FunctionCopy link to clipboard
a!pageResponse( data, nextPage )
Identifies the data in the current integration response, and the path of the next set of data to request. This function should be used to return data in a record data source expression when the integration uses a non-integer pagination value.
See also: Choose a Data Source
ParametersCopy link to clipboard
| Keyword | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Any Type |
In the integration response, the path of the data returned from the integration. |
|
|
Text |
The path of the next page of results within the header or body of the response. This could be a URL, URI, cursor, or token. |
ReturnsCopy link to clipboard
List of Variant
Usage considerationCopy link to clipboard
Where to use the functionCopy link to clipboard
This function allows you to use data returned from an integration to identify the next page of results.
You should use this function in a record data source expression when you want to sync more than 1,000 rows of data from a web service, and the web service pages by a URI, URL, cursor, or token.
Using the nextPage parameterCopy link to clipboard
The nextPage parameter identifies the location of the next page of results from an integration. This location can be found in either the response body or header.
Each web service can return the next page of results in a different way. Some web services will simply provide the next page value as a property in the response body or header, like a next_page property. Other web services may require you to extract the next page value from the integration response. See an example extracting the next page URL from the response header.
The nextPage parameter must return null value when the next page is null or empty to stop the record type from syncing any more data. You should test your integration response with the value from the last page of data to see if it automatically returns null. If it doesn't, you must modify the nextPage parameter so it returns null when the next page is empty or null. See an example of this in this example.
ExampleCopy link to clipboard
These examples illustrate the different ways you can use the a!pageResponse() function to extra and return data for your record type.
For examples using this function in a full record data source expression, see:
Extracting a URL from a response bodyCopy link to clipboard
In this example, an integration's response header has a link property that returns the URLs for the next page and the last page:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
Dictionary
success true(Boolean)
result HttpResponse
statusLine"HTTP/1.1 200 OK"(Text)
statusCode200(Number (Integer))
headers Dictionary
Date"Mon, 25 Nov 2024 14:30:20 GMT"(Text)
Content-Type"application/json;charset=utf-8"(Text)
Transfer-Encoding"chunked"(Text)
Connection"keep-alive"(Text)
Vary"Accept-Encoding"(Text)
link"<https://harvest.greenhouse.io/v1/applications?created_after=2020-01-01T00%3A00%3A00.000Z&page=2&per_page=200>; rel="next",<https://harvest.greenhouse.io/v1/applications?created_after=2020-01-01T00%3A00%3A00.000Z&page=4&per_page=200>; rel="last""(Text)
x-ratelimit-limit"50"(Text)
x-ratelimit-remaining"49"(Text)
x-content-type-options"nosniff"(Text)
x-request-id"b3d868dc5d5a86189e40f31009d95a23"(Text)
Strict-Transport-Security"max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains"(Text)
contentType"application/json;charset=utf-8"(Text)
Copy
To provide the link for the next page of results, you can use familiar functions to extract this value in your record data source expression.
This expression identifies the location of the next page in the link property in the response body. Then, it uses the split() function to return the two links separately. Finally, the index() function will only return the first link (the next page) and return null if there is no next page.
1
2
3
4
a!pageResponse(
data: local!integrationResponse.result.body.responseDetails.data,
nextPage: index(split(index(split(local!integrationResponse.result.headers.link,"""next"",<"), 2, null),">;") 1, null)
)
Copy
Casting fields to consistent data typesCopy link to clipboard
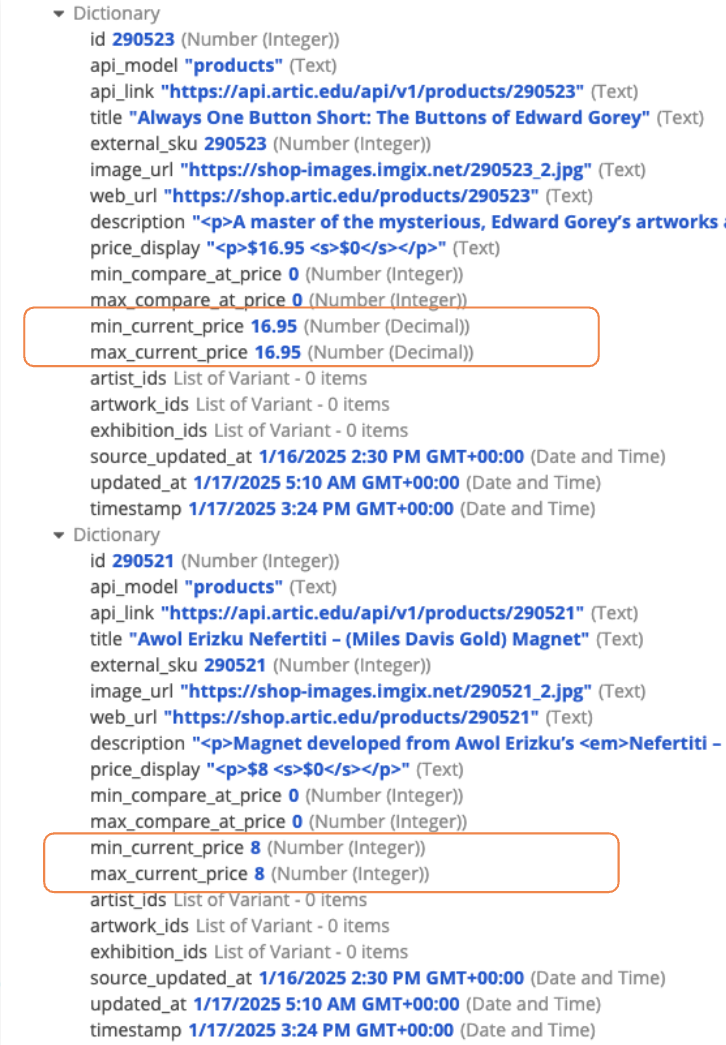
In this example, the integration response returns the fields min_current_price and max_current_price as two different data types: Number (Decimal) and Number (Integer). However, to sync this data in a record type, these fields must be returned as a consistent data type.
To return the fields as a consistent data type, you can cast the values of min_current_price and max_current_price to return Number (Decimal) in your record data source expression.
In this expression, the a!forEach() function extracts the field value from each row and creates key value pairs using the a!map() function. To map the minimum and maximum price, the todecimal function will convert all values from min_current_price and max_current_price to type Number (Decimal).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
a!pageResponse(
data: a!forEach(
items: local!integrationResponse.result.body.data,
expression:
a!map(
id: fv!item.id,
title: fv!item.title,
description: fv!item.description,
price: fv!item.price_display,
min_price: todecimal(fv!item.min_current_price)
max_price: todecimal(fv!item.max_current_price)
)
),
nextPage: local!integrationResponse.result.body.pagination.next_url
),
Copy
Feature compatibilityCopy link to clipboard
The table below lists this function's compatibility with various features in Appian.
| Feature | Compatibility | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Portals | Compatible | |
| Offline Mobile | Compatible | |
| Sync-Time Custom Record Fields | Compatible | Can be used to create a custom record field that only evaluates at sync time. |
| Real-Time Custom Record Fields | Incompatible | Custom record fields that evaluate in real time must be configured using one or more Custom Field functions. |
| Process Reports | Incompatible | Cannot be used to configure a process report. |
| Process Events | Incompatible | Cannot be used to configure a process event node, such as a start event or timer event. |
| Process Autoscaling | Compatible |