- Checking the status of their in-flight processes.
- Viewing information about your products or services.
- Searching public records.
Or they may need to add or update data through actions, such as:
- Filling out a questionnaire.
- Responding to an anonymous survey.
- Requesting rebates or services.
- Applying for grants.
- Kicking-off their own onboarding process.
While you're reaching a broader audience with more information, you still need your data to stay safe. The isolated architecture of Appian Portals gives you peace of mind while allowing portal users to query and write data from Appian.
The best way to work with data in portals is using record types. However, you can also write and query data using CDTs, as long as you create a custom integration using a web API and integration object. And, if you have a publicly-available external database, you can directly write to or query from the database. See Working with Data in Appian to help you understand when to use a record type and when to use a CDT.
This page walks through how to work with data using all of the methods available from a portal.
Working with data using record typesCopy link to clipboard
Record types makes it easy to work with your data in portals, without creating a custom integration. Use them to:
- Query record data: Use a!queryRecordType() or a!queryRecordByIdentifier() directly in your portal interface, or use a record type as the source for read-only grids, charts, and card choices. See Recipes querying records for examples.
- Create, update, or delete record data: Use a!startProcess() in your portal interface, along with the Write Records or Delete Records smart services in your process model.
Tip: You can also use a!startProcess() in a portal interface to perform anything else possible with a process model, like creating a user or sending an email. You can use these same steps to create a portal that starts any other Appian process.
Let's look at some ways to use records in a portal.
Example: Querying records in a read-only gridCopy link to clipboard
The following steps walk you through building a read-only grid that uses a record type as its source, and then publish it in a portal.
Note: When you select a record type as the source for a read-only grid, the populated grid may include record components that aren't compatible with portals, like record links. You will need to remove these incompatible components before publishing the portal. See Using records-powered grids in a portal for more information.
Step 1: Access Appian Community EditionCopy link to clipboard
This example uses data from the Appian Retail application, available for free in Appian Community Edition. To follow along with this example, go to Appian Community to request the latest Appian Community Edition site.
If you do not see the Appian Retail application available in your existing Appian Community Edition site, request a new Appian Community Edition site to get the latest application contents available.
This example uses data from the following record types in the Appian Retail application:
- Product Category record type: Contains product categories. For example, Bikes.
- Product Subcategory record type: Contains product subcategories. For example, Mountain Bikes, Road Bikes, and Touring Bikes.
- Product record type: Contains specific products, including their names, numbers, and stock level. For example, the Guide Pulley product, number GP-0982, has a stock level of 800.
Step 2: Create a portal object and an interfaceCopy link to clipboard
We'll start this example by creating a portal and an interface. The portal object makes it super simple to create your interface from the object itself.
To create a portal object and interface:
- In your Appian Community Edition environment, open the Appian Retail application.
- Go to the Build
 view.
view. - Click NEW > Portal.
- Configure the portal properties and click CREATE.
- Go to the Pages section and click ADD PAGE.
- Configure the page properties.
- Click to create a new interface.
- Configure the interface properties. A new interface object opens.
- In the portal object, click ADD, then click SAVE CHANGES.
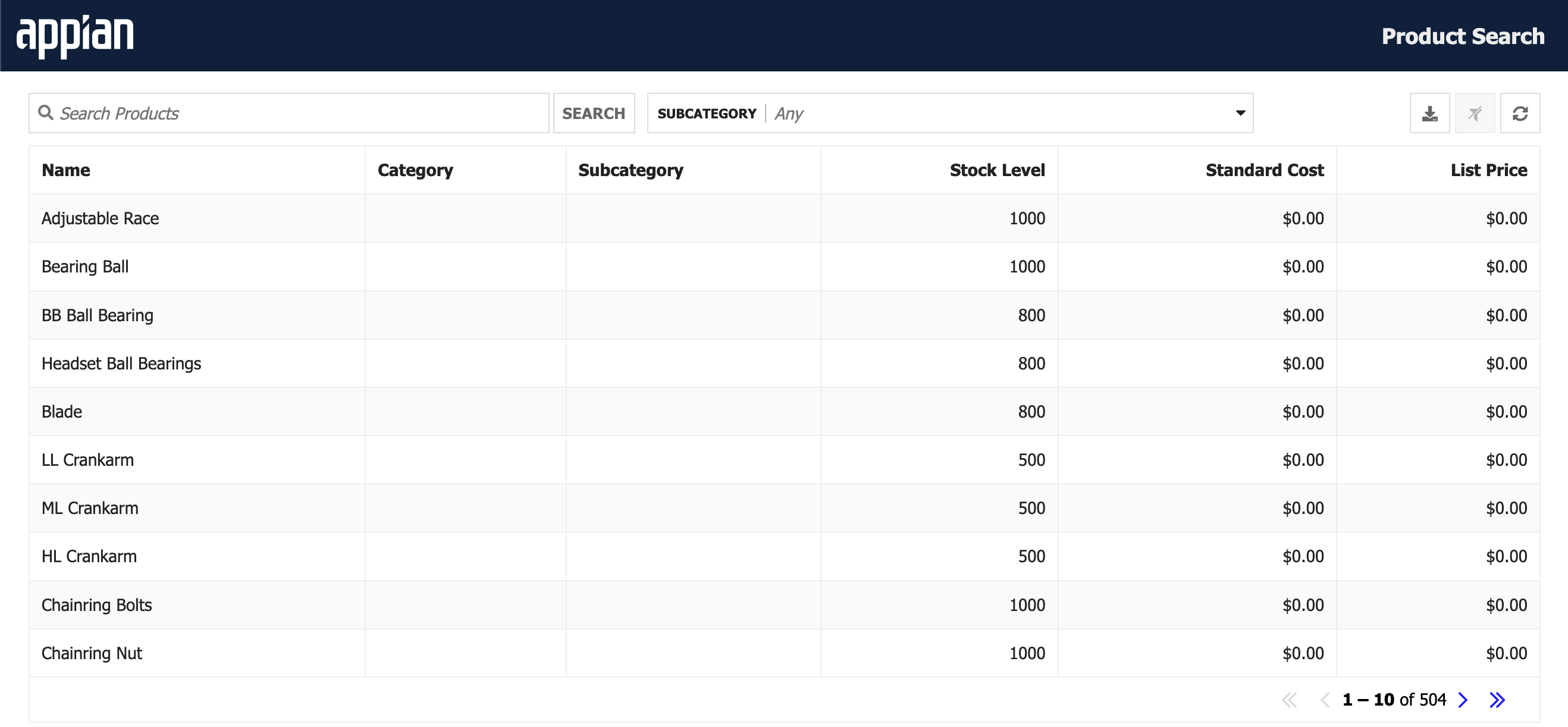
Step 3: Populate the read-only gridCopy link to clipboard
Next, we'll configure the interface to display the product information in a grid, including its category and subcategory. This is simple to do using a record type as the source of a read-only grid.
To populate the grid with record data:
- In the interface object, from the COMPONENT PALETTE, drag the READ-ONLY GRID component onto your empty interface.
- In the DATA section of the COMPONENT CONFIGURATION pane, leave Record Type selected.
- In the Search record types field, find and select the Product record type.
The grid populates with the Product records, including the Category and Subcategory related records. You can add, remove, and reorganize the columns in the Columns section.
Tip: Some of the columns may seem empty, but that is likely due to the fields not being populated for every record.
Step 4: Remove record links from the gridCopy link to clipboard
You now have a shiny, new grid with the product information already populated. Before we publish the portal, let's remove the record link from the Name column, since that component is not compatible with portals.
To remove the record links:
- Under Columns, click Name (Grid Column).
- In the Grid Column section, next to Display Value, click Edit as Expression .
-
In the expression editor, replace the expression with the following, and click OK.
1
fv!row['recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{afc5b005-2317-4c13-a132-62714c994bc9}name']
Copy - Click SAVE CHANGES.
- Close the interface object.
Step 3: Grant permissions to the record dataCopy link to clipboard
Before you can view the record data in a published portal, you need to give the portal the appropriate permissions to view the data. This is done using a service account, which acts on behalf of your portal users.
To provide the portal the appropriate permissions:
- In the portal object, go to the Service Access section.
- Next to the Service Account picker, click to create a new service account.
- If you don't see , contact a system administrator to create a service account for you, or select an existing one.
- Enter a unique username for your service account.
- Click CREATE.
- Return to the Build view of the Appian Retail app and add the new service account to the AR Users group. This way, the service account has access to any objects that include AR Users in their security role map.
- Return to the portal object.
- Click View record type permissions for the service account to verify the service account can view the Product, Product Subcategory, and Product Category record types, then click CLOSE.
Step 4: View the record data in a published portalCopy link to clipboard
In this last step, we'll publish the portal so we can see the record data in our grid.
To publish and view the portal:
- In the portal object, turn on Published and click SAVE CHANGES.
- After the portal status updates to Published, in the Configurations section, click the URL under Web Address to view the published portal.
Example: Starting a process to write data using a record typeCopy link to clipboard
The best way to create, update, and delete data from a portal is to use a!startProcess() in the saveInto parameter of a portal interface. Then write that data directly to a record using the Write Records or Delete Records smart services.
You can use these instructions for more than just writing data. Simply call any process model using a!startProcess().
This simplified example uses a form to add a new product to the Product record type.
Step 1: Access Appian Community EditionCopy link to clipboard
This example uses data from the Appian Retail application, available for free in Appian Community Edition. To follow along with this example, go to Appian Community to request the latest Appian Community Edition site.
If you do not see the Appian Retail application available in your existing Appian Community Edition site, request a new Appian Community Edition site to get the latest application contents available.
This example uses data from the following record types in the Appian Retail application:
- Product Subcategory record type: Contains product subcategories. For example, Mountain Bikes, Road Bikes, and Touring Bikes.
- Product record type: Contains specific products, including their names, numbers, and stock level. For example, the Guide Pulley product, number GP-0982, has a stock level of 800.
Step 2: Create a process model to write to a recordCopy link to clipboard
In this step, we'll create a process model to add new products. We'll then create a constant to point to the process model so we can reference it in an interface later.
We'll just go through the basics of setting up a process model in this example. For more information on setting up process models with additional capabilities, see the Process Modeling Tutorial.
To create the process model:
- In your Appian Community Edition environment, open the Appian Retail application.
- Go to the Build
 view.
view. - Click NEW > Process Model.
- Configure the process model properties and click CREATE.
- Click File > Properties.
- Go to Variables.
- Click + Add Variable.
- Enter the following properties:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Name | Enter productRecords. |
| Type | Select Product (Record Type). |
| Parameter | Select the Allow the value for the variable to be provided when starting a process checkbox. |
- Click OK to close the dialog.
- Click OK the close the properties.
- Add a WRITE RECORDS smart service node to the process.
-
In the Data tab of the Write Records smart service node, on the Inputs tab, set the Value of Records to
=pv!productRecordsand click OK.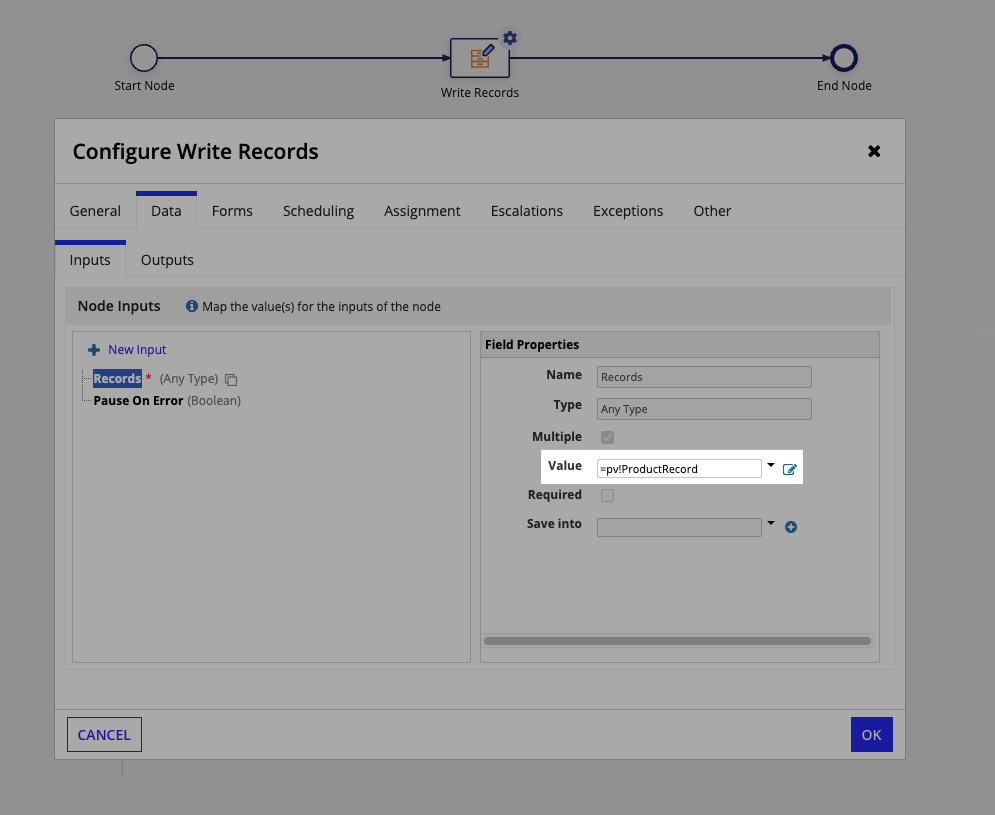
- Select File > Save & Publish.
- Create a constant of type Process Model that points to the new process model and name it
AR_ADD_PRODUCT_PROCESS_MODEL.
Step 3: Create a portal object and an interfaceCopy link to clipboard
In this step, we'll create an interface so portal users can add new products.
Since the record picker component is incompatible with portals, this example includes adding a dropdown list using a related record type to help illustrate how to do this manually. See the Querying records in a read-only grid example for more information on how to query related record types in a portal.
In the onSuccess parameter of a!startProcess(), we are using the ProcessInfo data type to save just the record values, instead of all of the process information.
To create an interface that starts a process:
- In the Appian Retail application of your Appian Community Edition site, go to the Build
 view.
view. - Click NEW > Portal.
- Configure the portal properties and click CREATE.
- Go to the Pages section and click ADD PAGE.
- Configure the page properties.
- Click to create a new interface.
- Configure the interface properties. A new interface object opens.
- In the portal object, click ADD and click SAVE CHANGES.
- In the interface object, click EXPRESSION in the title bar.
-
Copy and paste the following expression:
Note: These record type references are specific to the Appian Retail application. If you're following along in the Appian Retail application, you can copy and paste this expression without updating the record type references.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214
a!localVariables( local!result, local!productRecordData: 'recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product'( 'recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{afc5b005-2317-4c13-a132-62714c994bc9}name': null, 'recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{06fac494-e9bc-4abe-a3a3-6cdfa6d8db49}productNumber': null, 'recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{debc9655-4313-49e4-b906-8ba472326d97}safetyStockLevel': null, 'recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{6e28c019-12ab-4859-a8b3-8d52764e4944}reorderPoint': null, 'recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{3779db6a-45a8-49b4-8dd9-23087c00dde7}standardCost': null, 'recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{6380baa1-23f9-409a-9b48-10e37d587fa3}listPrice': null, 'recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{7f3e3cd2-6023-4190-9607-17d62448c592}daysToManufacture': null, 'recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.relationships.{d3a62d4a-3268-48dc-9563-3b99c33715d1}productSubcategory.fields.{b0f94c2f-cba6-4565-ae39-fa81da69b1d5}productSubcategoryId': null ), /* Query to return each product subcategory to use in the dropdown component */ local!subcategory: a!queryRecordType( recordType: 'recordType!{ef54f217-d426-4f2b-9955-3859c9919525}Product Subcategory', fields: { 'recordType!{ef54f217-d426-4f2b-9955-3859c9919525}Product Subcategory.fields.{6f4fce8f-2487-4997-a365-985b895f90d8}name', 'recordType!{ef54f217-d426-4f2b-9955-3859c9919525}Product Subcategory.fields.{b0f94c2f-cba6-4565-ae39-fa81da69b1d5}productSubcategoryId' }, pagingInfo: a!pagingInfo(startIndex: 1, batchSize: 50) ).data, local!submitted: false, if( local!submitted = false, a!formLayout( label: "Add a Product", contents: { a!cardLayout( contents: { a!columnsLayout( columns: { a!columnLayout( contents: { a!textField( label: "Name", labelPosition: "ABOVE", value: local!productRecordData['recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{afc5b005-2317-4c13-a132-62714c994bc9}name'], saveInto: local!productRecordData['recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{afc5b005-2317-4c13-a132-62714c994bc9}name'], refreshAfter: "UNFOCUS", required: true ), a!textField( label: "Product Number", labelPosition: "ABOVE", value: local!productRecordData['recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{06fac494-e9bc-4abe-a3a3-6cdfa6d8db49}productNumber'], saveInto: local!productRecordData['recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{06fac494-e9bc-4abe-a3a3-6cdfa6d8db49}productNumber'], refreshAfter: "UNFOCUS", required: true ), a!textField( label: "Standard Cost", labelPosition: "ABOVE", value: a!currency( value: local!productRecordData['recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{3779db6a-45a8-49b4-8dd9-23087c00dde7}standardCost'], isoCode: "USD" ), saveInto: local!productRecordData['recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{3779db6a-45a8-49b4-8dd9-23087c00dde7}standardCost'], refreshAfter: "UNFOCUS", required: true ), a!textField( label: "List Price", labelPosition: "ABOVE", value: a!currency( value: local!productRecordData['recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{6380baa1-23f9-409a-9b48-10e37d587fa3}listPrice'], isoCode: "USD" ), saveInto: local!productRecordData['recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{6380baa1-23f9-409a-9b48-10e37d587fa3}listPrice'], refreshAfter: "UNFOCUS", required: true ), /* Because the record picker component is incompatible with portals, we manually set up a dropdown component using the local!subcategory query*/ a!dropdownField( label: "Subcategory", labelPosition: "ABOVE", placeholder: "--- Select a Subcategory ---", choiceLabels: local!subcategory['recordType!{ef54f217-d426-4f2b-9955-3859c9919525}Product Subcategory.fields.{6f4fce8f-2487-4997-a365-985b895f90d8}name'], choiceValues: local!subcategory['recordType!{ef54f217-d426-4f2b-9955-3859c9919525}Product Subcategory.fields.{b0f94c2f-cba6-4565-ae39-fa81da69b1d5}productSubcategoryId'], value: local!productRecordData['recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{1deb35f9-8529-4f2f-b336-6774c614531d}productSubcategoryId'], saveInto: local!productRecordData['recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{1deb35f9-8529-4f2f-b336-6774c614531d}productSubcategoryId'], searchDisplay: "AUTO" ) } ), a!columnLayout( contents: { a!integerField( label: "Safety Stock Level", labelPosition: "ABOVE", value: local!productRecordData['recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{debc9655-4313-49e4-b906-8ba472326d97}safetyStockLevel'], saveInto: local!productRecordData['recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{debc9655-4313-49e4-b906-8ba472326d97}safetyStockLevel'], refreshAfter: "UNFOCUS", required: true ), a!integerField( label: "Reorder Point", labelPosition: "ABOVE", value: local!productRecordData['recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{6e28c019-12ab-4859-a8b3-8d52764e4944}reorderPoint'], saveInto: local!productRecordData['recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{6e28c019-12ab-4859-a8b3-8d52764e4944}reorderPoint'], refreshAfter: "UNFOCUS", required: true ), a!integerField( label: "Days to Manufacture", labelPosition: "ABOVE", value: local!productRecordData['recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{7f3e3cd2-6023-4190-9607-17d62448c592}daysToManufacture'], saveInto: local!productRecordData['recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{7f3e3cd2-6023-4190-9607-17d62448c592}daysToManufacture'], refreshAfter: "UNFOCUS", required: true ), a!dateField( label: "Sell Start Date", labelPosition: "ABOVE", value: local!productRecordData['recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{726cc562-42a3-47b7-b8c7-ddcdc3e26540}sellStartDate'], saveInto: local!productRecordData['recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{726cc562-42a3-47b7-b8c7-ddcdc3e26540}sellStartDate'], required: true ) } ) } ) }, height: "AUTO", style: "TRANSPARENT", marginBelow: "STANDARD" ) }, buttons: a!buttonLayout( primaryButtons: { a!buttonWidget( label: "Add Product", saveInto: a!startProcess( processModel: cons!AR_ADD_PRODUCT_PROCESS_MODEL, processParameters: { /* This is the name of the process variable from the process model*/ productRecords: local!productRecordData }, onSuccess: { /* Sets local!submitted to true so that a confirmation message can display, instead of the form*/ a!save(local!submitted, true), a!save( local!result, /* Index into the productRecords process variable to save just the record values, instead of all of the process information*/ fv!processInfo.pv.productRecords ), a!save( /* This resets the form values to null to reset the form*/ local!productRecordData, 'recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product'( 'recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{afc5b005-2317-4c13-a132-62714c994bc9}name': null, 'recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{06fac494-e9bc-4abe-a3a3-6cdfa6d8db49}productNumber': null, 'recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{debc9655-4313-49e4-b906-8ba472326d97}safetyStockLevel': null, 'recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{6e28c019-12ab-4859-a8b3-8d52764e4944}reorderPoint': null, 'recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{3779db6a-45a8-49b4-8dd9-23087c00dde7}standardCost': null, 'recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{6380baa1-23f9-409a-9b48-10e37d587fa3}listPrice': null, 'recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.fields.{7f3e3cd2-6023-4190-9607-17d62448c592}daysToManufacture': null, 'recordType!{dee327a7-3854-45e5-a952-d3d7d3edcc82}Product.relationships.{d3a62d4a-3268-48dc-9563-3b99c33715d1}productSubcategory.fields.{b0f94c2f-cba6-4565-ae39-fa81da69b1d5}productSubcategoryId': null ) ) } ), submit: true, style: "SOLID", loadingIndicator: true ) }, secondaryButtons: { a!buttonWidget( label: "Cancel", value: true, saveInto: {}, submit: true, style: "OUTLINE", color: "ACCENT", validate: false ) } ) ), /* Success message that displays when local!submitted=true*/ { a!richTextDisplayField( labelPosition: "COLLAPSED", value: a!richTextItem( text: "Product added.", size: "MEDIUM_PLUS", style: "STRONG" ), align: "CENTER" ), a!richTextDisplayField( labelPosition: "COLLAPSED", value: a!richTextItem( text: "Thank you for submitting a new product." ), align: "CENTER" ), /* This link reopens the form. Replace the link with a link to your portal */ a!linkField( labelPosition: "COLLAPSED", align: "CENTER", links: { a!safeLink( label: "Add another product.", uri: "REPLACE THIS WITH A LINK TO YOUR PORTAL", openLinkIn: "SAME_TAB" ) } ) } ) )
Copy - Click SAVE CHANGES.
- Close the interface object.
Step 4: Grant permissions to the record dataCopy link to clipboard
Before you can view the record data in a published portal, you need to give the portal the appropriate permissions to view the data. This is done using a service account, which acts on behalf of your portal users.
To provide the portal the appropriate permissions:
- In the portal object, go to the Service Access section.
- Next to the Service Account picker, click to create a new service account.
- If you don't see , contact a system administrator to create a service account for you.
- Enter a unique username for your service account.
- Click CREATE.
- Return to the Build view of the Appian Retail app and add the new service account to the AR Users group. This way, the service account has access to any objects that include AR Users in their security role map.
- Return to the portal object.
- Click View record type permissions for the service account to verify the service account can view the Product and Product Subcategory record types, then click CLOSE.
- Go to the process model object and make sure the group that the service account is in has at least Initiator permissions to the process model.
Step 5: Test the process in a published portalCopy link to clipboard
In order to make sure the process executes correctly in a portal, you need to publish the portal in order to test that the portal starts the process and writes the data correctly.
To test the process in a published portal:
- In the portal object, turn on Published and click SAVE CHANGES.
- After the portal status updates to Published, in the Configurations section, click the URL under Web Address to open the published portal.
- Fill out the fields in the form and click ADD PRODUCT.
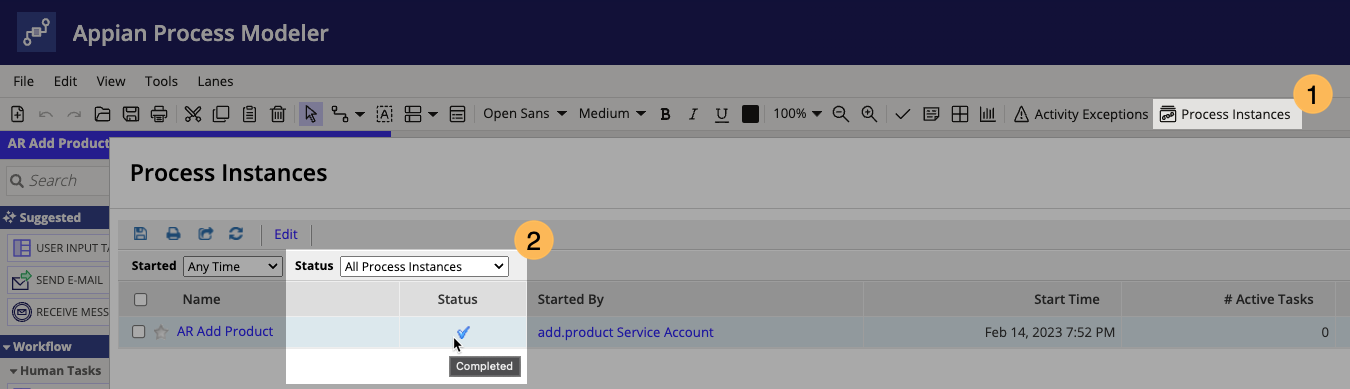
- Open the process model and click Process Instances.
-
For Status, choose All Process Instances and verify an instance is listed with a completed status.
Working with data using CDTsCopy link to clipboard
If there are scenarios where you cannot use record types, you can query and write data using custom data types (CDTs) and data stores.
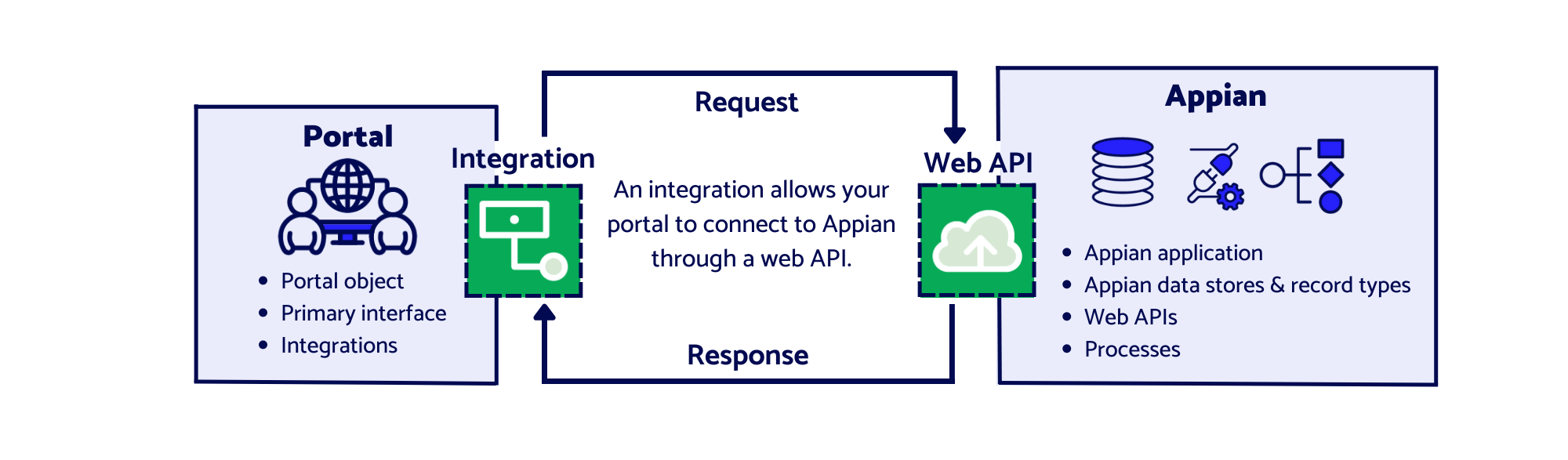
To work with CDTs in a portal, you can call an integration object in the portal interface to request to write to or query data from Appian. The integration talks directly to a web API in Appian, which completes the request and sends a response back to the integration in the portal.
The integration and web API form a bridge that connects your portal to Appian and allows data to pass through. The integration is on one side—in your portal—and the web API is on the other side—in Appian.
The diagram below shows how the portal and Appian work together to allow for the flow of data, without the use of records.
Querying data using CDTsCopy link to clipboard
You can query data in your portal using a CDT by creating a custom integration using a web API, integration object, and connected system.
This section outlines how to query data in a portal using a CDT and data store.
Step 1: Create a web APICopy link to clipboard
You'll first need to create a web API that queries your data store. This is pretty simple since you can use an API template that automatically populates some common fields and selections to start you out.
To create a web API:
- Create a constant that points to your data store.
- Create a web API using the Query Data Store template.
- Note: This template gives query results formatted in JSON, which you'll convert to an Appian value in your integration object.
For general help creating a web API, check out Creating web APIs. For help creating a web API that queries data, go through the web API Tutorial, which walks you through creating a web API that queries a record type.
Step 2: Create an API key and service accountCopy link to clipboard
In order to connect to the web API, you'll need an API key that is associated with a service account.
To create a new API Key:
- In the Admin Console, go to the Web API Authentication page.
- On the API Keys tab, click Create.
- Enter a unique Description.
- Select a Service Account to associate with the key. To create a new service account:
- Click Create Service Account .
- Enter a username and click CREATE.
- Tip: "Service Account" will automatically be added to the end of the service account name. See Service accounts.
-
Click CREATE.
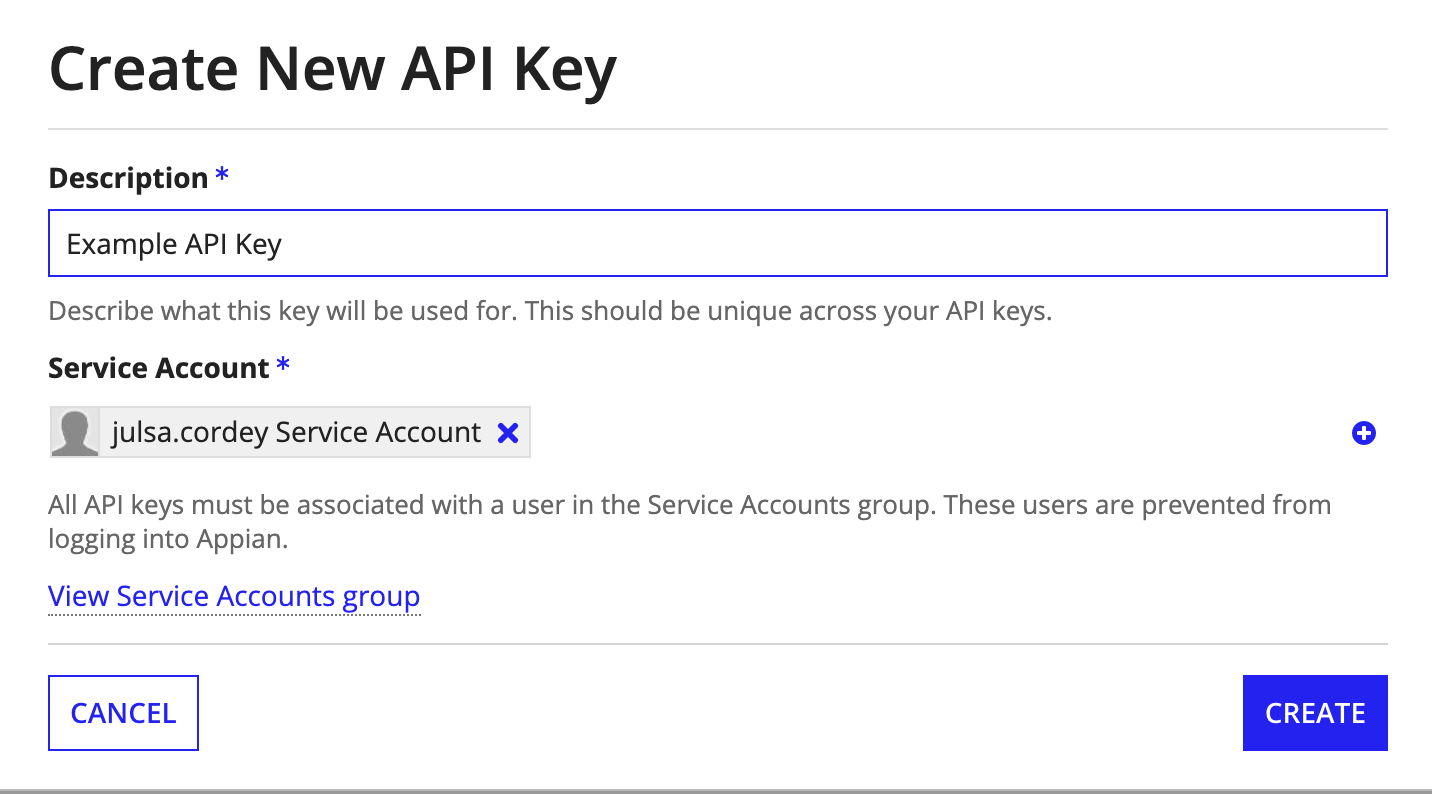
- Copy the API Key and store it externally. Appian will never show the value of the API key a second time.
- Repeat these steps in each environment, making sure the following are the same in each environment:
- API key Description.
- Service account Username.
- Service account permissions and group membership.
In order to query data, the service account needs to have Viewer permissions to the web API and data store.
To give your service account the appropriate access:
- Add the service account to a user group in your application.
- Give the group Viewer permissions to the web API and data store.
You can use the same service account that you set up with your API key as the portal service account that you add in the portal object. Just be sure to use the same service account to grant the required permissions to other design objects used in your portal.
Step 3: Create a connected systemCopy link to clipboard
Now you need to add your API key and credentials to a connected system to use with the integration.
To create a connected system for authentication:
- Create a new HTTP connected system.
- For Authentication, select API Key.
- For Header, enter
appian-api-key. - For Value, provide the API key from when you created the API key.
Step 4: Create an integration objectCopy link to clipboard
Once you've created your API and authentication objects, create an integration object that is set up to query data using the connected system that you just created.
To configure your integration:
- In the Connection section, configure the following fields:
- Select Use a connected system and choose the connected system you created in Step 3.
- For URL, enter the web API URL as the endpoint for the integration.
- For Method, select GET.
- In the Response section, for Response Body Parsing, select Convert JSON to Appian value.
-
Click TEST REQUEST and verify the result that is returned.
Note: If there are unexpected question marks (?) in the response body, it may be because you need to modify the header parameter in the a!httpResponse() function of the web API expression to handle special characters. See this Knowledge Base article for more information.
For more help, see Create an Integration.
Step 5: Call the integration from your portal interfaceCopy link to clipboard
In your portal interface, call your integration. Cast the dictionary results returned by your integration into the CDT that you're using for your data. This will let you easily reference your queried data throughout your portal without extra formatting.
Tip: Instead of casting your integration results from a dictionary to a CDT directly within your interface, you have the option to create individual or reusable expression rules to cast your integration results. You would then call the integration from your interface and wrap it in the expression rule.
Example: Cast integration results to CDT in a portalCopy link to clipboard
Using local variables within an interface, you can cast your integration results from a dictionary to whichever CDT you're using to work with your data.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
a!localVariables(
local!data: cast(
type!myCDT,
rule!myQueryIntegration().result.body
),
a!gridField(
data: local!data
)
)
Copy
For further examples, check out calling an integration to query data.
Step 6: Test your portalCopy link to clipboard
After creating a portal object, adding the interface, and publishing the portal, be sure to fully test the published portal.
Step 7: Deploy your portalCopy link to clipboard
When you deploy a portal to another environment, do the following:
- Make sure the target environment has the following:
- An API key with the same Description as the one in the source environment.
- A service account with the same Username, permissions, and group membership as the one in the source environment.
- Include an import customization file (ICF) in the app or deployment package. In the ICF, provide the API key from your target environment as well as any other connected system credentials and information.
Writing data using CDTsCopy link to clipboard
You can write data from your portal using a CDT by creating a custom integration using a web API, integration object, and connected system.
This section outlines how to write data from a portal using a CDT and data store.
Step 1: Create a web APICopy link to clipboard
You'll first need to create a web API that writes data directly to your data store. This is pretty simple since you can use an API template that automatically populates some common fields and selections to start you out.
To create a web API:
- Create a constant that points to your data store.
- Create a web API using the Write to Data Store template.
- Note: This template casts the body of your integration first to a dictionary and then to the CDT you're using for your data. This casting becomes relevant later on when setting up your integration.
If you need help creating a web API that writes data, go through the Web API Tutorial Level II, which walks you through creating a web API that writes data to a record type.
Step 2: Create an API key and service accountCopy link to clipboard
In order to connect to the web API, you'll need an API key that is associated with a service account.
To create a new API Key:
- In the Admin Console, go to the Web API Authentication page.
- On the API Keys tab, click Create.
- Enter a unique Description.
- Select a Service Account to associate with the key. To create a new service account:
- Click Create Service Account .
- Enter a username and click CREATE.
- Tip: "Service Account" will automatically be added to the end of the service account name. See Service accounts.
-
Click CREATE.

- Copy the API Key and store it externally. Appian will never show the value of the API key a second time.
- Repeat these steps in each environment, making sure the following are the same in each environment:
- API key Description.
- Service account Username.
- Service account permissions and group membership.
In order to write data, the service account needs to have Viewer permissions to the web API and data store.
To give your service account the appropriate access:
- Add the service account to a user group in your application.
- Give the group Viewer permissions to the web API and data store.
You can use the same service account that you set up with your API key as the portal service account that you add in the portal object. Just be sure to use the same service account to grant the required permissions to other design objects used in your portal, like records, processes, and document folders.
Step 3: Create a connected systemCopy link to clipboard
Now you need to add your API key to a connected system for the integration.
To create a connected system for authentication:
- Create a new HTTP connected system.
- For Authentication, select API Key.
- For Header, enter
appian-api-key. - For Value, provide the API key from when you created the API key.
Step 4: Create an integrationCopy link to clipboard
Once you've created your API and authentication objects, create an integration that is set up to modify data using the connected system that you just created.
To configure your integration:
- On the right side under RULE INPUTS, add the CDT that you're using for your data as a rule input.
- In the Connection section, configure the following fields:
- Select Use a connected system and choose the connected system you created in Step 3.
- For URL, enter the web API URL as the endpoint for the integration.
- For Method, select POST.
- In the Request Body section, do the following:
- For Content Type, select JSON.
- Call your rule input into the request body of your integration.
- In the Automatic Output Parsing section, make sure Automatically convert CDT, dictionary, or list to JSON is selected. This converts your integration results from the CDT in your rule input into JSON, which will then be converted to a dictionary and back into your CDT when it's called into your web API.
For more help, see Create an Integration.
Step 5: Call the integration from your portal interfaceCopy link to clipboard
Next, call your integration from your portal interface. For examples on how and where to call your integration in the portal, check out Calling an Integration to Modify Data.
Step 6: Test your portalCopy link to clipboard
After creating a portal object, adding the interface, and publishing the portal, be sure to fully test the published portal.
Step 7: Deploy your portalCopy link to clipboard
When you deploy a portal to another environment, do the following:
- Make sure the target environment has the following:
- An API key with the same Description as the one in the source environment.
- A service account with the same Username, permissions, and group membership as the one in the source environment.
- Include an import customization file (ICF) in the app or deployment package. In the ICF, provide the API key from your target environment as well as any other connected system credentials and information.
Working with data in a publicly-accessible external databaseCopy link to clipboard
The best way to work with data in portals is using record types. However, you also have the option of directly connecting to a publicly-available external database.
There are a couple of reasons why you might want to take this approach:
- Scalability: When you connect directly to an external database, calls to the database don't pass through Appian. This means that your portal isn't bound to scalability of Appian. Instead, it is bound by the scalability of the database.
- Isolation: When you connect directly to an external database, your portal is not connected to your Appian applications via web APIs and integrations. During heavy usage, this isolation means that you don't have to worry about a lot of web API calls from your portal impacting the performance of your Appian applications.
In order to connect a portal in this way, the database you're connecting to must meet the following criteria:
- It must be a supported external database.
- It must not be behind a VPN.
- It must be accessible at a public IP address.
This section explains how to directly connect to an external database to query or write data in your portal.
Step 1: Set up your external data sourceCopy link to clipboard
To set up your external data source to query or write data:
- Provide a supported database that can be accessed at a public IP address.
- Create a data source connected system to connect to the database.
- Create a corresponding data store object.
Step 2: Set up your service accountCopy link to clipboard
To write and query data in the external database, you need to give the portal the appropriate permissions to the data store. This is done using a service account, which acts on behalf of your portal users.
In order to write and query data, the service account needs have Viewer permissions to the data store.
To give your service account the appropriate access:
- In the portal object, add a service account.
- Add the service account to a user group in your application.
- Give the group Viewer permissions to the data store for the external database.
You can only link one service account in the portal object. If you're using a service account to give access to records, processes, or documents, use the same service account for the data store.
Step 3: Set up your portal interfaceCopy link to clipboard
In your portal interface, use a!writeToDataStoreEntity(), a!writeToMultipleDataStoreEntities(), a!deleteDataStoreEntity(), and/or a!queryEntity() just as you normally would in Appian.
If you are querying data, we recommend that you cast the dictionary returned from your query to a CDT.
Be aware that any calls to your external database go directly to the database and don't pass through Appian.
Step 4: Provide connection information in the import customization fileCopy link to clipboard
When you deploy your portal object to a different environment, include an import customization file (ICF) in the app or deployment package. In the ICF, provide your data source connected system credentials.
For more information on deploying portals, see Deploying a portal.
For more information on deploying data source connected systems, see Deploying data source connected systems.