The Delete Records smart service is a powerful tool that allows you to easily delete data from the source system and then automatically sync the changes in Appian. The service lets you delete one or more records at a time per node.
To use this smart service, the record type you want to affect must meet the following conditions:
Records can only be deleted from one record type at a time. To delete a record and its related records, you must delete records in the base record type and related record types in separate Delete Records nodes.
The user executing this activity must have Viewer permissions for the selected record type in order to delete information. If the user does not, the node will fail and pause the process with an exception.
Note: Since the Delete Records Smart Service works directly with your record type's source, read the recommendations in Data Modeling with Appian Records before implementing this smart service.
Icon: ![]()
This section contains configuration details specific to this smart service. For more information about common configurations, see the Process Node Properties page.
| Name | Data Type | Description | Required | Multiple |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Records | List of Any Type | A list of records to be deleted for a single record type. The list can include up to 1,000 records. Each item in the list must include the primary key for the record. Any related record data is ignored. | Yes | Yes |
| Pause On Error | Boolean | Determines whether the node should pause by exception if an error occurs deleting data in the source. Default: true. |
No | No |
See also: Record Type
| Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Count of Records Deleted | Number (Integer) | The number of records deleted from the source |
| Error Occurred | Boolean | Returns true if any write to the source system or Appian fails; returns false if all writes succeed |
| Errors | List of Any Type | The error that occurred when writing the records and the list of records that failed to write. This is only returned when the Pause On Error input is false. |
Appian can automatically generate a Delete record action. The generated design objects use the Delete Records smart service in the workflow powering the new action. The generated interface has a rule input called record that uses the record type as its data type. The data needed to identify the record being deleted is seamlessly passed from the interface to the process model. See Delete a record using a process model for an example.
You can also use the record type constructor syntax when deleting records. In the constructor, include the primary key field to identify the record you want to delete. For example, if you have a Customer record type and want to delete the customer with the ID of 72, the data passed to the process model would look similar to the following example.
1
2
3
4
5
{
recordType!Customer(
recordType!Customer.fields.customerId: 72
)
}
The Delete Records smart service permanently removes data from the source (that is, it performs a hard deletion). If your app or database design requires data to be soft deleted for auditing or to maintain referential integrity, you can use the Write Records smart service to mark a record as deleted according to your schema. For example, your data source may have a field like isDeleted or deletedTime. You could configure a source filter so rows that are marked as deleted are no longer synced in Appian.
The Delete Records smart service does not support deleting from related record types through the base record type. Instead, you must delete related records and the base record in separate Delete Records nodes. For example, you may have a Customer record type that has a one-to-many relationship with a Payment Type record type storing credit card data. If you delete a customer record, you also want to delete any payment data associated with the customer. A process model of this workflow would look similar to the following example:
The Delete Records smart service is available as an expression function that can be executed inside a saveInto on a Interface Component or as part of a Web API. When creating a web API, select the Delete Records template to generate the object with this function automatically configured.
a!deleteRecords( records, onSuccess, onError )
| Keyword | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Any Type |
A list of records to be deleted (up to a maximum of 1,000 records). Each item in the list must include the primary key for the record. Use the |
|
|
Any Type |
A list of saves or an HTTP response to execute after the smart service successfully deletes rows. Created with |
|
|
Any Type |
A list of saves or an HTTP response to execute when the smart service fails to delete records. Created with |
When you use this smart service on a record view, the view will automatically refresh with the latest record data.
This means that when your record view interface has a Record Action component that triggers the Delete Records smart service, or a button component that triggers the a!deleteRecords() function, the record view data will automatically refresh after the delete occurs.
This refresh behavior only applies to data supplied by rv!record. If your record view definition uses rv!identifier or a local variable to supply the record data, the data will not automatically refresh; instead, you will need to configure additional refresh behavior.
This section explains some of the common reasons the Delete Records smart service might fail.
Configuration errors can occur when node inputs are misconfigured and attempts to write to the source will not succeed. Some examples of misconfiguration include:
a!deleteRecords() function.Appian is unable to change data in the source in some circumstances. These situations include:
If Appian is unable to write to the database, the record data will still remain available even if the smart service fails.
When Appian attempts to sync changes to the source data, the sync will fail when one of the following occurs:
If Appian is unable to sync changes from the source, the record data will be unavailable. For more information on the different types of sync errors and steps to resolve these errors, see Troubleshooting Syncs.
The following examples show the different ways you can use the a!deleteRecords() function to delete your record data.
The following example data is from the Appian Retail application, available for free in Appian Community Edition. To try the example code yourself, sign in to Appian Community to request the latest Appian Community Edition site.
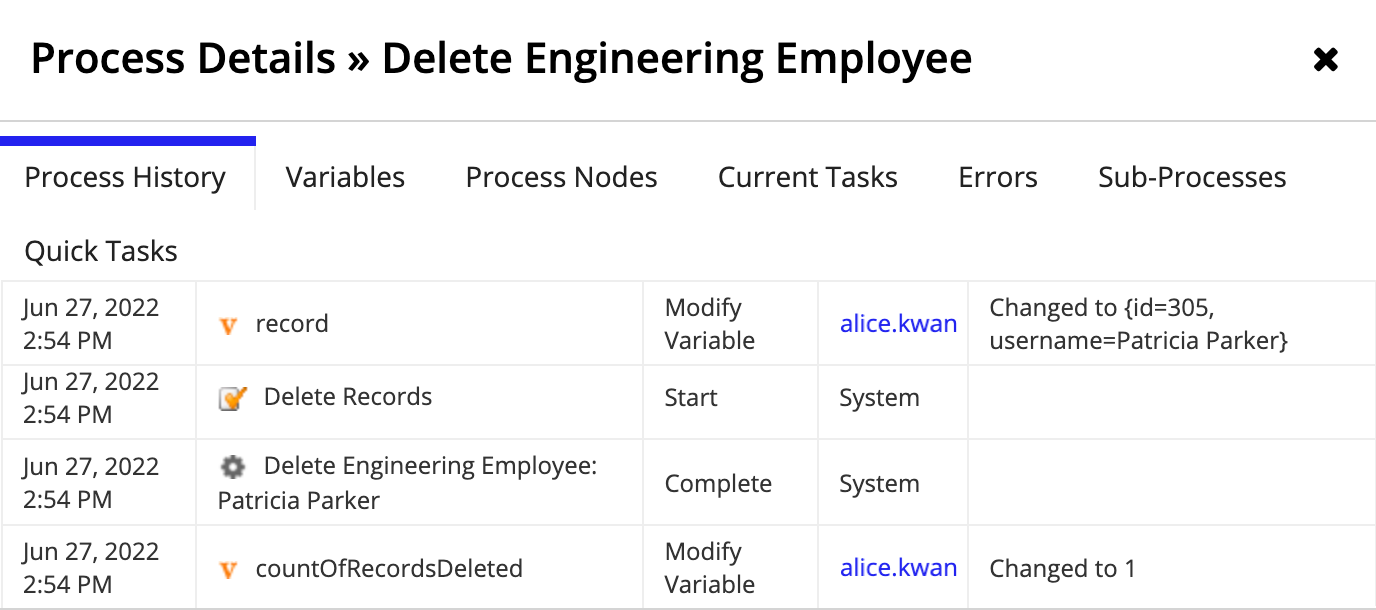
Imagine you need to remove an Employee from the Appian Retail application. You can let users delete record data using a related action connected to a process model. Set a process variable using the record type as the data type to pass the user's selection to the Delete Records node.
The process node examines the primary key field (in this case, the id field) and deletes that record from the source.
You can also delete a record using the a!deleteRecords() function. For example, to delete an Address record, use a record type constructor in the records parameter and provide the identifier of the record to be deleted. In the following example, the Address record we want to delete has the addressId value of 322.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
a!deleteRecords(
records: {
recordType!Address(
recordType!Address.fields.addressId: 322
)
}
)
The Address record type has other fields (like city and postalCode) which are not included in the expression. Only the primary key is required to identify the record being deleted.
The a!deleteRecords() expression returns data similar to the following:
1
countOfRecordsDeleted: 1
| Feature | Compatibility | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Portals | Partially compatible | Can be used with Appian Portals if it is connected using an integration and web API. |
| Offline Mobile | Incompatible | |
| Sync-Time Custom Record Fields | Incompatible | |
| Real-Time Custom Record Fields | Incompatible | |
| Process Reports | Incompatible | You cannot use this function to configure a process report. |
| Process Events | Incompatible | You cannot use this function to configure a process event node, such as a start event or timer event. |
A smart service consists of a function and a node. There are some instances when the smart service function is evolved separately from the smart service node. When the function or node is evolved, a new version of the function or node is available.
The following sections detail the different versions of the Delete Records function and Delete Records node.
You can identify the version of a smart service node by looking at node type and version.
To review a node's type and version:
If you are using a previous version, be sure to refer to the corresponding documentation from the list below. To use the latest version of the node, replace the old version of the node with a new node.
| Appian Version | Node Type | Node Version | Reason for Update |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22.3 | delete_records_from_source | 1 (Current) |
Original version of the Delete Records node. |
Delete Records Smart Service