Benefits of SAIL
Overview
SAIL makes development faster and easier. Developing with SAIL involves a simple, low-code approach.
This page provides an overview of the benefits that SAIL brings to Appian's Low-Code Platform.
No HTML, CSS, or Javascript
Most of today's web design systems are high-code: designers use HTML and CSS to define UIs, then developers use Javascript to make the front-end design and back-end data and logic work together. With SAIL, even designers without development experience can design beautiful, functional interfaces.
Perfect handoff between design and development
Using our simple drag-and-drop framework, designers can easily create mockups that capture the entire scope of their intended user experience. They can then hand off their work to developers, knowing that the interface will continue to look and behave exactly as they intended.
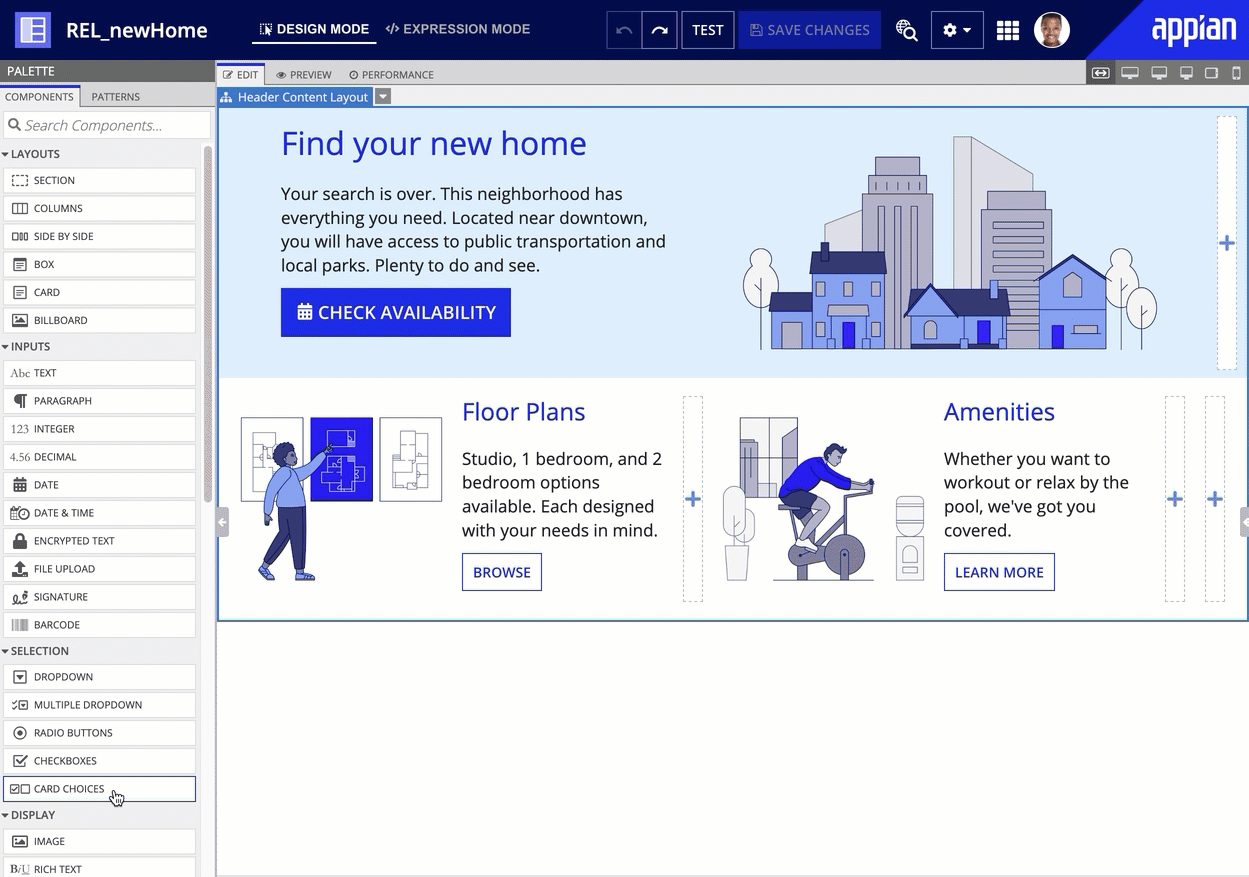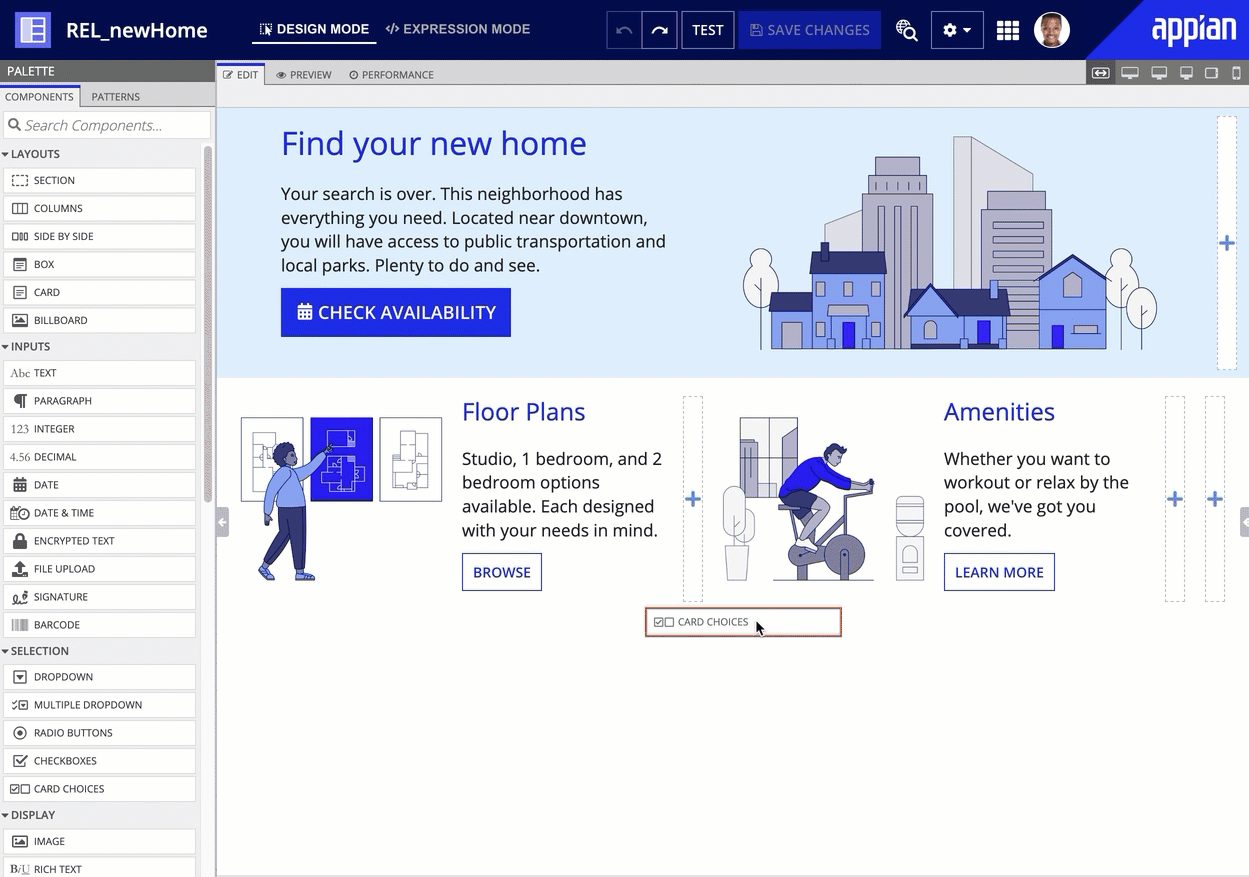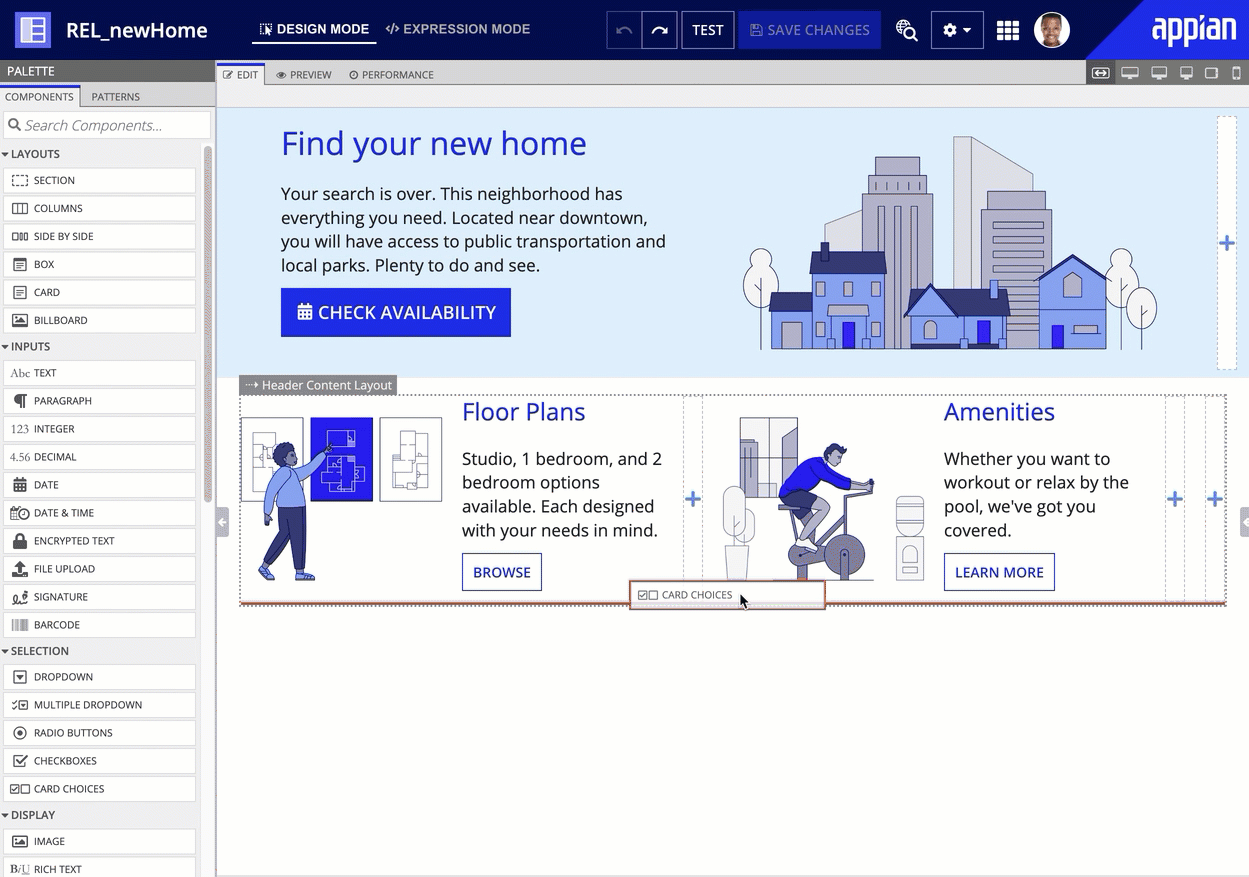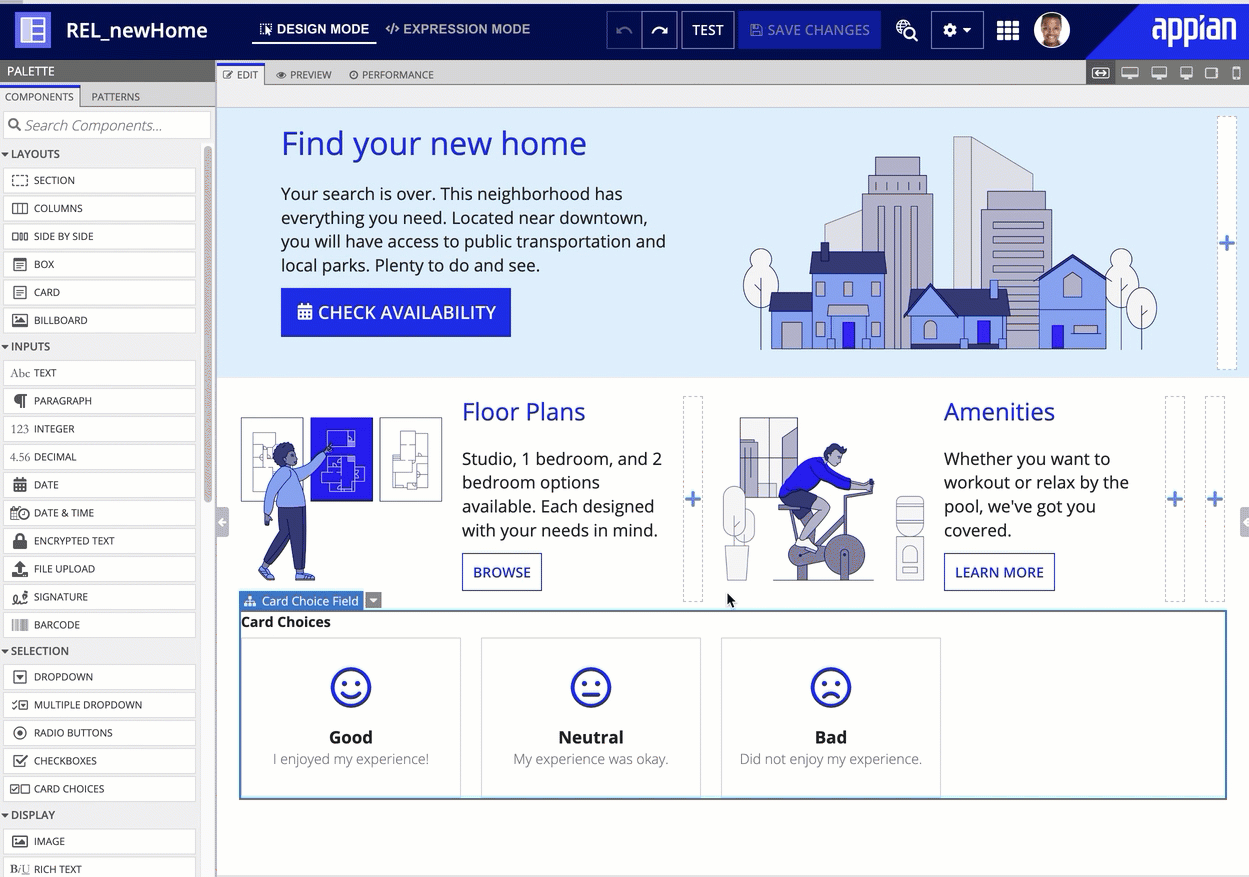
Works automatically on web and native mobile
You only have to design a SAIL interface once to support users on desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. SAIL translates your design decisions into interfaces that look good on both web browsers and the Appian Mobile app, across a variety of screen sizes.
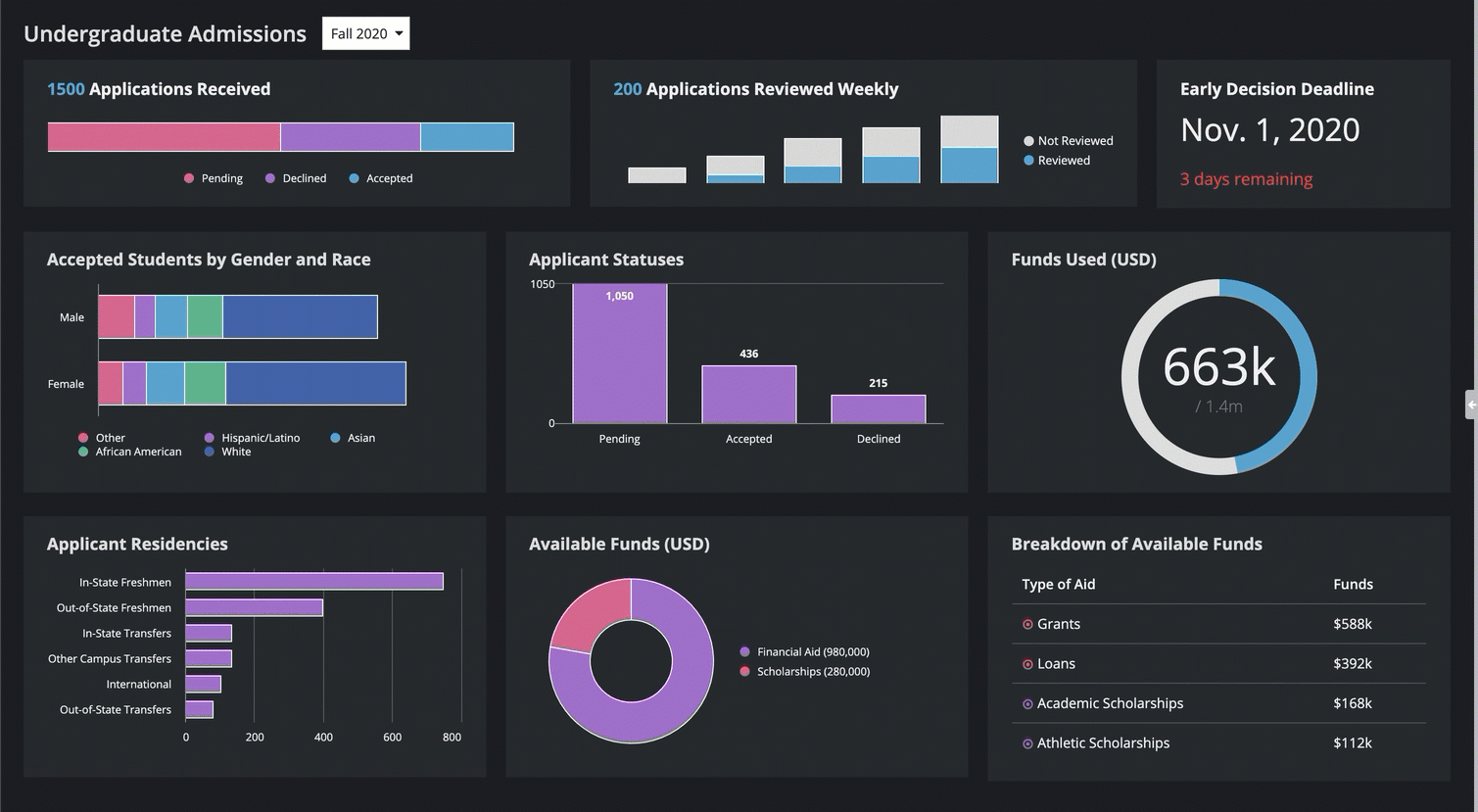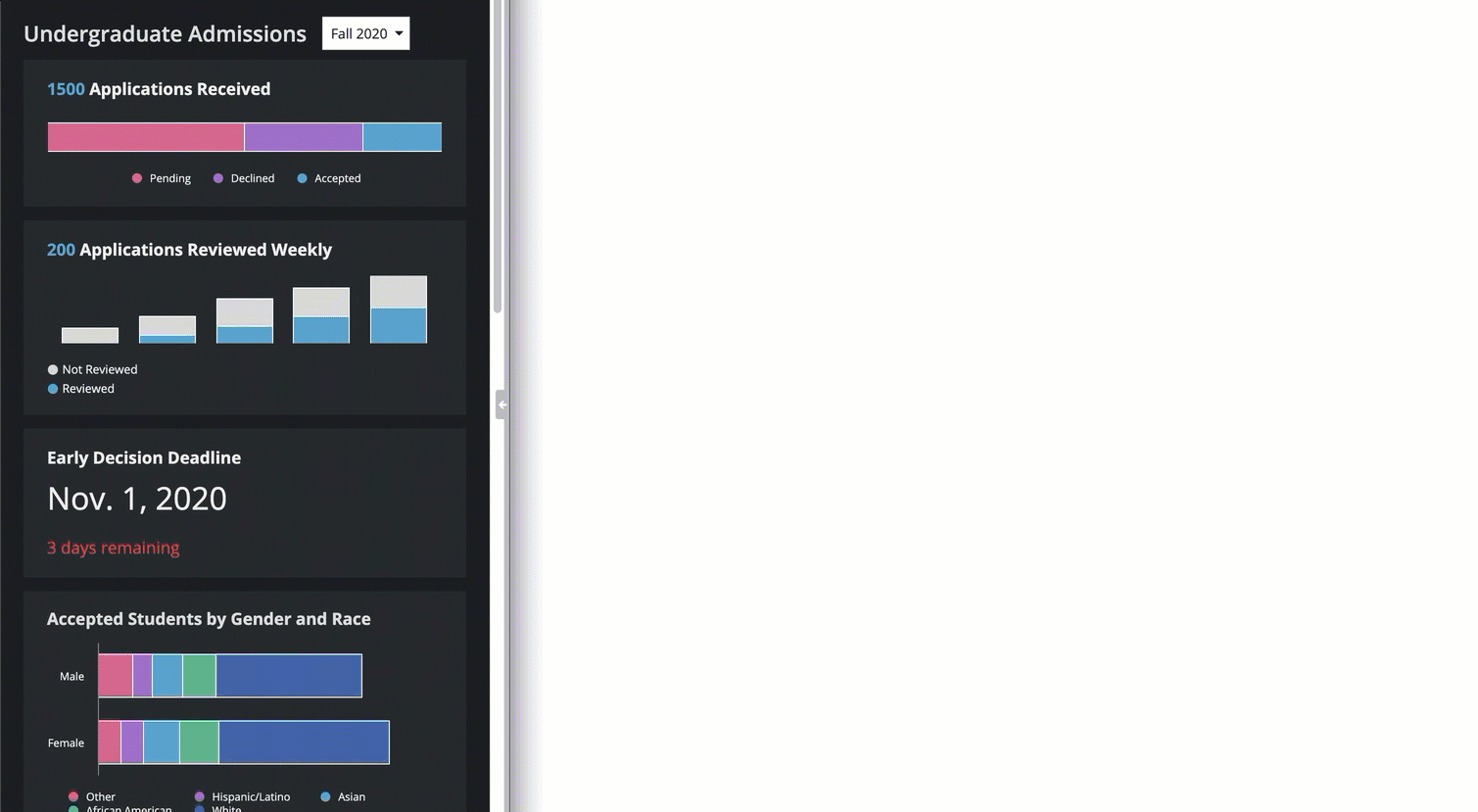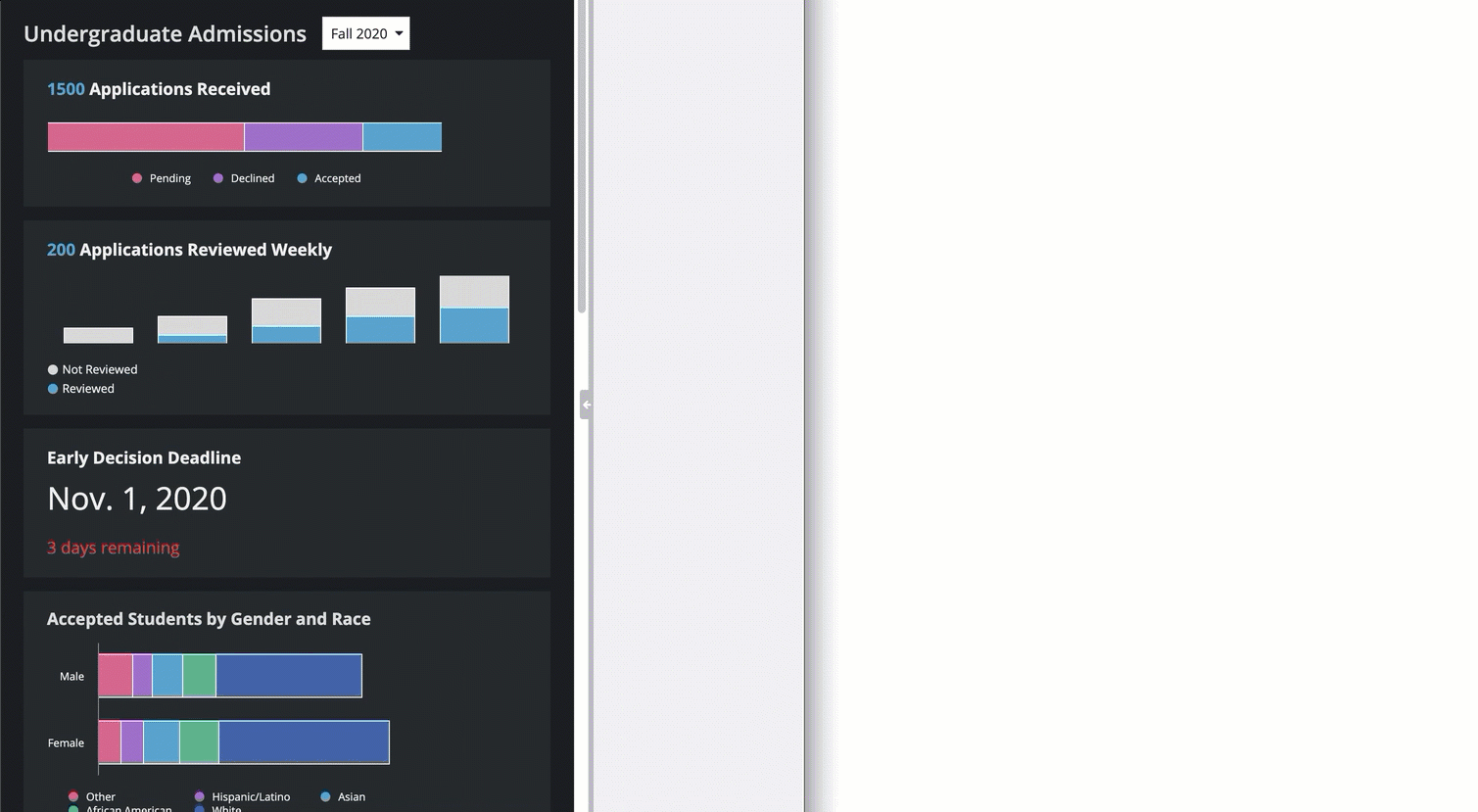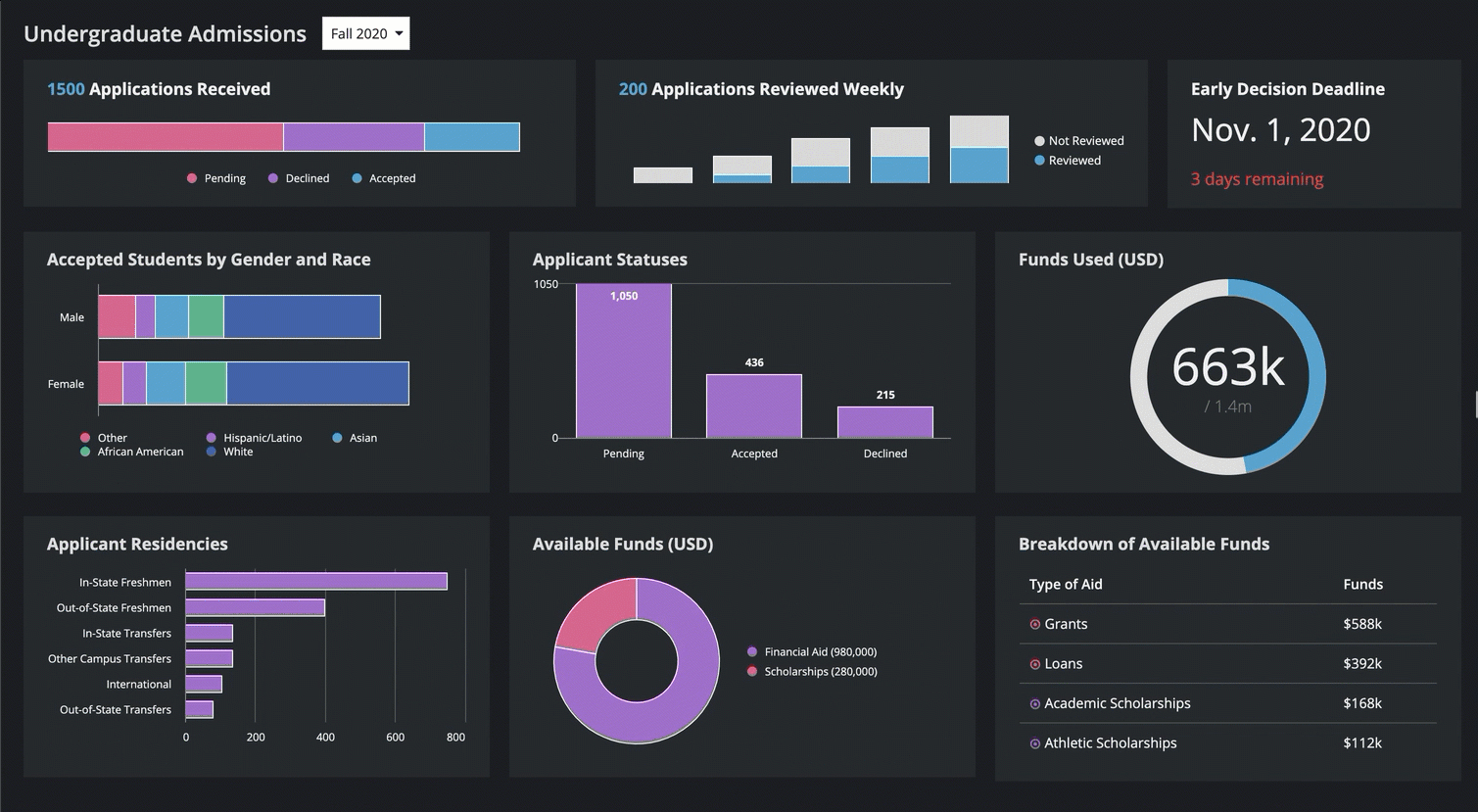
This means that SAIL interfaces are responsive by default—they automatically adjust to fill the screen, no matter the device width.
You can also define adaptive behaviors based on the screen size, such as stacking columns, showing or hiding content, and changing the font size.
Built-in accessibility
User interfaces built with SAIL meet global standards for accessibility (WCAG 2.1 Level-AA) to make your applications inclusive to all users. Just follow published best practices when configuring SAIL components—no need to worry about crafting the proper markup or ARIA attributes.
Along with out-of-the-box accessibility features, Designers can also configure further accessibility behaviors, such as:
- Specify descriptive alternative text on images.
- Add screen reader text to give context to non-sighted users.
- Define heading tags for screen readers.


